I need an answer for question 4 especially .
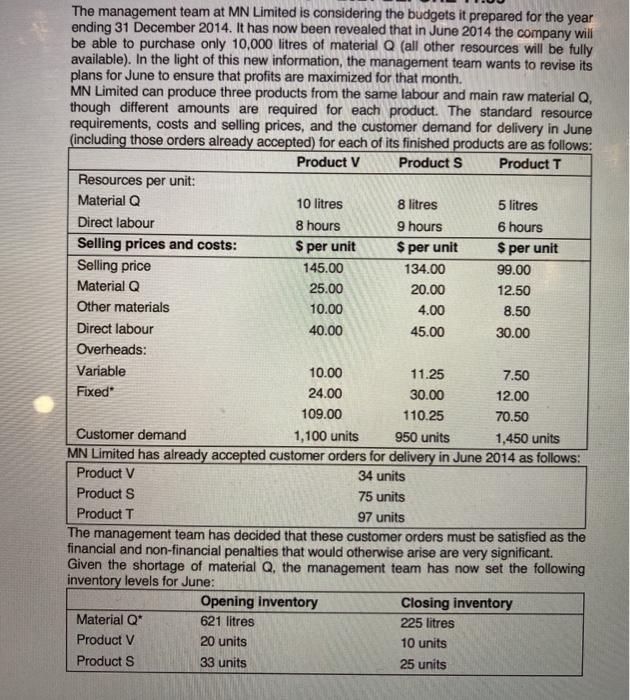
The management team at MN Limited is considering the budgets it prepared for the year ending 31 December 2014. It has now been revealed that in June 2014 the company will be able to purchase only 10,000 litres of material Q (all other resources will be fully available). In the light of this new information, the management team wants to revise its plans for June to ensure that profits are maximized for that month. MN Limited can produce three products from the same labour and main raw material Q, though different amounts are required for each product. The standard resource requirements, costs and selling prices, and the customer demand for delivery in June (including those orders already accepted) for each of its finished products are as follows: Product V Products Product T Resources per unit: Material Q 10 litres 3 litres 5 litres Direct labour 8 hours 9 hours 6 hours Selling prices and costs: $ per unit $ per unit $ per unit Selling price 145.00 134.00 99.00 Material Q 25.00 20.00 12.50 Other materials 10.00 4.00 8.50 Direct labour 40.00 45.00 30.00 Overheads: Variable 10.00 11.25 7.50 Fixed 24.00 30.00 12.00 109.00 110.25 70.50 Customer demand 1,100 units 950 units 1,450 units MN Limited has already accepted customer orders for delivery in June 2014 as follows: Product V 34 units Products 75 units Product T 97 units The management team has decided that these customer orders must be satisfied as the financial and non-financial penalties that would otherwise arise are very significant Given the shortage of material Q, the management team has now set the following inventory levels for June: Opening inventory Closing inventory Material Q* 621 litres 225 litres Product V 20 units 10 units Products 33 units 25 units Product T 46 units 20 units Required 1. Prepare a production budget for June 2014 that clearly shows the number of units of each product that should be produced to maximize the profits of MN Limited for June 2014 2. Using your answer to requirement 1 above, calculate the number of units of each product that will be sold in June 2014. 3. Using your answer to requirement 2 above, calculate the profit for June 2014 using: (a)marginal costing; (b) absorption costing. The Managing Director of MN Limited is concerned about the effect on cashflow caused by the scarcity of material Q during June 2014. She is aware that monthly profit and cashflow are often unequal and has heard that marginal costing profits more closely resemble cashflow than do absorption costing profits. 4 (a)Explain briefly why there is a difference between cashflow and profit. (b)Briefly discuss the assertion that marginal costing profits are a better indicator of cashflow than absorption costing profits









