I have some problems with my code. Pls help, show all the code.


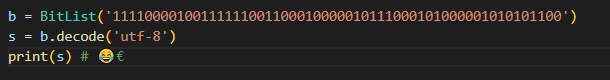
my output like that. I wanna the exact same output as above. pls help
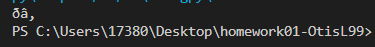
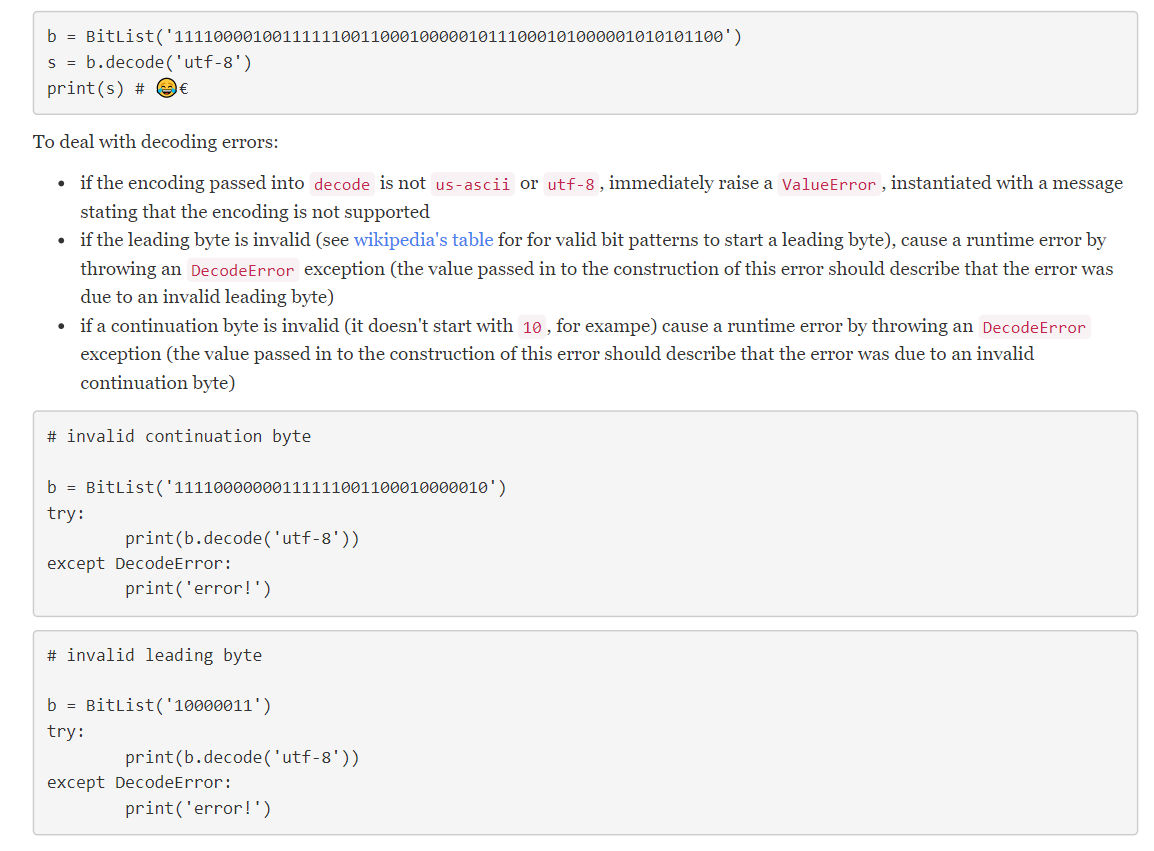
- decode(encoding='utf- ' ) This method has a single parameter, the encoding (a str), and it returns a string: 1. the encoding can only be or utf-8 - the default encoding should be utf-8 - consequently, decode can be called with no arguments 2. it returns a string An instance of Bitlist can be decoded. In the example below, the bits are treated as 7-bit ASCII : bits = BitList.from_ints (1,1,0,0,0,0,1) ch = bits.decode('us-ascii') print ( ch )# a This should work if there are multiple characters encoded: new_bit_list = BitList ( ' 11000011000001 ') s= new_bit_list.decode('us-ascii') print(s) \# aA One way to implement this is to: 1. calculate the decimal value from the bits 2. convert the decimal value into a character with chr This is a little tricky, as chunking bits into equivalent lengths isn't adequate: - utf-8 is variable length - the "leading byte" must be examined to determine how many bytes total are required - for example, encountering the byte 11101010 means that there should be three bytes total (there are 31 's) - the continuation bits are all prefixed with 10 - see the slides / notebook on unicode for more details b= BitList(' 11110000100111111001100010000010111000101000001010101100 ') s=bdecode( utf-8') print(s) \# (. To deal with decoding errors: - if the encoding passed into decode is not us-ascii or utf-8, immediately raise a ValueError, instantiated with a message stating that the encoding is not supported - if the leading byte is invalid (see wikipedia's table for for valid bit patterns to start a leading byte), cause a runtime error by throwing an DecodeError exception (the value passed in to the construction of this error should describe that the error was due to an invalid leading byte) - if a continuation byte is invalid (it doesn't start with 10 , for exampe) cause a runtime error by throwing an DecodeError exception (the value passed in to the construction of this error should describe that the error was due to an invalid continuation byte) \# invalid continuation byte b = BitList(' 11110000000111111001100010000010) try: except DecodeError: print('error!') \# invalid leading byte b= BitList ( ' 10000011 ') try: print(b.decode('utf-8')) except DecodeError: print('error!') b= BitList(' 11110000100111111001100010000010111000101000001010101100 ) s=bdecode(utf8 ') print(s) \# , \[ \text { PS C: \Users } \backslash 17380 \backslash D e s k t o p \backslash \text { homework01-0tisL99 } \]











