I just need help finishing problems 5 and 6 because there is info missing that I can't figure out. I attached pictures of problems 1-4 as references. Thank you!
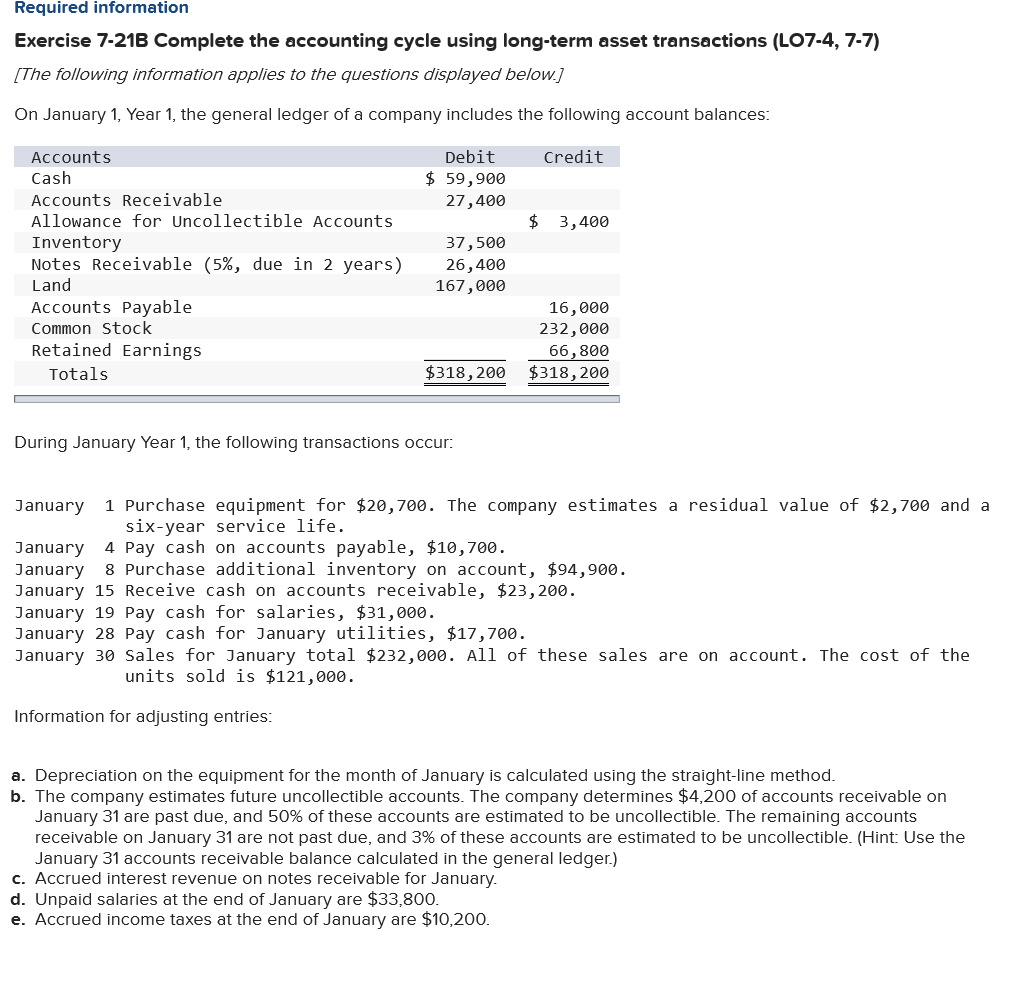
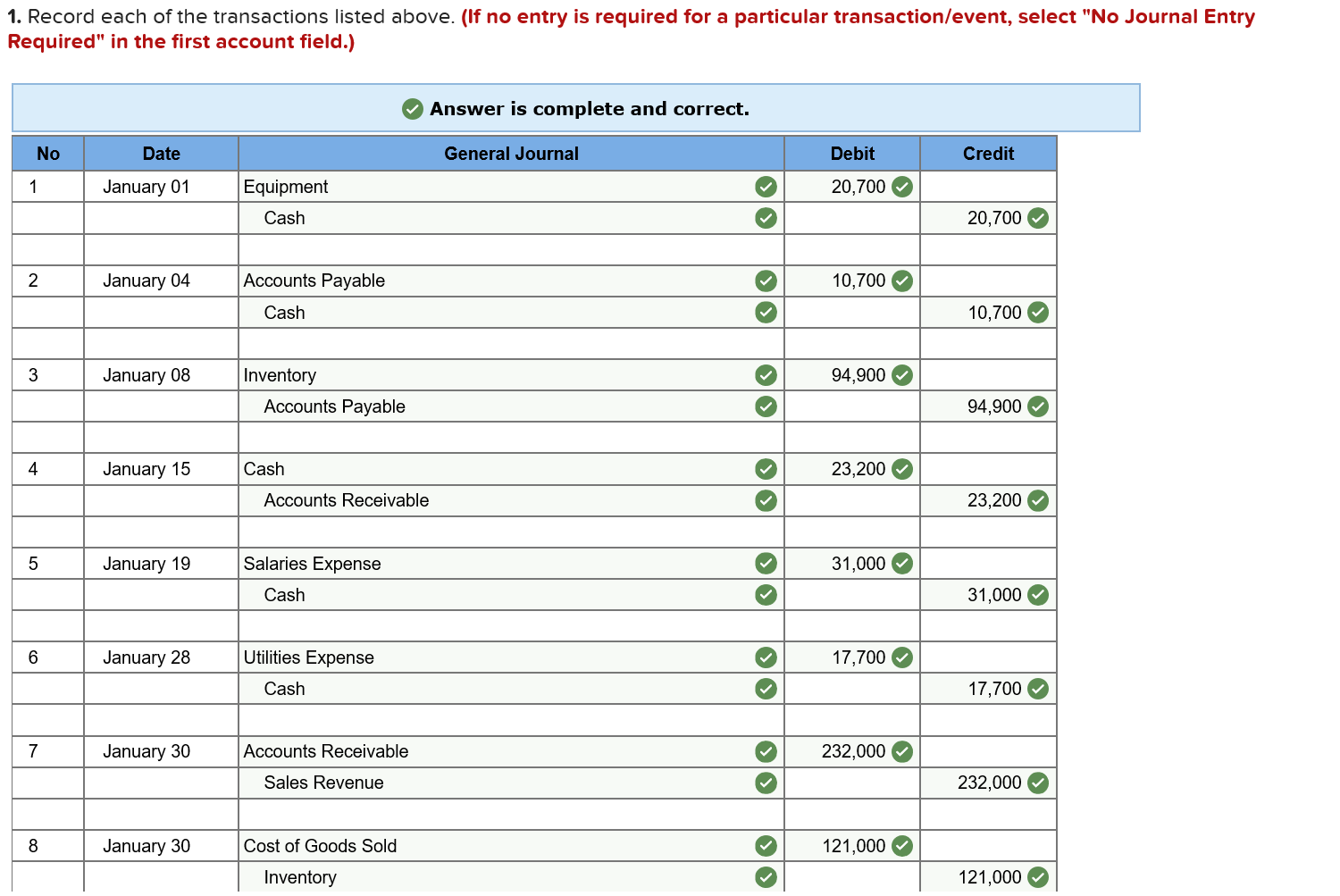
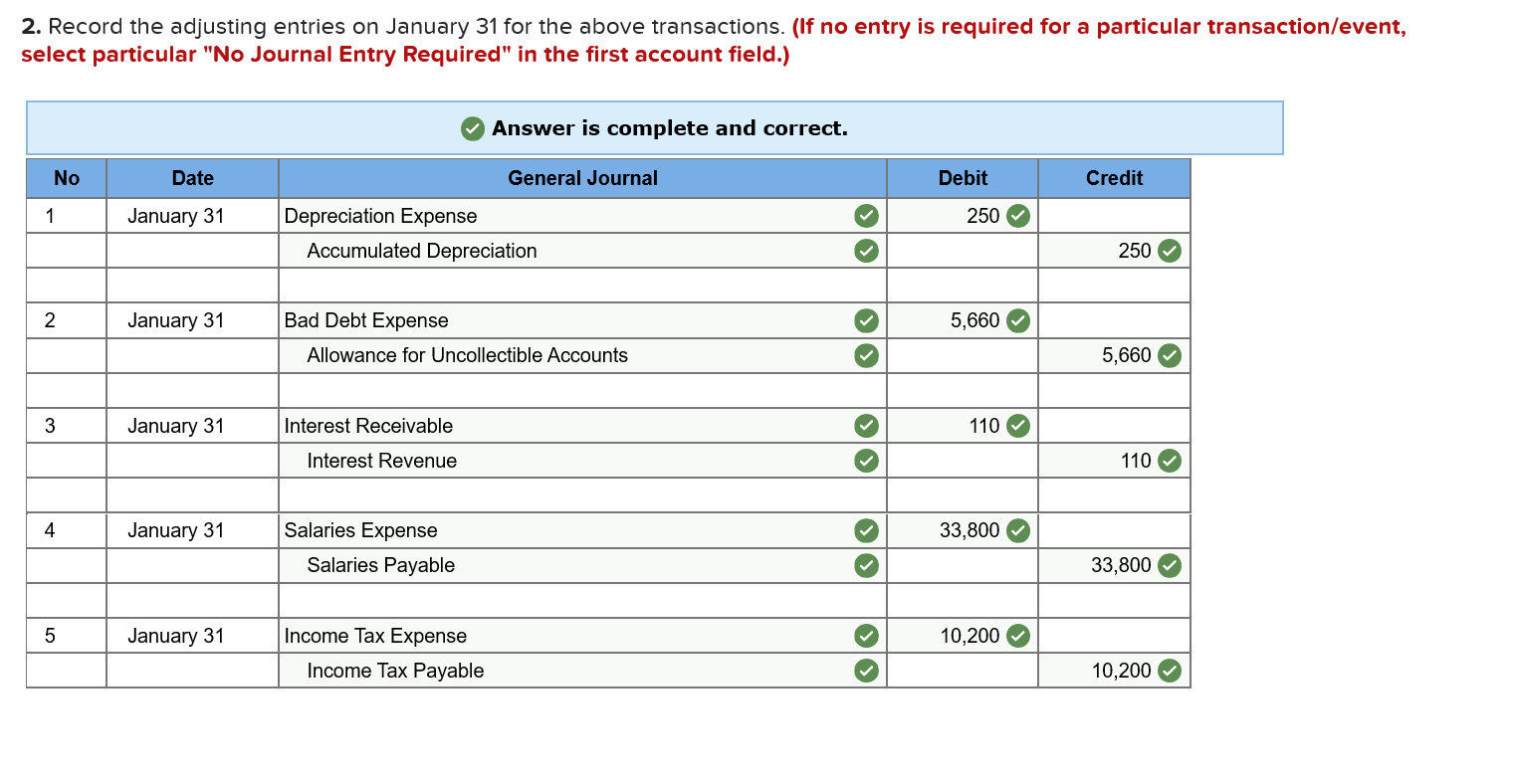
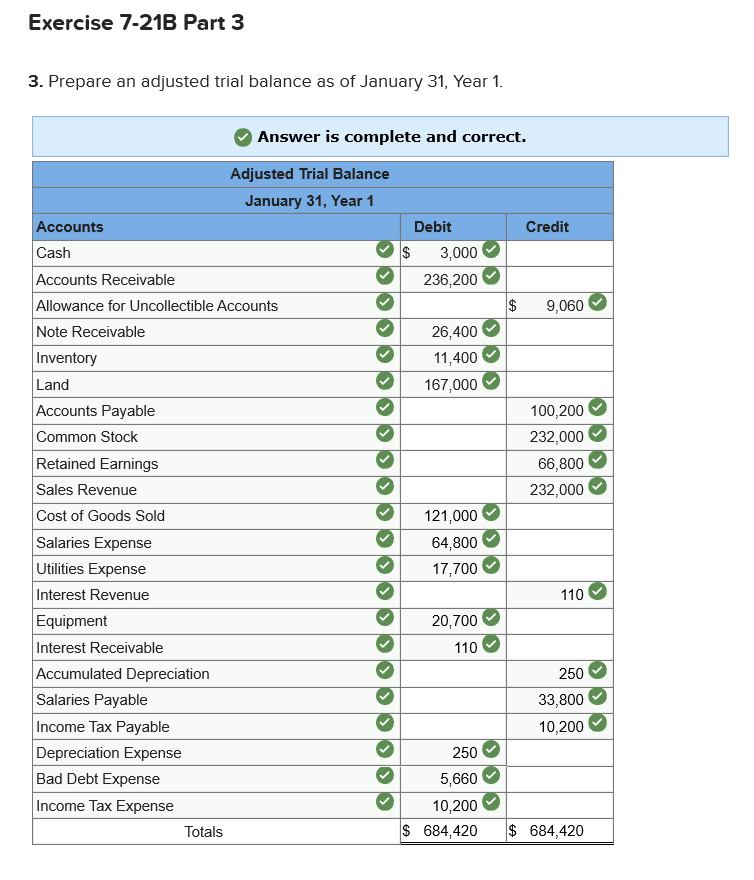
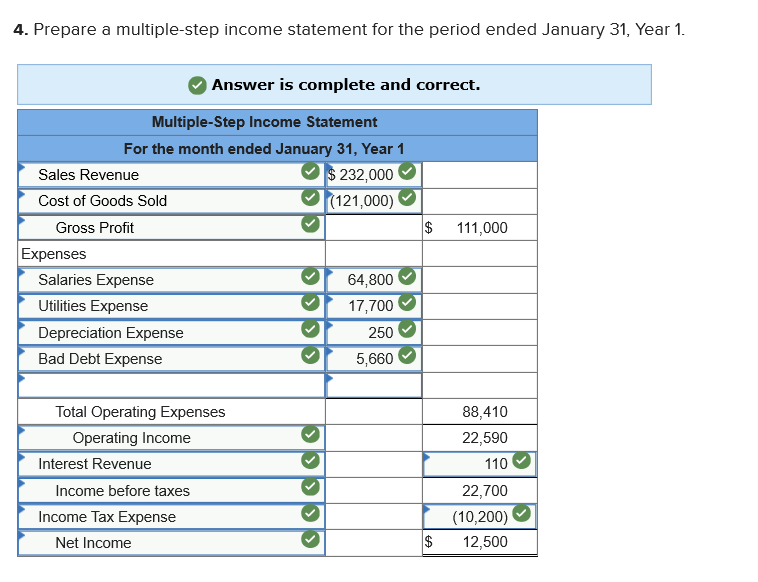
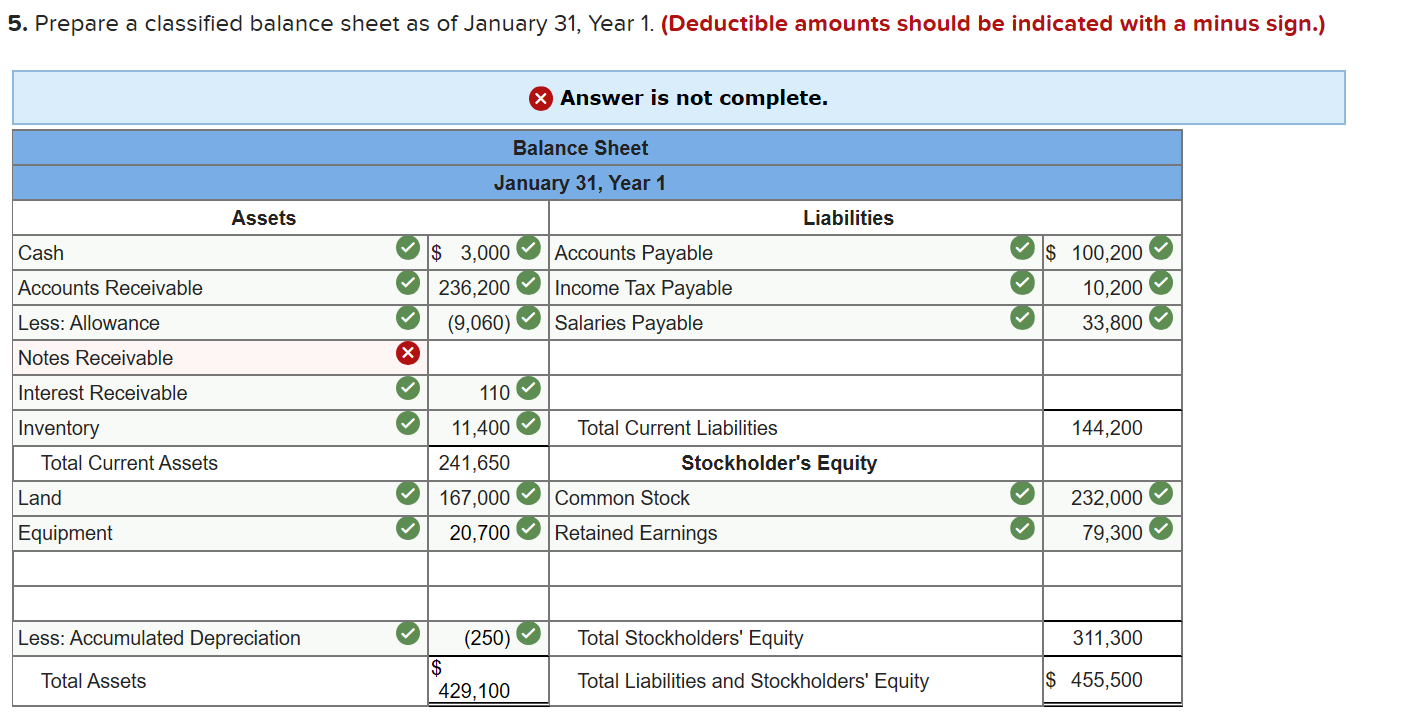
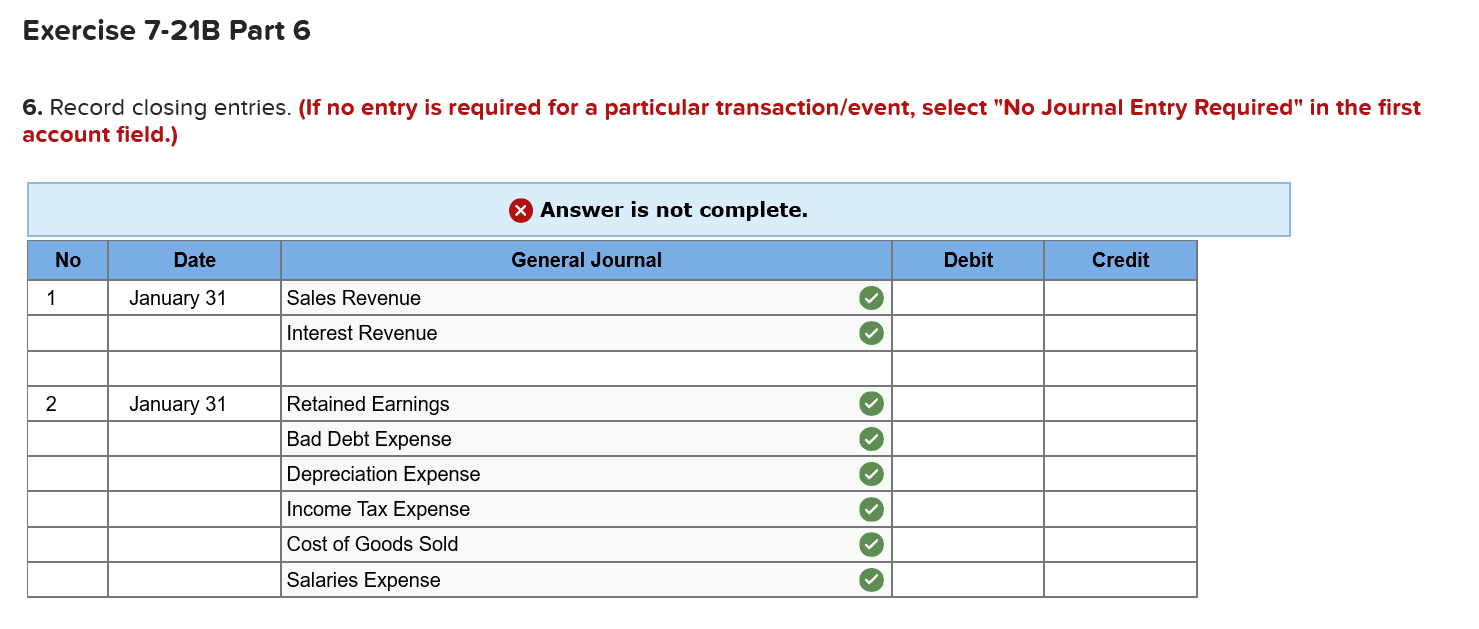
Required information Exercise 7-21B Complete the accounting cycle using long-term asset transactions (LO7-4, 7-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, Year 1, the general ledger of a company includes the following account balances: Credit Debit $ 59,900 27,400 $ 3,400 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Inventory Notes Receivable (5%, due in 2 years) Land Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Totals 37,500 26,400 167,000 16,000 232,000 66,800 $318, 200 $318,200 During January Year 1, the following transactions occur: January 1 Purchase equipment for $20,700. The company estimates a residual value of $2,700 and a six-year service life. January 4 Pay cash on accounts payable, $10,700. January 8 Purchase additional inventory on account, $ 94,900. January 15 Receive cash on accounts receivable, $23,200. January 19 Pay cash for salaries, $31,000. January 28 Pay cash for January utilities, $17,700. January 30 Sales for January total $232,000. All of these sales are on account. The cost of the units sold is $121,000. Information for adjusting entries: a. Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. b. The company estimates future uncollectible accounts. The company determines $4,200 of accounts receivable on January 31 are past due, and 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger.) c. Accrued interest revenue on notes receivable for January d. Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $33,800. e. Accrued income taxes at the end of January are $10,200. 1. Record each of the transactions listed above. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) Answer is complete and correct. No Date General Journal Credit Debit 20,700 January 01 Equipment Cash 20,700 January 04 10,700 Accounts Payable Cash 10,700 January 08 94,900 Inventory Accounts Payable 94,900 January 15 23,200 Cash Accounts Receivable 23,200 January 19 31,000 Salaries Expense Cash 31,000 January 28 Utilities Expense 17,700 Cash 17,700 January 30 232,000 Accounts Receivable Sales Revenue 232,000 January 30 121,000 Cost of Goods Sold Inventory 121,000 2. Record the adjusting entries on January 31 for the above transactions. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select particular "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) Answer is complete and correct. No Date Credit General Journal Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Debit 250 January 31 250 2 January 31 5,660 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts 5,660 January 31 110 Interest Receivable Interest Revenue 110 4 January 31 33,800 Salaries Expense Salaries Payable 33,800 | 5 | January 31 Income Tax Expense Income Tax Payable o 10,200 10,200 | 10.2009 10,200 Exercise 7-21B Part 3 3. Prepare an adjusted trial balance as of January 31, Year 1. Answer is complete and correct. Credit $ Debit 3.000 236,200 $ 9,060 26,400 11,400 167,000 100,200 232,000 66,800 232,000 Adjusted Trial Balance January 31, Year 1 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Note Receivable Inventory Land Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold Salaries Expense Utilities Expense Interest Revenue Equipment Interest Receivable Accumulated Depreciation Salaries Payable Income Tax Payable Depreciation Expense Bad Debt Expense Income Tax Expense Totals 121,000 64,800 17,700 110 20,700 110 250 33,800 10,200 250 5,660 10,200 $ 684,420 $ 684,420 4. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the period ended January 31, Year 1. Answer is complete and correct. $ 111,000 Multiple-Step Income Statement For the month ended January 31, Year 1 Sales Revenue $ 232,000 Cost of Goods Sold (121,000) Gross Profit Expenses Salaries Expense 64,800 Utilities Expense 17,700 Depreciation Expense 250 Bad Debt Expense 5,660 Total Operating Expenses Operating Income Interest Revenue Income before taxes Income Tax Expense Net Income 88,410 22,590 110 22,700 (10,200) 12,500 | $ 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31, Year 1. (Deductible amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.) X Answer is not complete. Balance Sheet January 31, Year 1 Assets Liabilities Cash Accounts Receivable Less: Allowance Notes Receivable Interest Receivable $ 3,000 236,200 (9,060) Accounts Payable Income Tax Payable Salaries Payable $ 100,200 10,200 33,800 144,200 Inventory Total Current Assets Land Equipment 110 11,400 241,650 167,000 20,700 Total Current Liabilities Stockholder's Equity Common Stock Retained Earnings 232,000 79,300 Less: Accumulated Depreciation (250) Total Stockholders' Equity 311,300 Total Assets 429,100 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $ 455,500 Exercise 7-21B Part 6 6. Record closing entries. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) Answer is not complete. No General Journal Debit Credit Date January 31 Sales Revenue Interest Revenue Z 2 January 31 Retained Earnings Bad Debt Expense Depreciation Expense Income Tax Expense Cost of Goods Sold Salaries Expense













