I have two different questions. I'm going to separate and make them as clear as I can. The online class I use resets the values each time I retry the questions so the full question (as the process is step by step and will not let you see the next until you do one section of the question) will be shown along with the values. That way you can see what needs to be answered. Then, a new set of values/information will be below for the new version of the question I have to do.
Incorrect but full view of question 1: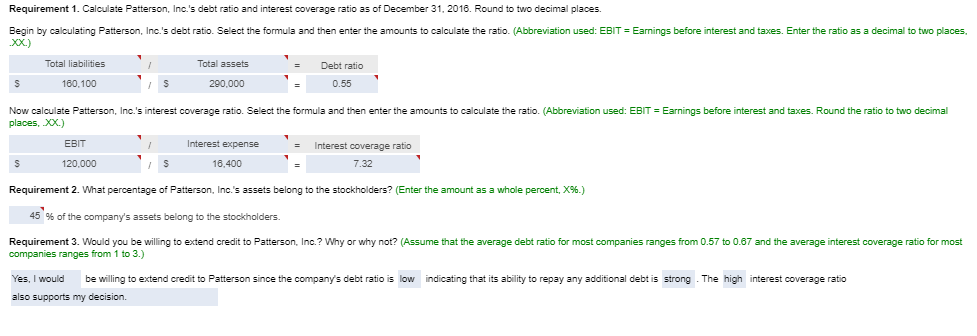
Information for that question:
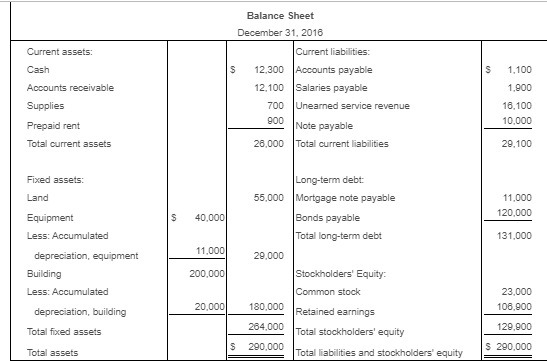
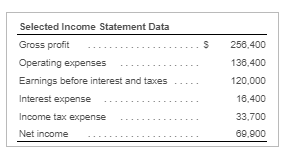
New values and information for a copy of that question.
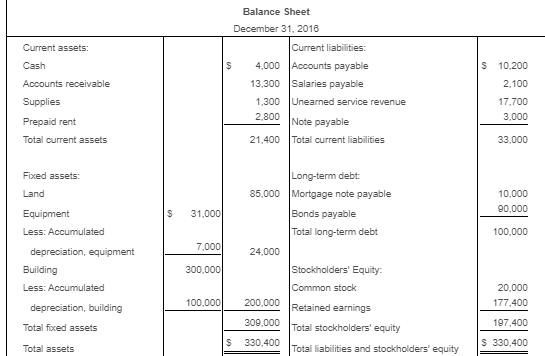
A second question:
New values for the second questions
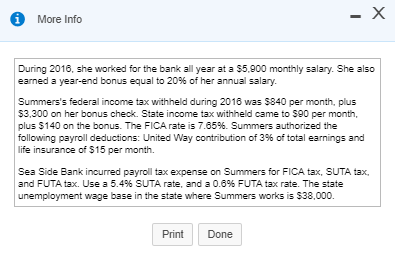
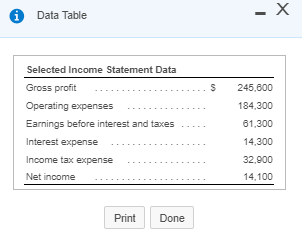
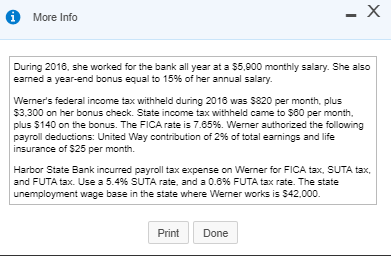
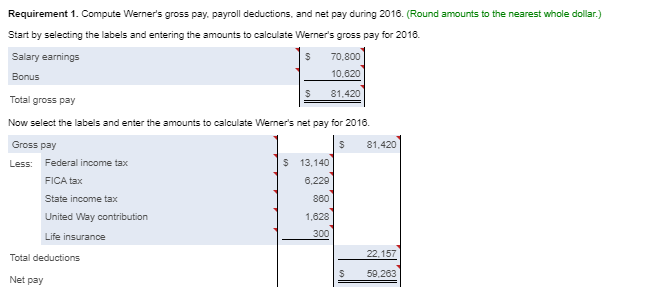
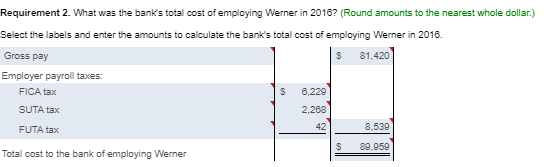
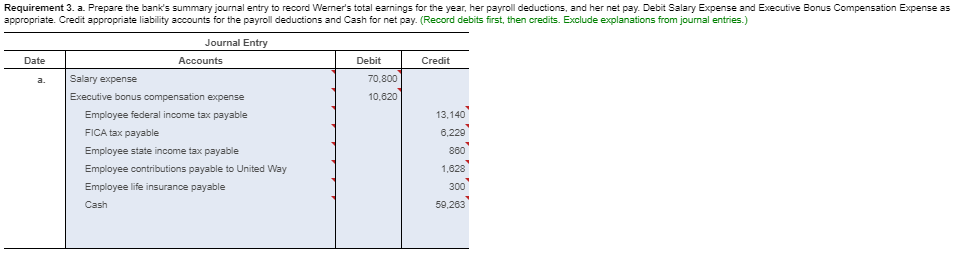
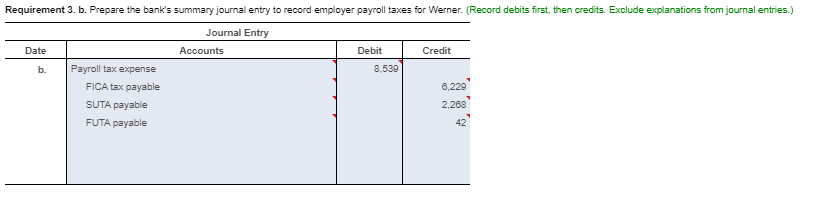
Requirement 1. Calculate Patterson, Inc.'s debt ratio and interest coverage ratio as of December 31, 2016. Round to two decimal places. Begin by calculating Patterson, Inc.'s debt ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the ratio. (Abbreviation used: EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxes. Enter the ratio as a decimal to two places, XX.) Total liabilities Total assets Debt ratio $ 160,100 S 290.000 0.55 Now calculate Patterson, Inc.'s interest coverage ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the ratio. (Abbreviation used: EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxes. Round the ratio to two decimal places. XX.) EBIT Interest expense = Interest coverage ratio S 120.000 IS 16.400 7.32 Requirement 2. What percentage of Patterson, Inc.'s assets belong to the stockholders? (Enter the amount as a whole percent, X%.) 45 % of the company's assets belong to the stockholders. Requirement 3. Would you be willing to extend credit to Patterson, Inc.? Why or why not? (Assume that the average debt ratio for most companies ranges from 0.57 to 0.67 and the average interest coverage ratio for most companies ranges from 1 to 3.) indicating that its ability to repay any additional debt is strong. The high interest coverage ratio Yes, I would be willing to extend credit to Patterson since the company's debt ratio is low also supports my decision. Current assets: Cash Balance Sheet December 31, 2016 Current liabilities: 12,300 Accounts payable 12.100 Salaries payable 700 Unearned service revenue Note payable Total current liabilities Accounts receivable Supplies 1,100 1.000 16.100 10,000 29.100 Prepaid rent Total current assets Fixed assets: Land Long-term debt: 55,000 Mortgage note payable Bonds payable Total long-term debt 11.000 120.000 Equipment 40.000 Less: Accumulated 131.000 11,000 20.000 depreciation, equipment Building Less: Accumulated 200,000 depreciation, building 20.000 180.000 Stockholders' Equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 23.000 106,900 129.900 Total fixed assets 284,000 $ 290,000 $ 290,000 Total assets Selected Income Statement Data Gross profit Operating expenses ... Earnings before interest and taxes ..... Interest expense ..... Income tax expense Net income 256,400 136,400 120,000 16,400 33.700 69,900 Current assets: Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Balance Sheet December 31, 2016 Current liabilities: 4,000 Accounts payable 13.300 Salaries payable 1,300 Unearned service revenue 10.200 2,100 17.700 3.000 33.000 Prepaid rent 2.800 Note payable Total current assets 21.400 Total current liabilities Fixed assets: Land 85.000 Long-term debt: Mortgage note payable Bonds payable Total long-term debt $ 31,000 Equipment Less: Accumulated 10,000 90.000 100,000 24.000 depreciation, equipment Building Less: Accumulated 7.000 300.000 100.000 200.000 depreciation, building Total fixed assets Total assets Stockholders' Equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 20.000 177.400 197,400 $ 330,400 $ 330,400 * Data Table Selected Income Statement Data Gross profit Operating expenses Earnings before interest and taxes ..... 245,600 184,300 61,300 14.300 32,900 14,100 Interest expense Income tax expense Net income Print Done * More Info During 2018, she worked for the bank all year at a $5.900 monthly salary. She also earned a year-end bonus equal to 15% of her annual salary Werner's federal income tax withheld during 2016 was $820 per month, plus $3,300 on her bonus check. State income tax withheld came to $60 per month plus $140 on the bonus. The FICA rate is 7.65%. Werner authorized the following payroll deductions: United Way contribution of 2% of total earnings and life insurance of $25 per month Harbor State Bank incurred payroll tax expense on Werner for FICA tax, SUTA tax, and FUTA tax. Use a 5.4% SUTA rate, and a 0.6% FUTA tax rate. The state unemployment wage base in the state where Werner works is $42.000 Print Done Requirement 1. Compute Werner's gross pay, payroll deductions, and net pay during 2016. (Round amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Start by selecting the labels and entering the amounts to calculate Werner's gross pay for 2016 Salary earnings S 70.800 10.620 Bonus 81,420 Total gross pay Now select the labels and enter the amounts to calculate Werner's net pay for 2016 Gross pay s 81.420 Less: Federal income tax $ 13,140 FICA tax 6.229 State income tax 360 United Way contribution Life insurance 300 1.628 Total deductions 22.157 59.263 Net pay Requirement 2. What was the bank's total cost of employing Werner in 2016? (Round amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Select the labels and enter the amounts to calculate the bank's total cost of employing Werner in 2016. Gross pay 81.4201 Employer payroll taxes: FICA tax 1 $ 6.2291 SUTA tax FUTA tax Total cost to the bank of employing Werner Requirement 3. a. Prepare the bank's summary journal entry to record Werner's total earnings for the year, her payroll deductions, and her net pay. Debit Salary Expense and Executive Bonus Compensation Expense as appropriate. Credit appropriate liability accounts for the payroll deductions and Cash for net pay. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from journal entries.) Date Credit Debit 70.800 10,620 13.140 Journal Entry Accounts Salary expense Executive bonus compensation expense Employee federal income tax payable FICA tax payable Employee state income tax payable Employee contributions payable to United Way Employee life insurance payable Cash 6,229 860 1,828 300 59,263 Requirement 3. b. Prepare the bank's summary journal entry to record employer payroll taxes for Werner. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from journal entries.) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit b. 8.539 6.229 Payroll tax expense FICA tax payable SUTA payable FUTA payable 2.289 * More Info During 2016, she worked for the bank all year at a $5.900 monthly salary. She also earned a year-end bonus equal to 2096 of her annual salary. Summers's federal income tax withheld during 2016 was $840 per month, plus $3,300 on her bonus check. State income tax withheld came to S90 per month plus $140 on the bonus. The FICA rate is 7.65%. Summers authorized the following payroll deductions: United Way contribution of 3% of total earnings and life insurance of $15 per month. Sea Side Bank incurred payroll tax expense on Summers for FICA tax, SUTA tax, and FUTA tax. Use a 5.4% SUTA rate, and a 0.6% FUTA tax rate. The state unemployment wage base in the state where Summers works is $38,000. Print Done Requirement 1. Calculate Patterson, Inc.'s debt ratio and interest coverage ratio as of December 31, 2016. Round to two decimal places. Begin by calculating Patterson, Inc.'s debt ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the ratio. (Abbreviation used: EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxes. Enter the ratio as a decimal to two places, XX.) Total liabilities Total assets Debt ratio $ 160,100 S 290.000 0.55 Now calculate Patterson, Inc.'s interest coverage ratio. Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the ratio. (Abbreviation used: EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxes. Round the ratio to two decimal places. XX.) EBIT Interest expense = Interest coverage ratio S 120.000 IS 16.400 7.32 Requirement 2. What percentage of Patterson, Inc.'s assets belong to the stockholders? (Enter the amount as a whole percent, X%.) 45 % of the company's assets belong to the stockholders. Requirement 3. Would you be willing to extend credit to Patterson, Inc.? Why or why not? (Assume that the average debt ratio for most companies ranges from 0.57 to 0.67 and the average interest coverage ratio for most companies ranges from 1 to 3.) indicating that its ability to repay any additional debt is strong. The high interest coverage ratio Yes, I would be willing to extend credit to Patterson since the company's debt ratio is low also supports my decision. Current assets: Cash Balance Sheet December 31, 2016 Current liabilities: 12,300 Accounts payable 12.100 Salaries payable 700 Unearned service revenue Note payable Total current liabilities Accounts receivable Supplies 1,100 1.000 16.100 10,000 29.100 Prepaid rent Total current assets Fixed assets: Land Long-term debt: 55,000 Mortgage note payable Bonds payable Total long-term debt 11.000 120.000 Equipment 40.000 Less: Accumulated 131.000 11,000 20.000 depreciation, equipment Building Less: Accumulated 200,000 depreciation, building 20.000 180.000 Stockholders' Equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 23.000 106,900 129.900 Total fixed assets 284,000 $ 290,000 $ 290,000 Total assets Selected Income Statement Data Gross profit Operating expenses ... Earnings before interest and taxes ..... Interest expense ..... Income tax expense Net income 256,400 136,400 120,000 16,400 33.700 69,900 Current assets: Cash Accounts receivable Supplies Balance Sheet December 31, 2016 Current liabilities: 4,000 Accounts payable 13.300 Salaries payable 1,300 Unearned service revenue 10.200 2,100 17.700 3.000 33.000 Prepaid rent 2.800 Note payable Total current assets 21.400 Total current liabilities Fixed assets: Land 85.000 Long-term debt: Mortgage note payable Bonds payable Total long-term debt $ 31,000 Equipment Less: Accumulated 10,000 90.000 100,000 24.000 depreciation, equipment Building Less: Accumulated 7.000 300.000 100.000 200.000 depreciation, building Total fixed assets Total assets Stockholders' Equity Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 20.000 177.400 197,400 $ 330,400 $ 330,400 * Data Table Selected Income Statement Data Gross profit Operating expenses Earnings before interest and taxes ..... 245,600 184,300 61,300 14.300 32,900 14,100 Interest expense Income tax expense Net income Print Done * More Info During 2018, she worked for the bank all year at a $5.900 monthly salary. She also earned a year-end bonus equal to 15% of her annual salary Werner's federal income tax withheld during 2016 was $820 per month, plus $3,300 on her bonus check. State income tax withheld came to $60 per month plus $140 on the bonus. The FICA rate is 7.65%. Werner authorized the following payroll deductions: United Way contribution of 2% of total earnings and life insurance of $25 per month Harbor State Bank incurred payroll tax expense on Werner for FICA tax, SUTA tax, and FUTA tax. Use a 5.4% SUTA rate, and a 0.6% FUTA tax rate. The state unemployment wage base in the state where Werner works is $42.000 Print Done Requirement 1. Compute Werner's gross pay, payroll deductions, and net pay during 2016. (Round amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Start by selecting the labels and entering the amounts to calculate Werner's gross pay for 2016 Salary earnings S 70.800 10.620 Bonus 81,420 Total gross pay Now select the labels and enter the amounts to calculate Werner's net pay for 2016 Gross pay s 81.420 Less: Federal income tax $ 13,140 FICA tax 6.229 State income tax 360 United Way contribution Life insurance 300 1.628 Total deductions 22.157 59.263 Net pay Requirement 2. What was the bank's total cost of employing Werner in 2016? (Round amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Select the labels and enter the amounts to calculate the bank's total cost of employing Werner in 2016. Gross pay 81.4201 Employer payroll taxes: FICA tax 1 $ 6.2291 SUTA tax FUTA tax Total cost to the bank of employing Werner Requirement 3. a. Prepare the bank's summary journal entry to record Werner's total earnings for the year, her payroll deductions, and her net pay. Debit Salary Expense and Executive Bonus Compensation Expense as appropriate. Credit appropriate liability accounts for the payroll deductions and Cash for net pay. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from journal entries.) Date Credit Debit 70.800 10,620 13.140 Journal Entry Accounts Salary expense Executive bonus compensation expense Employee federal income tax payable FICA tax payable Employee state income tax payable Employee contributions payable to United Way Employee life insurance payable Cash 6,229 860 1,828 300 59,263 Requirement 3. b. Prepare the bank's summary journal entry to record employer payroll taxes for Werner. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from journal entries.) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit b. 8.539 6.229 Payroll tax expense FICA tax payable SUTA payable FUTA payable 2.289 * More Info During 2016, she worked for the bank all year at a $5.900 monthly salary. She also earned a year-end bonus equal to 2096 of her annual salary. Summers's federal income tax withheld during 2016 was $840 per month, plus $3,300 on her bonus check. State income tax withheld came to S90 per month plus $140 on the bonus. The FICA rate is 7.65%. Summers authorized the following payroll deductions: United Way contribution of 3% of total earnings and life insurance of $15 per month. Sea Side Bank incurred payroll tax expense on Summers for FICA tax, SUTA tax, and FUTA tax. Use a 5.4% SUTA rate, and a 0.6% FUTA tax rate. The state unemployment wage base in the state where Summers works is $38,000. Print Done

















