Question: i have some problems with all questions. With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design
i have some problems with all questions.
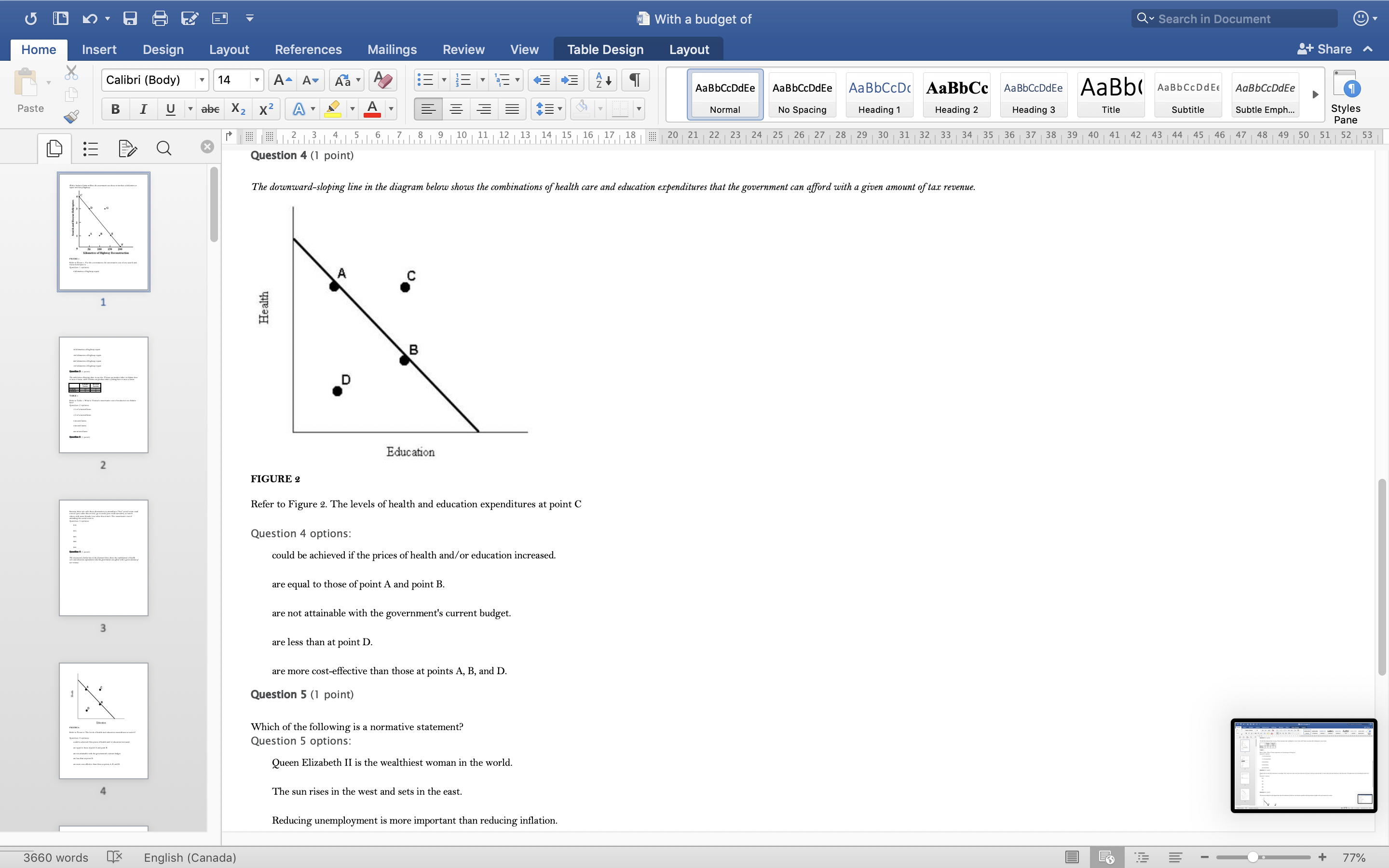
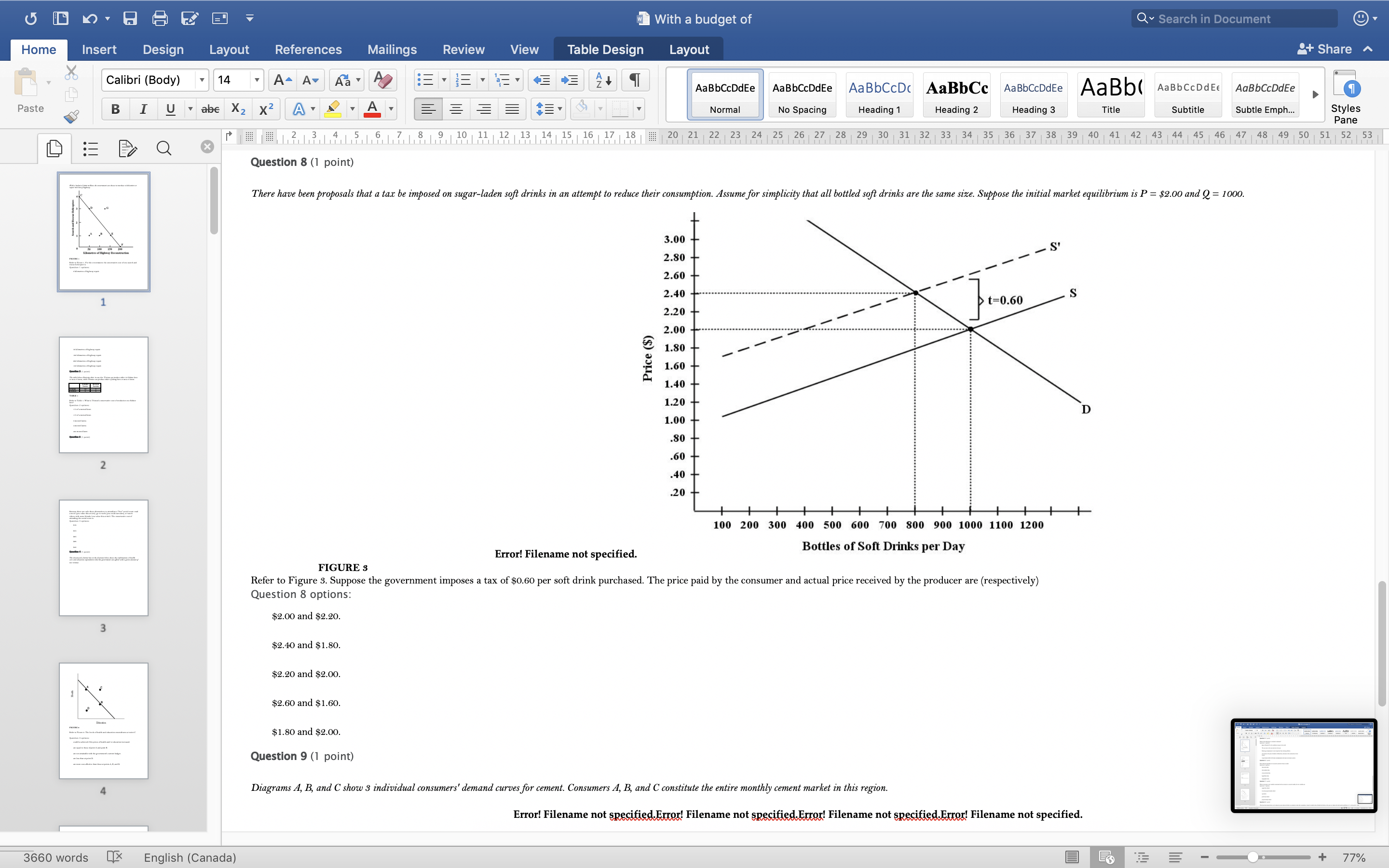
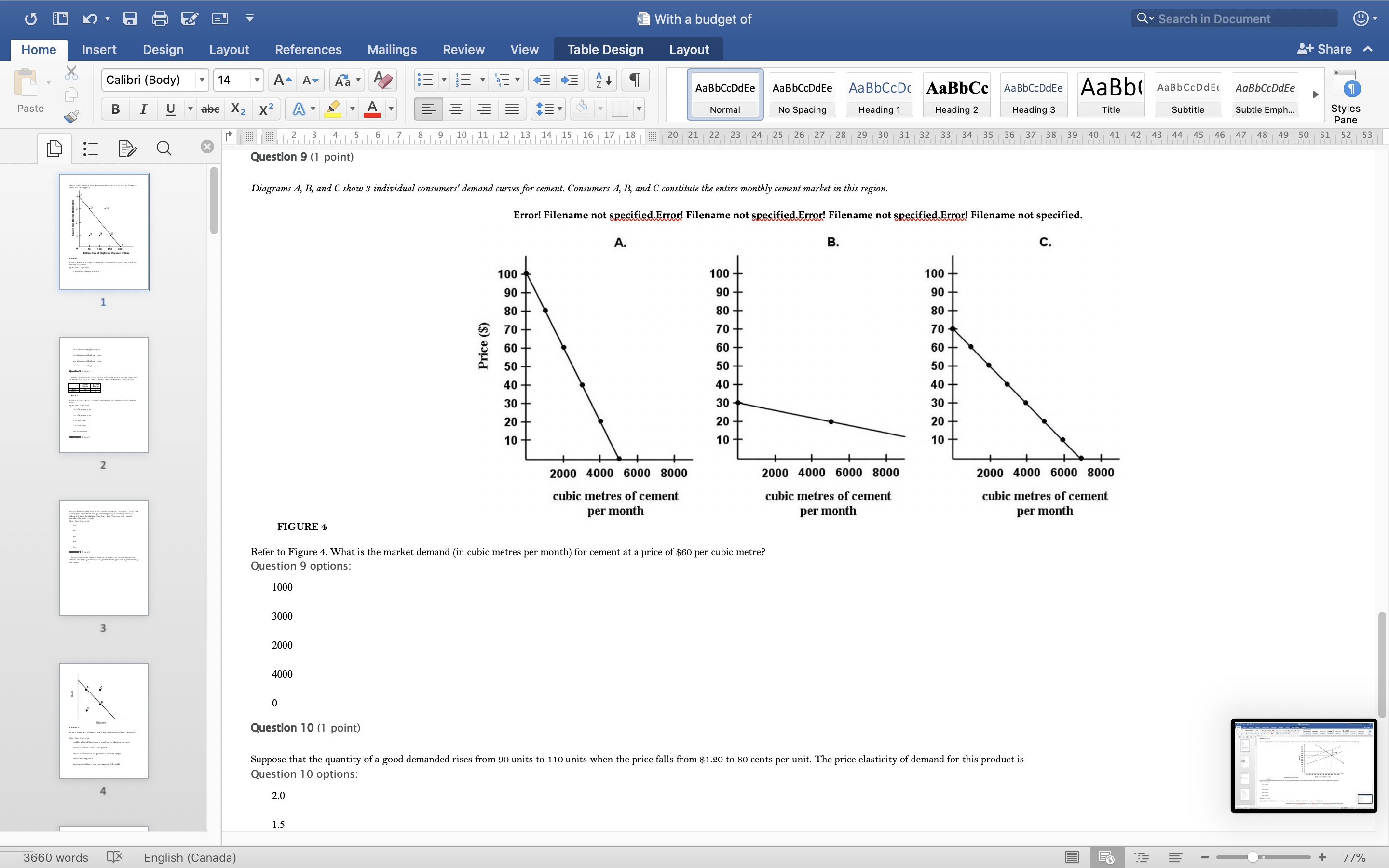
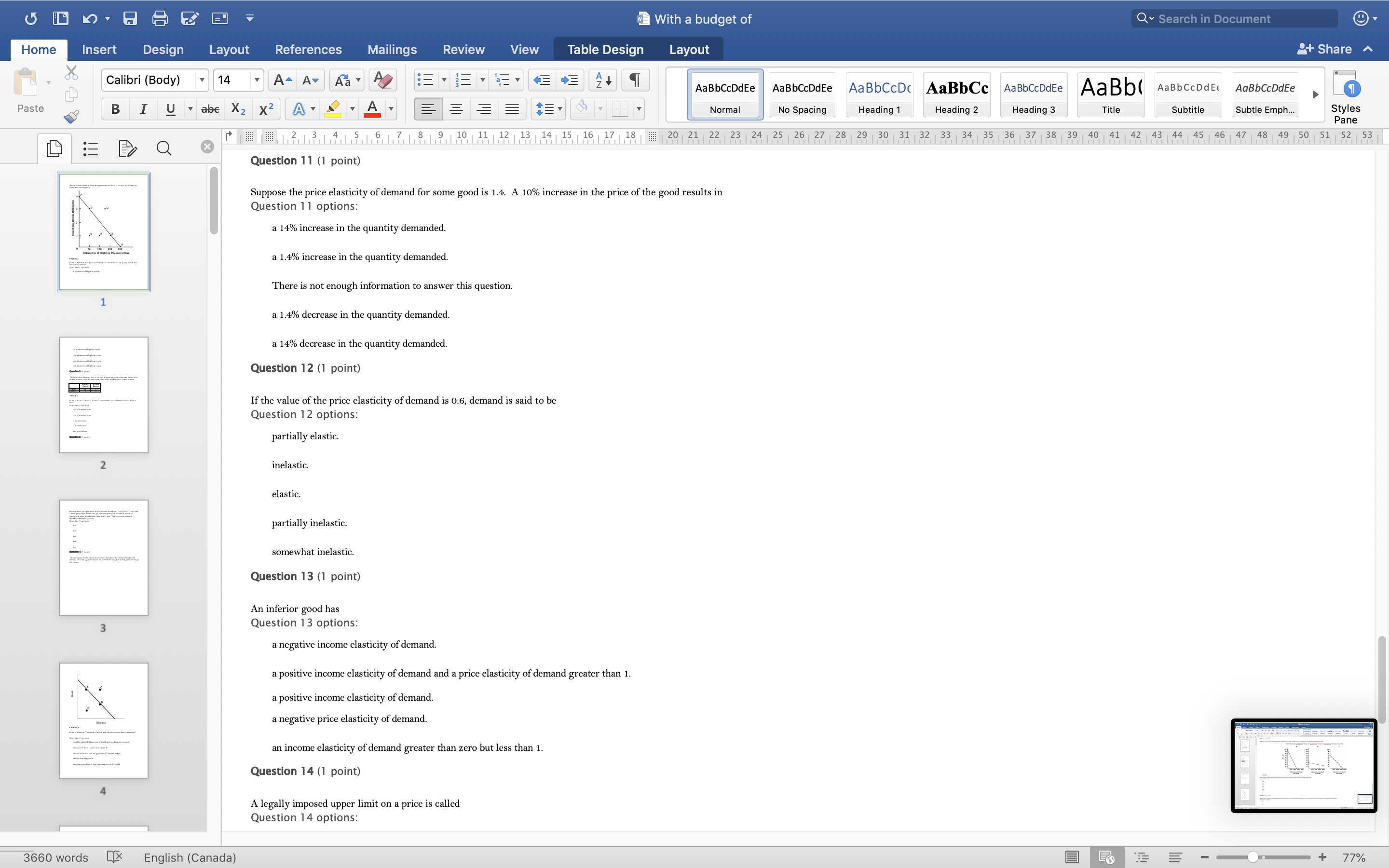
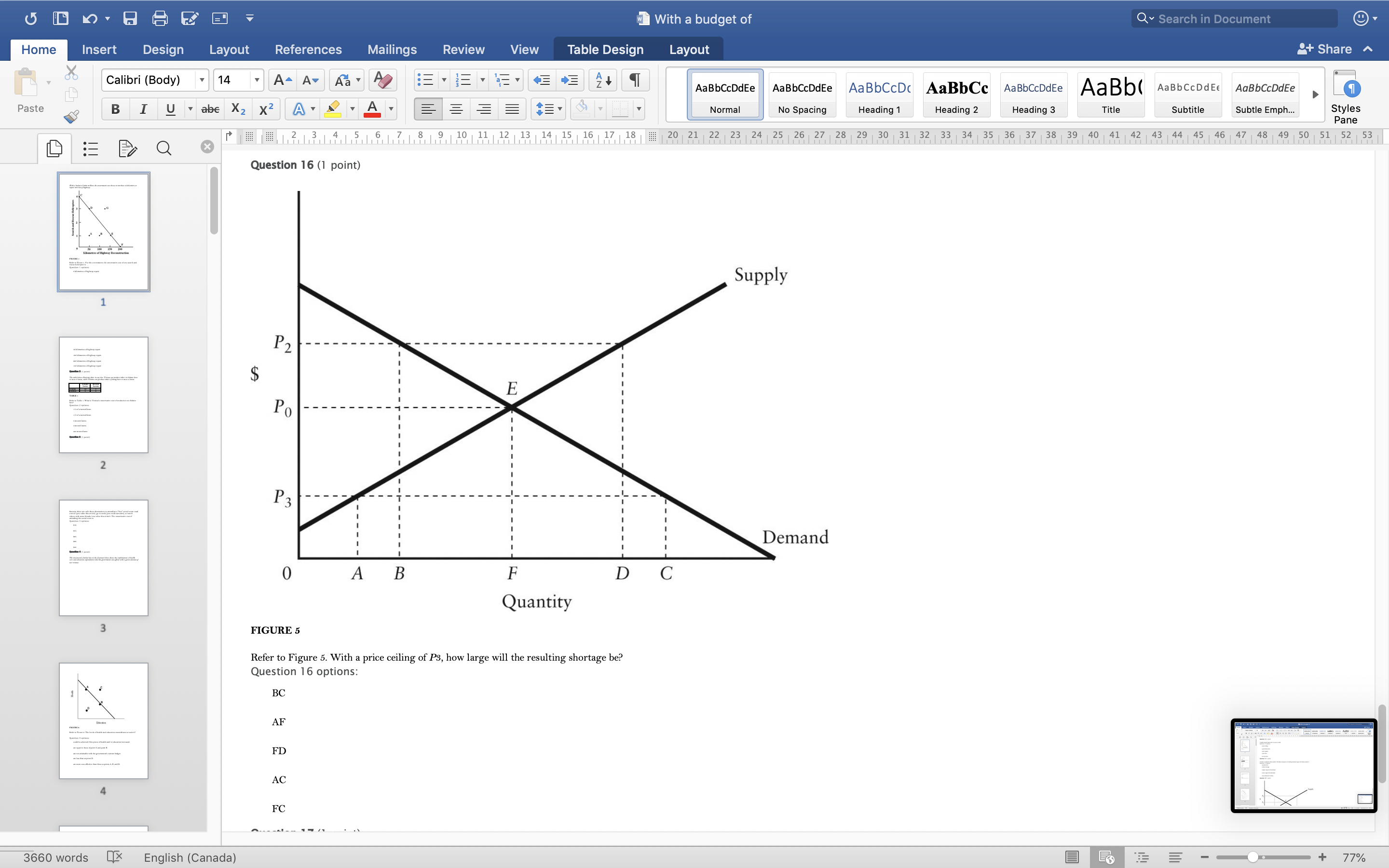
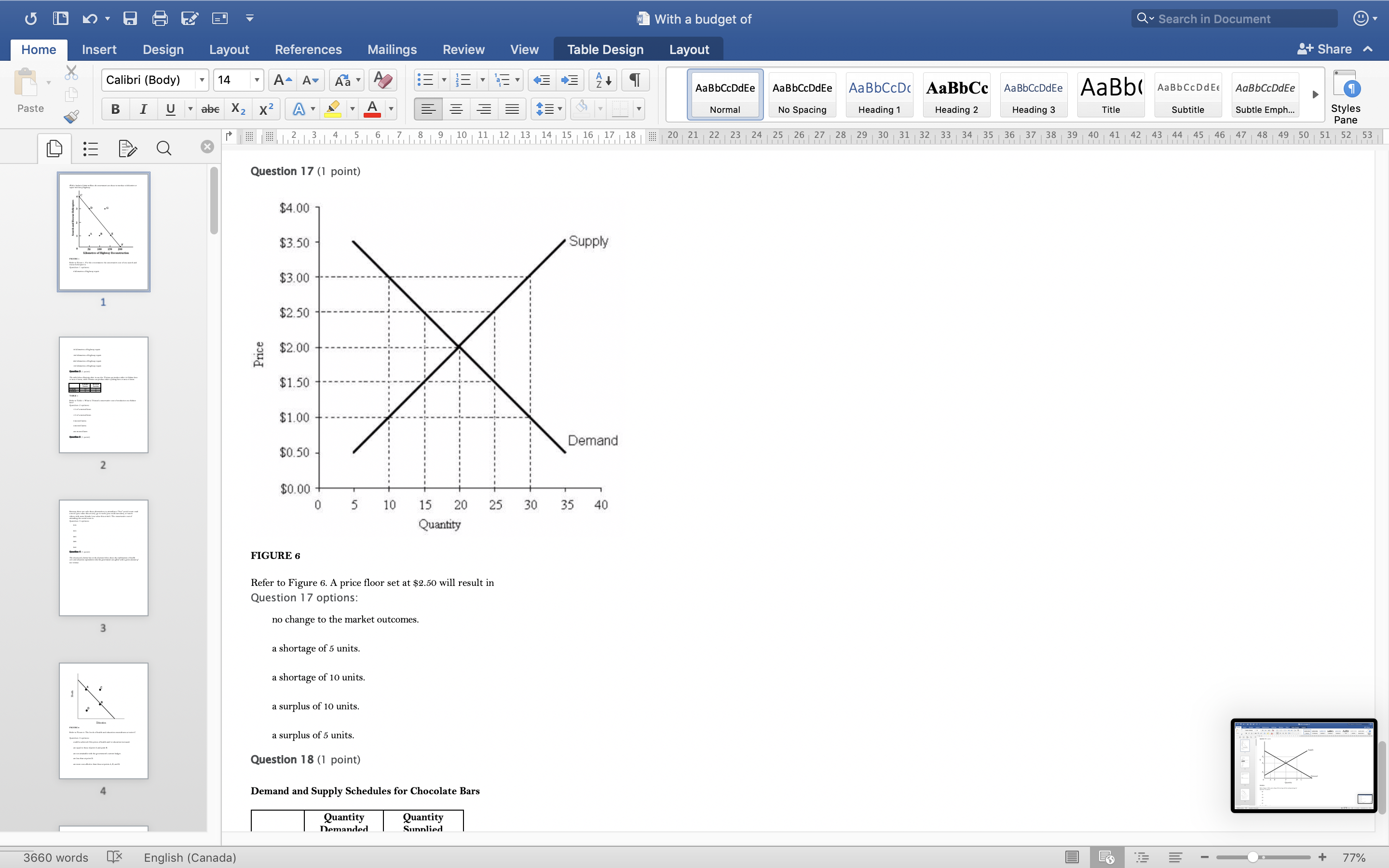
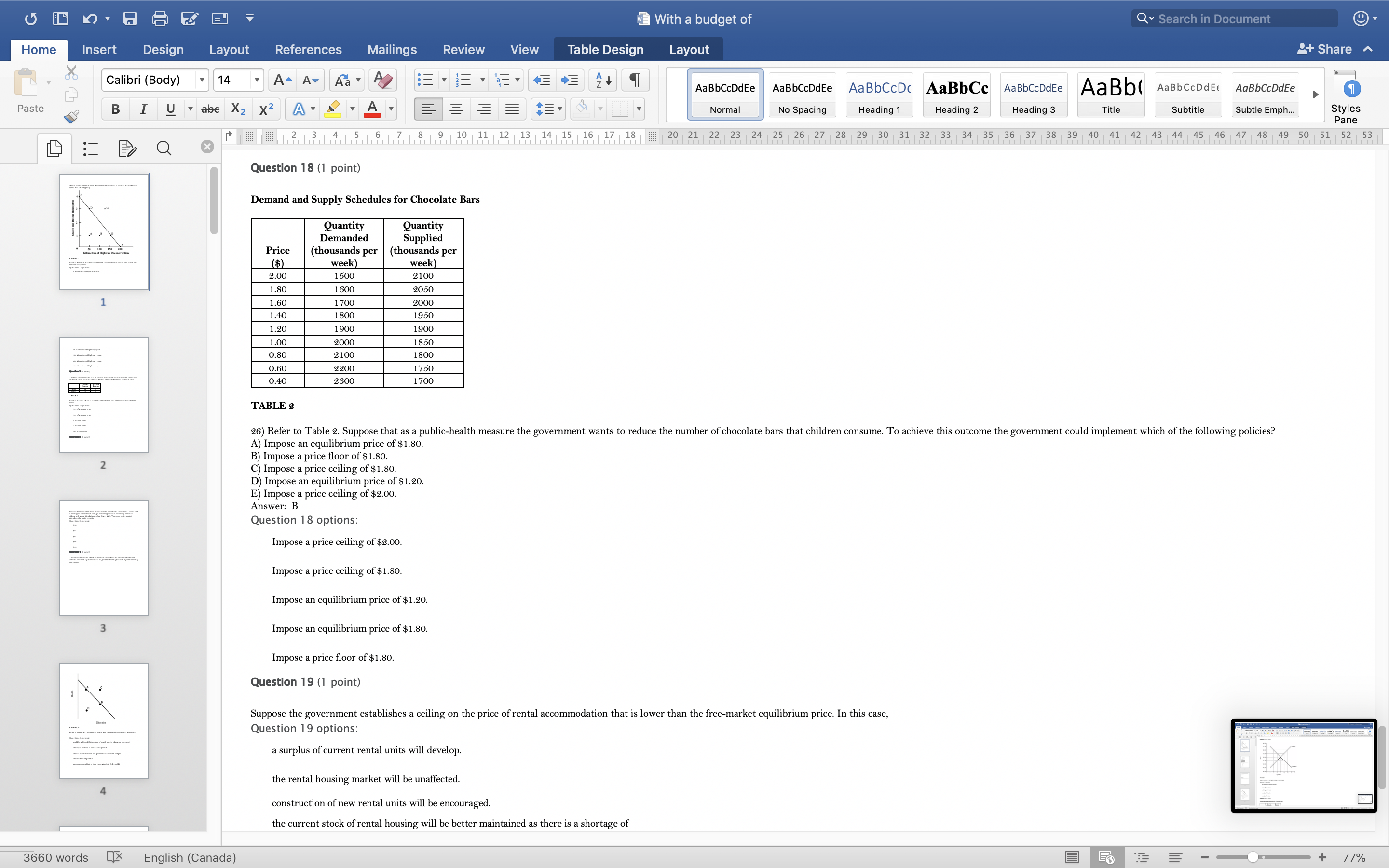
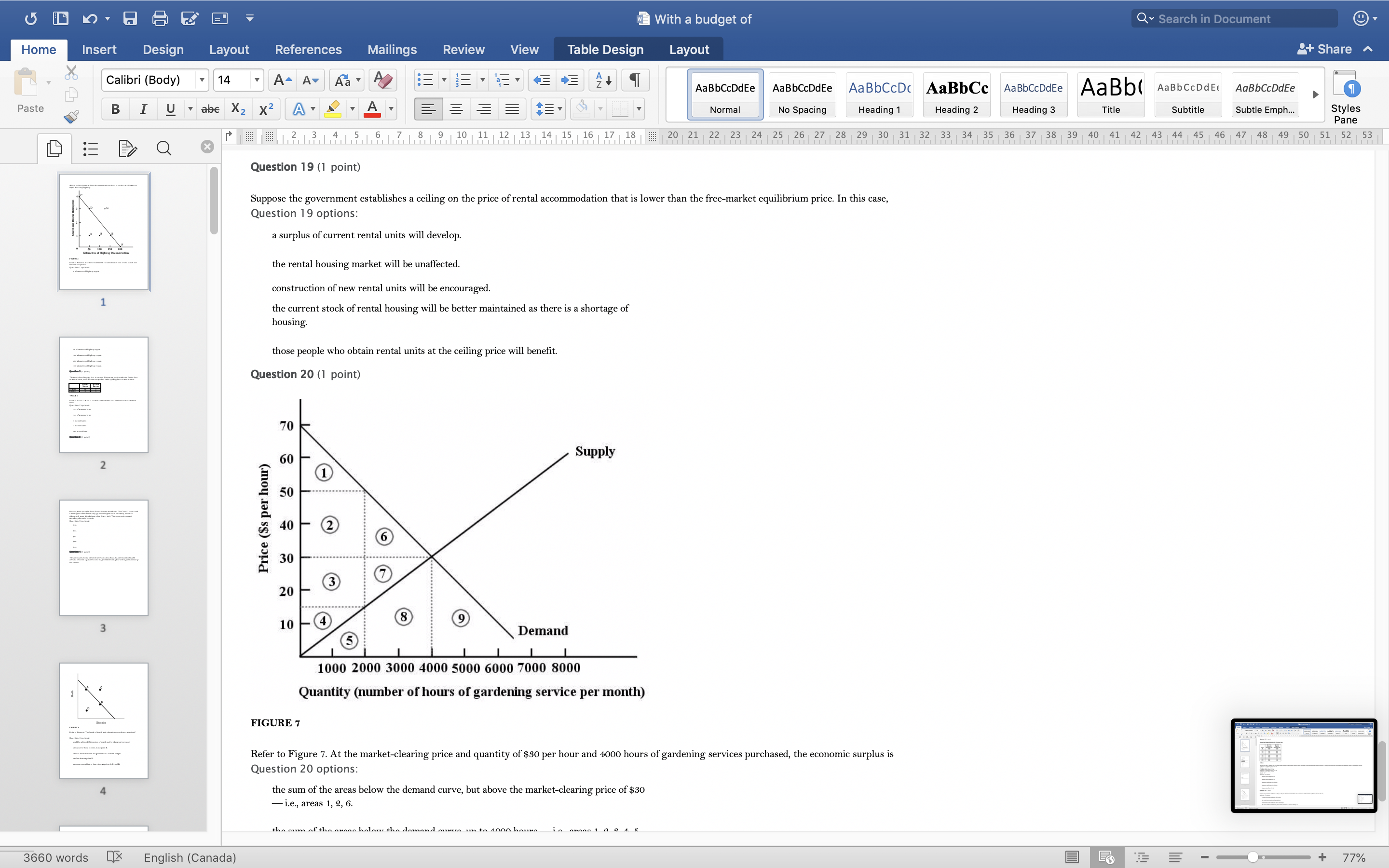
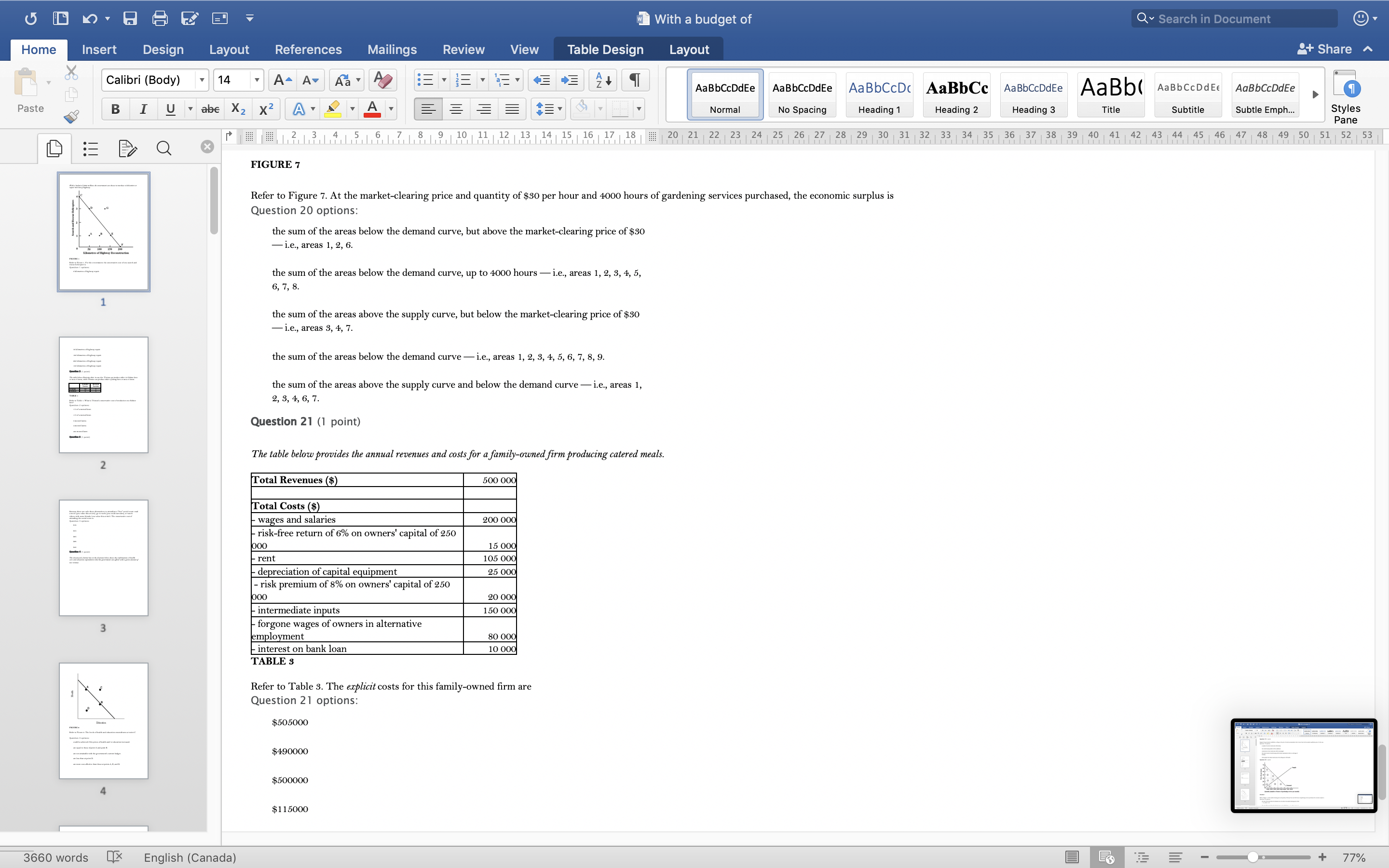
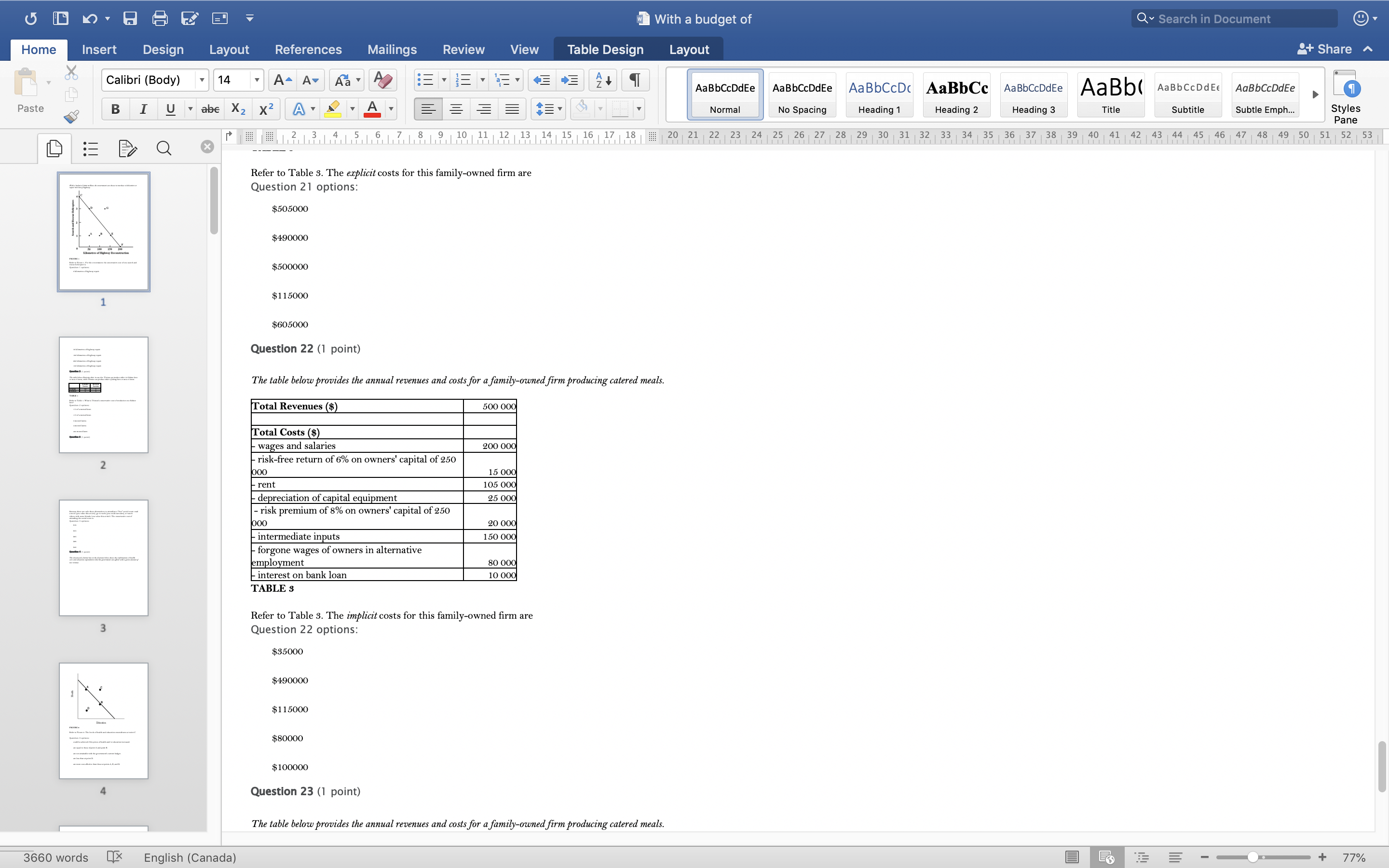
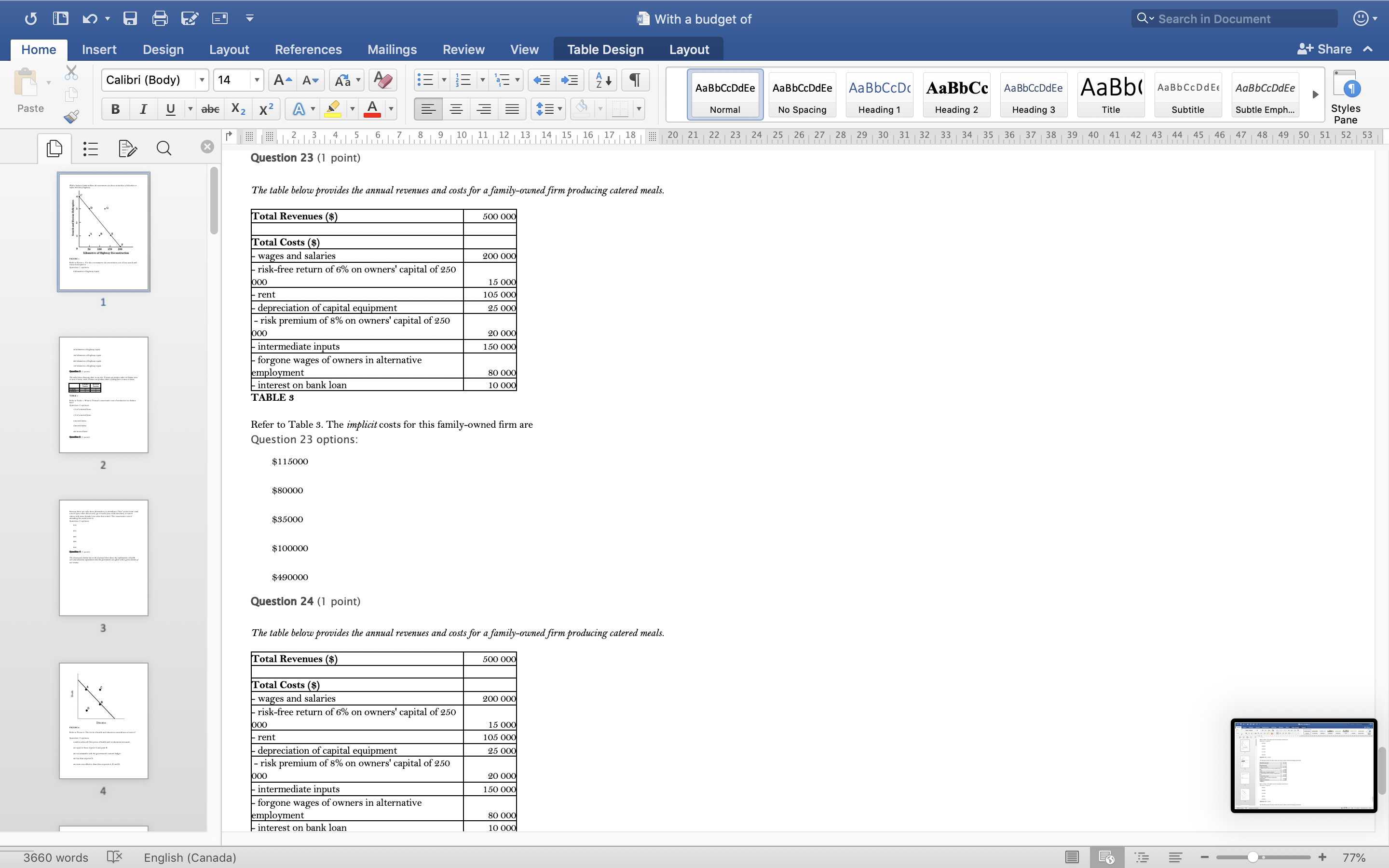
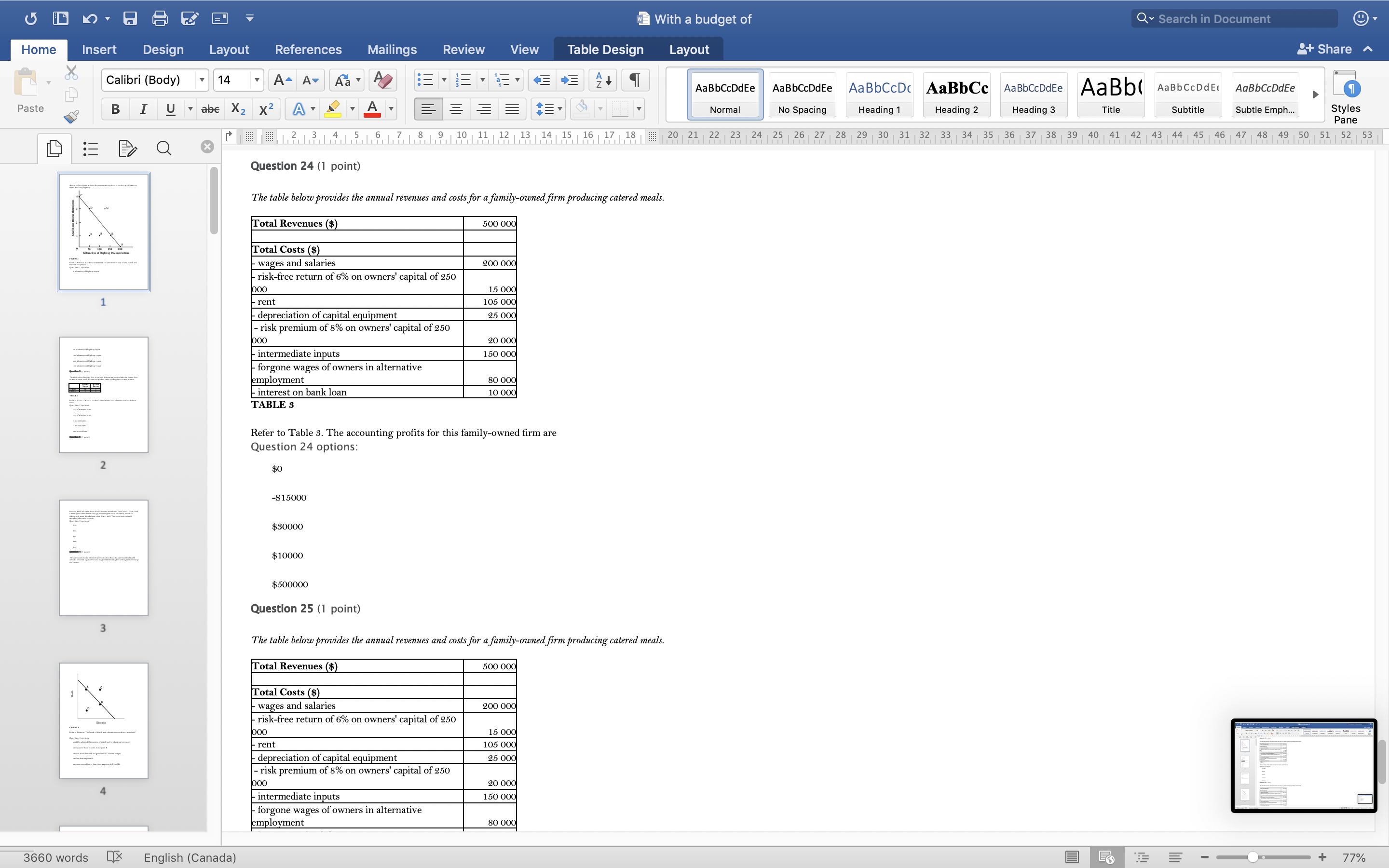
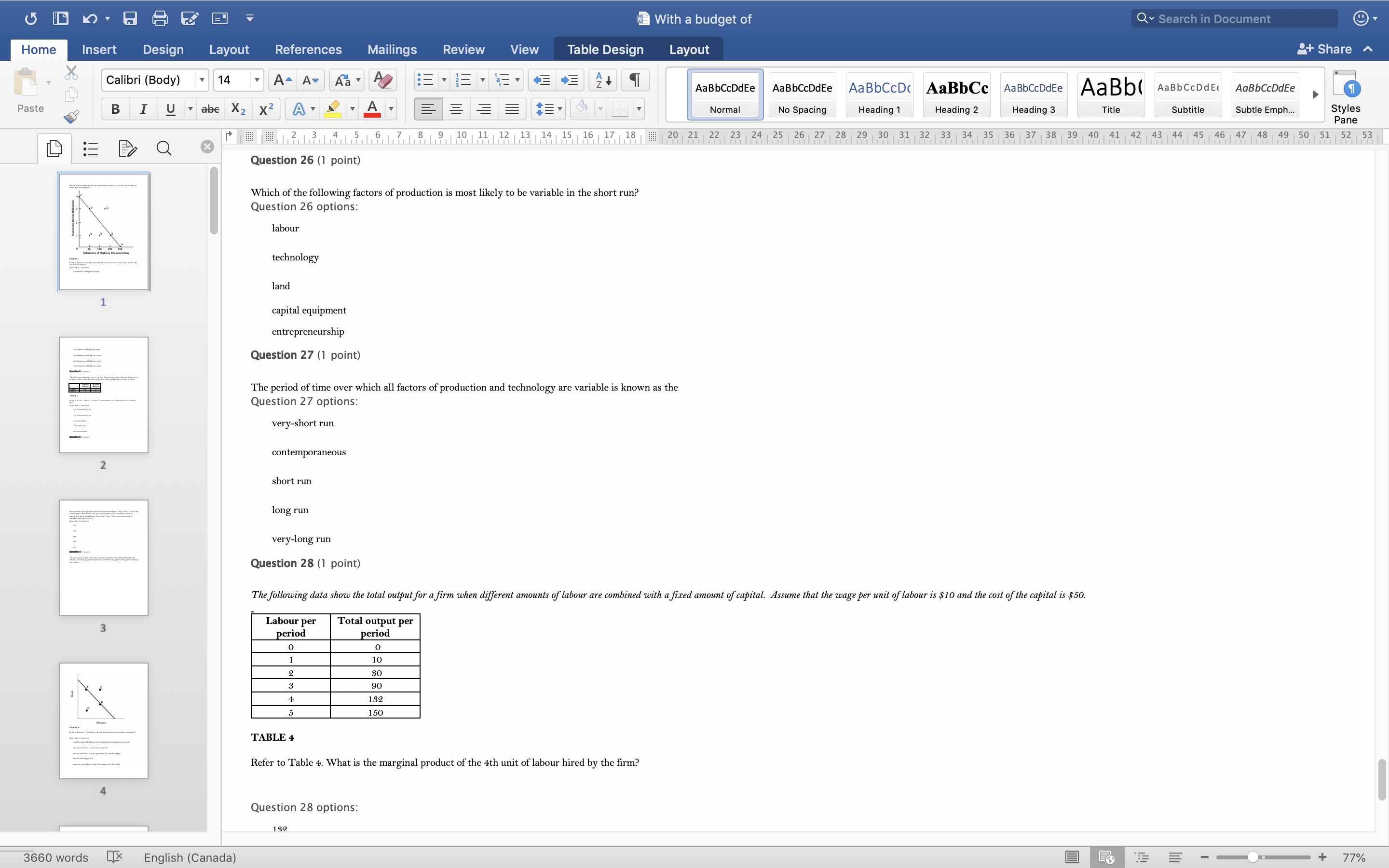
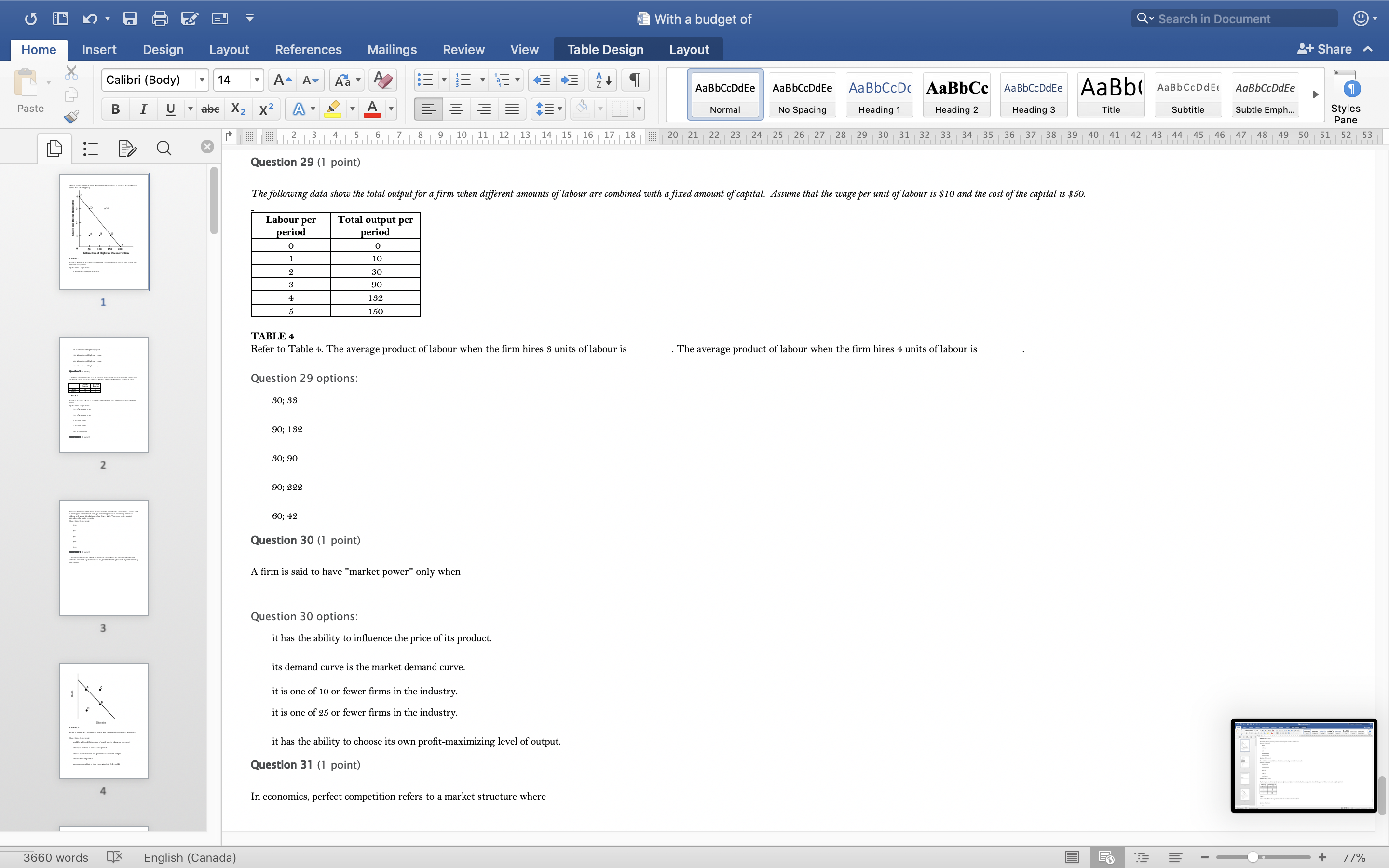
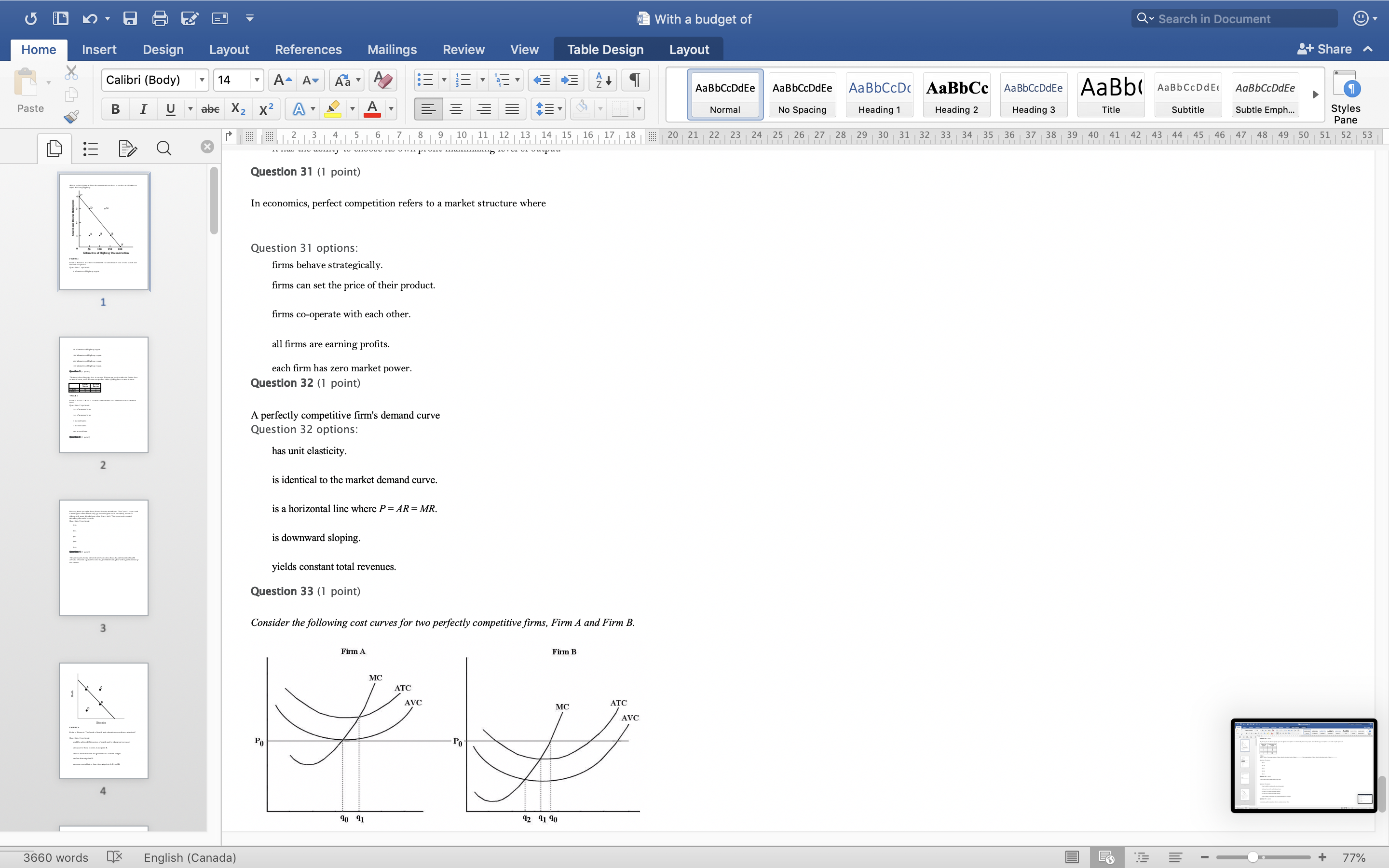
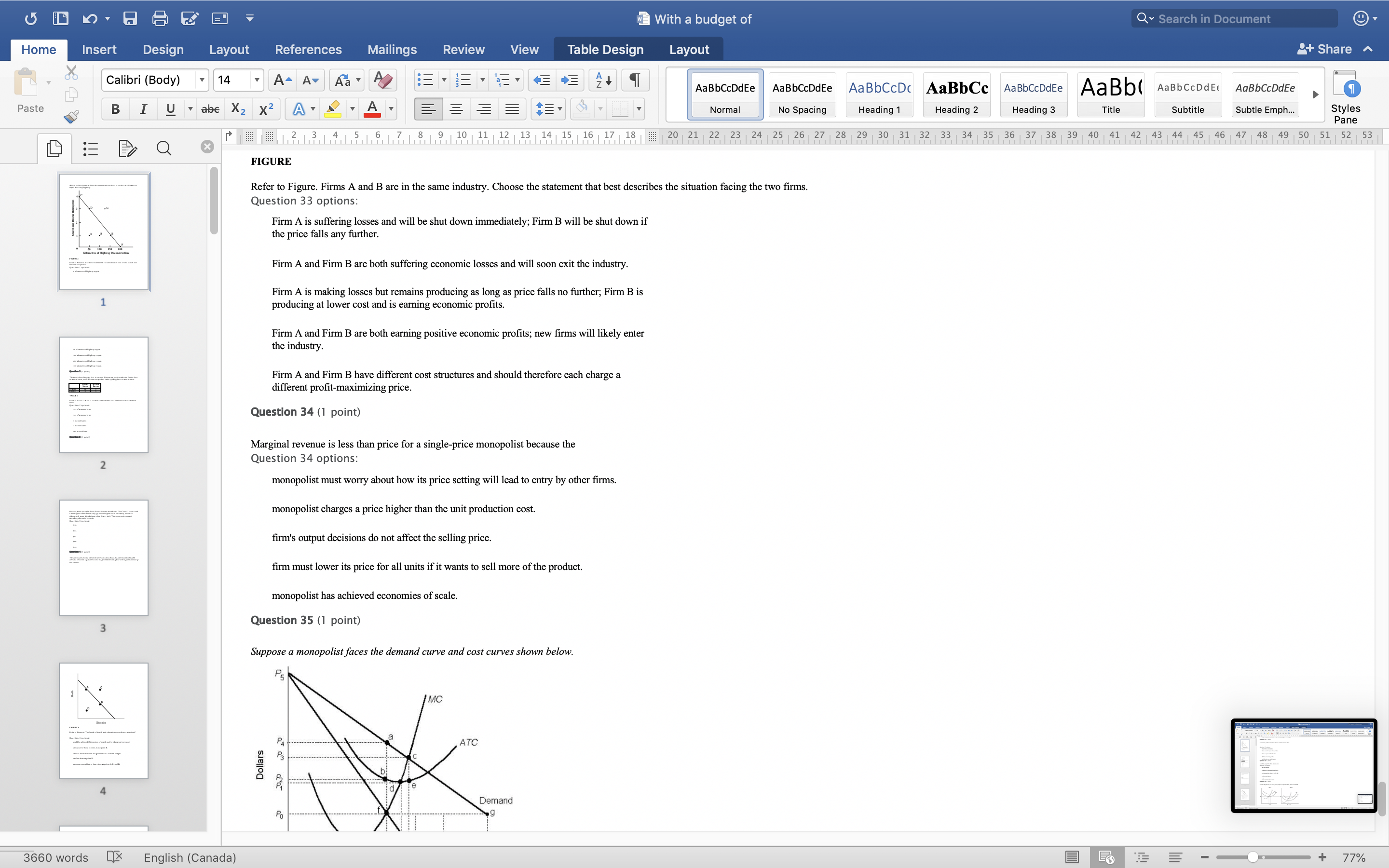
With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2|AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 1516171 8, 1 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 4 (1 point) The downward-sloping line in the diagram below shows the combinations of health care and education expenditures that the government can afford with a given amount of tax revenue. Health D Education FIGURE 2 Refer to Figure 2. The levels of health and education expenditures at point C Question 4 options could be achieved if the prices of health and/ or education increased. are equal to those of point A and point B. are not attainable with the government's current budget. are less than at point D. are more cost-effective than those at points A, B, and D. Question 5 (1 point) Which of the following is a normative statement? Question 5 options: Queen Elizabeth II is the wealthiest woman in the world. The sun rises in the west and sets in the east. Reducing unemployment is more important than reducing inflation. 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q CALL6171819 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 2 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 5 (1 point) Which of the following is a normative statement? Question 5 options: Queen Elizabeth II is the wealthiest woman in the world. The sun rises in the west and sets in the east. Reducing unemployment is more important than reducing inflation. An increase in the price of lumber is followed by a decrease in the construction of new houses. A government deficit will reduce unemployment and cause an increase in prices. Question 6 (1 point) Data collected repeatedly over successive periods of time are called Question 6 options: time-series data. time-analysis data. cross-sectional data. logarithmic data. opographic data. Question 7 (1 point) When an increase in one variable is associated with an increase in a second variable, the two variables are Question 7 options: negatively related. inversely proportionally related. equivalent. positively related. proportionally related. Question 8 (1 point) There have been brobosals that a tar be imbosed on sugar-laden soft drinks in an attempt to reduce their consumbtion. Assume for simblicity that all bottled soft drinks are the same size. Subbose the initial market equilibrium is P = $2.00 and O = 1000. 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane DED Q x CALL18191 10 14 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 8 (1 point) There have been proposals that a tax be imposed on sugar-laden soft drinks in an attempt to reduce their consumption. Assume for simplicity that all bottled soft drinks are the same size. Suppose the initial market equilibrium is P = $2.00 and 2 = 1000. 3.00- 2.80- - S' 2.60+ 2.40+ 2.20- t=0.60 S 2.00+ 1.80 1.60- 1.40- 1.20- 1.00 .80 .60 + .40+ .20+ 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 Error! Filename not specified. Bottles of Soft Drinks per Day FIGURE s Refer to Figure 3. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $0.60 per soft drink purchased. The price paid by the consumer and actual price received by the producer are (respectively) Question 8 options: $2.00 and $2.20. $2.40 and $1.80. $2.20 and $2.00. $2.60 and $1.60. $1.80 and $2.00. Question 9 (1 point) Diagrams A, B, and C show 3 individual consumers' demand curves for cement. Consumers A, B, and C constitute the entire monthly cement market in this region. Error! Filename not specified Error. Filename not specified. Error. Filename not specified.Error! Filename not specified. 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2|AL . A . = = = =13 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 31451617 1 8, 1 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 9 (1 point) Diagrams A, B, and C show 3 individual consumers' demand curves for cement. Consumers A, B, and C constitute the entire monthly cement market in this region. Error! Filename not specified. Error! Filename not specified. Error! Filename not specified.Error! Filename not specified. A. B. C. 100 100- 100- 90 -+ 90 90 - 80+ 80 - 80 - Price ($) 70+ 70- 70 60+ 60 - 60 - 50- 50 - 50 - 40 - 40- 40 - 30 30 30 - 20 - 20- 20 - 10 - 10 10 - 2000 4000 6000 8000 2000 4000 6000 8000 2000 4000 6000 8000 cubic metres of cement cubic metres of cement cubic metres of cement per month per month per month FIGURE 4 Refer to Figure 4. What is the market demand (in cubic metres per month) for cement at a price of $60 per cubic metre? Question 9 options: 1000 3000 2000 4000 0 Question 10 (1 point) Suppose that the quantity of a good demanded rises from 90 units to 110 units when the price falls from $1.20 to 80 cents per unit. The price elasticity of demand for this product is Question 10 options: 2.0 1.5 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane DED Q X 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 11 (1 point) Suppose the price elasticity of demand for some good is 1.4. A 10% increase in the price of the good results in Question 11 options: a 14% increase in the quantity demanded. a 1.4% increase in the quantity demanded. There is not enough information to answer this question. a 1.4% decrease in the quantity demanded. a 14% decrease in the quantity demanded. Question 12 (1 point) If the value of the price elasticity of demand is 0.6, demand is said to be Question 12 options: partially elastic inelastic. elastic. partially inelastic. somewhat inelastic. Question 13 (1 point) An inferior good has Question 13 options: a negative income elasticity of demand. a positive income elasticity of demand and a price elasticity of demand greater than 1. a positive income elasticity of demand. a negative price elasticity of demand. in income elasticity of demand greater than zero but less than 1. Question 14 (1 point) A legally imposed upper limit on a price is called Question 14 options: 660 words English (Canada) E E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q 5161718 19 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 2 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 14 (1 point) A legally imposed upper limit on a price is called Question 14 options: a price ceiling government price. a price support. price floor. an excise price. Question 15 (1 point) Consider a competitive labour market. The likely consequence of a binding minimum wage in this labour market is Question 15 options: unemployment. a labour shortage. a higher wage for all individuals. a lower wage for all individuals. excess demand for workers. Question 16 (1 point) Supply P2 $ Po 660 words LX English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste BI U abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q CALL1819 1 10 12 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 16 (1 point) Supply $ Po P3 Demand 0 A B F D C Quantity FIGURE 5 Refer to Figure 5. With a price ceiling of P3, how large will the resulting shortage be? Question 16 options: BC AF FD AC FC 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 16171819 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 2 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 17 (1 point) $4.00 $3.50 $3.00 - $2.50 Pric $2.00 $1.50 $1.00 $0.50 $0.00+ X 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Quantity FIGURE 6 Refer to Figure 6. A price floor set at $2.50 will result in Question 17 options: no change to the market outcomes. a shortage of 5 units. a shortage of 10 units. a surplus of 10 units. a surplus of 5 units. Question 18 (1 point) Demand and Supply Schedules for Chocolate Bars Quantity Quantity Demanded Sunnlied 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A- AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 5161718 19 1 101 12 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 18 (1 point) Demand and Supply Schedules for Chocolate Bars Quantity Quantity Demanded Supplied Price (thousands per (thousands per ($) week) week 2.00 1500 2100 1.80 1600 2050 1.60 700 2000 1.40 180 1950 1.20 1900 1900 1.00 2000 1850 0.80 2100 1800 0.60 2200 1750 0.40 2300 1700 TABLE 2 A) Impose an equilibrium price of $1.80. 26) Refer to Table 2. Suppose that as a public-health measure the government wants to reduce the number of chocolate bars that children consume. To achieve this outcome the government could implement which of the following policies? B) Impose a price floor of $1.80. C) Impose a price ceiling of $1.80 D) Impose an equilibrium price of $1.20. E) Impose a price ceiling of $2.00. Answer: B Question 18 options: Impose a price ceiling of $2.00. Impose a price ceiling of $1.80. Impose an equilibrium price of $1.20. Impose an equilibrium price of $1.80. Impose a price floor of $1.80. Question 19 (1 point) Suppose the government establishes a ceiling on the price of rental accommodation that is lower than the free-market equilibrium price. In this case, Question 19 options: a surplus of current rental units will develop. the rental housing market will be unaffected. construction of new rental units will be encouraged. the current stock of rental housing will be better maintained as there is a shortage of 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q CALL61718 19 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 19 (1 point) Suppose the government establishes a ceiling on the price of rental accommodation that is lower than the free-market equilibrium price. In this case, Question 19 options: a surplus of current rental units will develop. the rental housing market will be unaffected. construction of new rental units will be encouraged. the current stock of rental housing will be better maintained as there is a shortage of housing. those people who obtain rental units at the ceiling price will benefit. Question 20 (1 point) 70 Supply Price ($s per hour) 60 50 ............ 40 2 6 30 ....f.." 3 7 20 ..... ........" 10 (4 Demand 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 Quantity (number of hours of gardening service per month) FIGURE 7 Refer to Figure 7. At the market-clearing price and quantity of $30 per hour and 4000 hours of gardening services purchased, the economic surplus is Question 20 options: the sum of the areas below the demand curve, but above the market-clearing price of $30 -i.e., areas 1, 2, 6. the sum of the arane halour the dome in to Anon hours- 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x CALL6218191 10 12 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 FIGURE 7 Refer to Figure 7. At the market-clearing price and quantity of $30 per hour and 4000 hours of gardening services purchased, the economic surplus is Question 20 options: he sum of the areas below the demand curve, but above the market-clearing price of $30 -i.e., areas 1, 2, 6. the sum of the areas below the demand curve, up to 4000 hours -i.e., areas 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. the sum of the areas above the supply curve, but below the market-clearing price of $30 -i.e., areas 3, 4, 7. the sum of the areas below the demand curve - i.e., areas 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. the sum of the areas above the supply curve and below the demand curve - i.e., areas 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7. Question 21 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($) 500 000 Total Costs ($) - wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 looo 15 000 rent 105 000 - depreciation of capital equipment 25 000 - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 20 000 intermediate inputs 150 000 - forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 00 interest on bank loan 10 000 TABLE 3 Refer to Table 3. The explicit costs for this family-owned firm are Question 21 options $505000 $490000 $500000 $1 15000 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 16178191 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Refer to Table 3. The explicit costs for this family-owned firm are Question 21 options: $505000 $490000 $500000 $1 15000 $605000 Question 22 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($) 500 000 Total Costs ($) wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 15 000 - rent 105 000 - depreciation of capital equipment 25 000 - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 20 000 intermediate inputs 150 000 - forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 000 interest on bank loan 10 000 TABLE 3 Refer to Table 3. The implicit costs for this family-owned firm are Question 22 options: $35000 $490000 $1 15000 $80000 $ 100000 Question 23 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A A A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 ALA = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 23 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($) 500 000 Total Costs ($) - wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 15 000 - rent 105 000 - depreciation of capital equipment - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 25 000 ooo 20 00 intermediate inputs 150 000 - forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 000 interest on bank loan 10 000 TABLE 3 Refer to Table 3. The implicit costs for this family-owned firm are Question 23 options: $1 15000 $80000 $35000 $100000 $490000 Question 24 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($) 500 000 Total Costs ($) - wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 15 000 - rent 105 000 - depreciation of capital equipment 25 000 - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 000 20 000 intermediate inputs 150 000 forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 000 interest on bank loan 10 000 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U. abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 161718 19 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 24 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($ 500 000 Total Costs ($) - wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 15 000 - rent 05 000 depreciation of capital equipment 25 000 - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 20 000 intermediate inputs 150 000 forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 000 interest on bank loan 10 000 TABLE Refer to Table 3. The accounting profits for this family-owned firm are Question 24 options: $0 -$15000 $30000 $10000 $500000 Question 25 (1 point) The table below provides the annual revenues and costs for a family-owned firm producing catered meals. Total Revenues ($) 500 000 Total Costs ($ - wages and salaries 200 000 - risk-free return of 6% on owners' capital of 250 15 000 - rent 105 000 depreciation of capital equipment 25 000 - risk premium of 8% on owners' capital of 250 ooo 20 000 intermediate inputs 150 000 - forgone wages of owners in alternative employment 80 000 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A - A Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste BI U abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 26 (1 point) Which of the following factors of production is most likely to be variable in the short run? Question 26 options: labour technology land capital equipment entrepreneurship Question 27 (1 point) The period of time over which all factors of production and technology are variable is known as the Question 27 options: very-short run contemporaneous short run long run very-long run Question 28 (1 point) The following data show the total output for a firm when different amounts of labour are combined with a fixed amount of capital. Assume that the wage per unit of labour is $ 10 and the cost of the capital is $50. Labour per Total output per period period 0 10 2 30 90 132 150 TABLE 4 Refer to Table 4. What is the marginal product of the 4th unit of labour hired by the firm? Question 28 options: 189 660 words English (Canada) E + 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane DED Q x 1516171819 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 29 (1 point) The following data show the total output for a firm when different amounts of labour are combined with a fixed amount of capital. Assume that the wage per unit of labour is $10 and the cost of the capital is $50. Labour per Total output per period period 0 10 30 90 132 150 TABLE 4 Refer to Table 4. The average product of labour when the firm hires 3 units of labour is The average product of labour when the firm hires 4 units of labour is Question 29 options: 30; 33 90; 132 30; 90 90; 222 60; 42 Question 30 (1 point) A firm is said to have "market power" only when Question 30 options: it has the ability to influence the price of its product. its demand curve is the market demand curve. it is one of 10 or fewer firms in the industry. it is one of 25 or fewer firms in the industry. it has the ability to choose its own profit-maximizing level of output. Question 31 (1 point) In economics, perfect competition refers to a market structure where 660 words English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 A AV Aa A AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc|AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U . abe X2 X2 AL . A. Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q x 1213 14 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Question 31 (1 point) In economics, perfect competition refers to a market structure where Question 31 options: firms behave strategically. firms can set the price of their product. firms co-operate with each other. all firms are earning profits. each firm has zero market power. Question 32 (1 point) A perfectly competitive firm's demand curve Question 32 options: has unit elasticity. is identical to the market demand curve. is a horizontal line where P = AR = MR. is downward sloping yields constant total revenues. Question 33 (1 point) er the following cost curves for two perfectly competitive firms, Firm A and Firm B. Firm A Firm B 10 91 660 words OX English (Canada) E 77%With a budget of Q Search in Document Home Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Table Design Layout + Share ~ Calibri (Body) 14 AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDdEe AaBbCcDc AaBbCc AaBbCcDdEe AaBb( AaBbCCDdEE AaBbCcDdEe Paste B I U . abe X2 X2 AL A = = = =1 . Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Heading 3 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Styles Pane Q X CALL18191 10 14 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 FIGURE Refer to Figure. Firms A and B are in the same industry. Choose the statement that best describes the situation facing the two firms. Question 33 options Firm A is suffering losses and will be shut down immediately; Firm B will be shut down if the price falls any further. Firm A and Firm B are both suffering economic losses and will soon exit the industry. Firm A is making losses but remains producing as long as price falls no further; Firm B is producing at lower cost and is earning economic profits. Firm A and Firm B are both earning positive economic profits; new firms will likely enter the industry. Firm A and Firm B have different cost structures and should therefore each charge a different profit-maximizing price. Question 34 (1 point) Marginal revenue is less than price for a single-price monopolist because the Question 34 options: monopolist must worry about how its price setting will lead to entry by other firms. monopolist charges a price higher than the unit production cost. firm's output decisions do not affect the selling price. firm must lower its price for all units if it wants to sell more of the product. monopolist has achieved economies of scale. Question 35 (1 point) Suppose a monopolist faces the demand curve and cost curves shown below. P5 MC TC Dollars Demand 660 words LX English (Canada) E + 77%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


