Question: i found the answer to 1 in 7 iterations. I need help with question 2. my work for 1 is below 2hc2 B(,T) = he


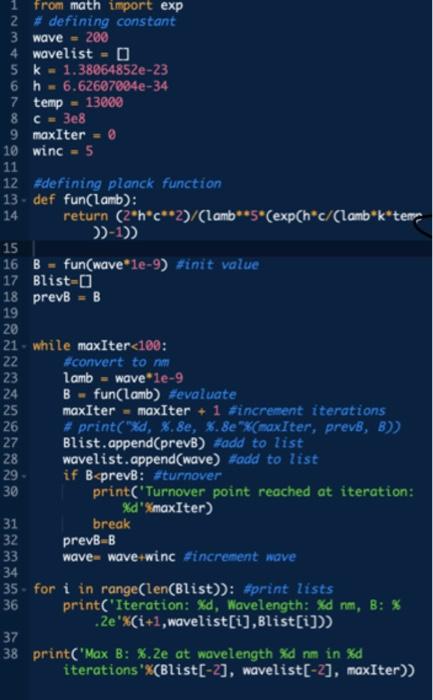
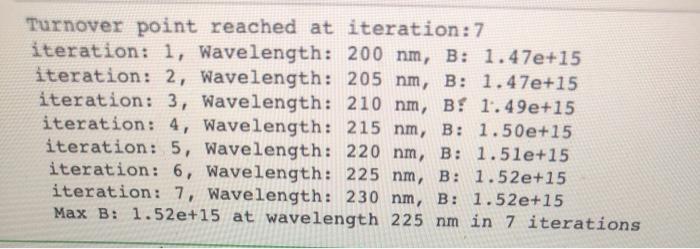
2hc2 B(,T) = he T where his Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, kis Boltzmann's constant, A is the emission wavelength, and Tis the temperature of the blackbody. Note that the 'exp' is e, as in the number that equals 2.72. Q1. Write a program that determines where the peak of the Planck function occurs in wavelength for a given temperature. You must use a while loop to do this. (12 pts) a) If the temperature of an object is 13,000 K, what is the peak wavelength? Use 200 nm as your initial guess, and a step-size of +5 nm. You cannot use the 'max' function in Python, nor should you take a derivative. You are essentially writing your own max function. You can solve this problem with a while loop. (8 pt) b) Print your list(s) of wavelength and B, values. Make sure to format your output so that wavelength has zero decimal points and is expressed in nm, and B, is expressed in scientific notation with 2 decimal points. (1 pt) c) How many iterations did it take for your algorithm to find it? 056 Q2. (2 pt) a) Calculate the peak wavelength of the blackbody curve using Wien's Displacement Law. Wien's Law calculates the peak wavelength of a blackbody curve based on the temperature of the object in question. Amax 2.898 10-3 where Imax is the peak wavelength in meters (m), T is the blackbody temperature in Kelvin [K], and the constant is in (m.K]. Use 13,000 K for the temperature. Your answer should have zero decimal points (for example: "300 nm"). (3 pt) b) How close is your result in the previous question (through Planck's law) to the analytical result (Wien's Law)? Calculate the difference and print it. (4 pts) c) Re-run your algorithm in Question 1 with a step-size of 1 nm. How many iterations did it take to find the peak? How close is your result to Wien's Law now? Again, print your list(s) of wavelength and B, values. 1 from math import exp 2 #defining constant 3 wave - 200 4 wavelist = 0 5 k = 1.38064852e-23 6 h = 6.62607084e-34 7 temp - 13000 8 C = 3e8 9 maxIter - 10 winc - 5 11 12 #defining planck function 13. def fun(lamb): 14 return (2*h*c**2)/(lamb**5*(exp(h*c/(lamb*k*terer 15 16 B - fun(wave*le-9) #init value 17 Blist- 18 prevB = B 19 20 21 - while maxIter
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


