Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I need an answer to question 4 CA-8 Greetings case 2 Cases for Management Decision-Making The second activity is inventory selection and management. The estimated
I need an answer to question 4 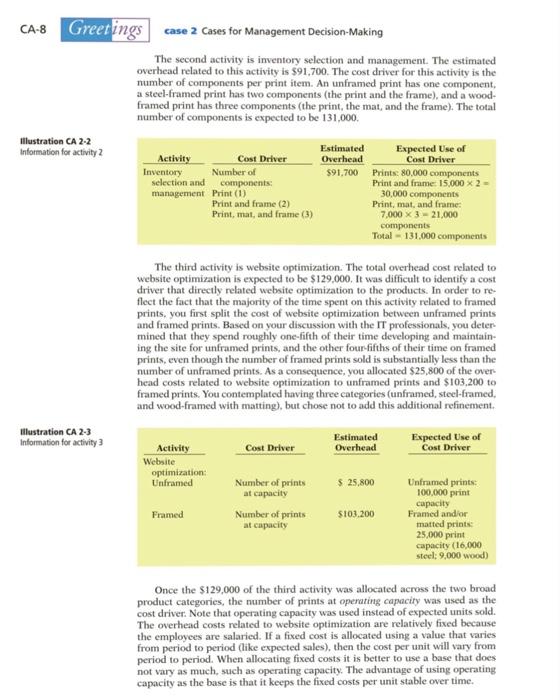
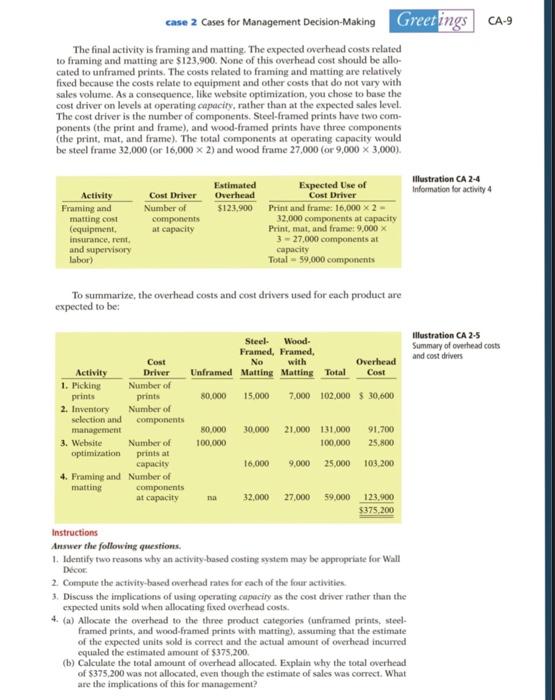

CA-8 Greetings case 2 Cases for Management Decision-Making The second activity is inventory selection and management. The estimated overhead related to this activity is $91,700. The cost driver for this activity is the number of components per print item. An unframed print has one component, a steel-framed print has two components (the print and the frame), and a wood- framed print has three components (the print, the mat, and the frame). The total number of components is expected to be 131,000. illustration CA 2-2 Information for activity 2 Estimated Expected Use of Activity Cost Driver Overhead Cost Driver Inventory Number of $91,700 Prints: 80,000 components selection and components Print and frame: 15.000 x 2 management Print (1) 30,000 components Print and frame (2) Print, mat, and frame: Print, mat, and frame (3) 7,000 X 321,000 components Total - 131,000 components The third activity is website optimization. The total overhead cost related to website optimization is expected to be $129,000. It was difficult to identify a cost driver that directly related website optimization to the products. In order to re flect the fact that the majority of the time spent on this activity related to framed prints, you first split the cost of website optimization between unframed prints and framed prints. Based on your discussion with the IT professionals, you deter mined that they spend roughly one-fifth of their time developing and maintain ing the site for unframed prints, and the other four-fifths of their time on framed prints, even though the number of framed prints sold is substantially less than the number of unframed prints. As a consequence, you allocated $25,800 of the over head costs related to website optimization to unframed prints and $103.200 to framed prints. You contemplated having three categories (unframed, steel-framed. and wood-framed with matting), but chose not to add this additional refinement Illustration CA 2-3 Information for activity 3 Cost Driver Estimated Overhead Expected Use of Cost Driver Activity Website optimization: Unframed $ 25,800 Number of prints at capacity Number of prints at capacity Framed $103.200 Unframed prints 100,000 print capacity Framed and/or matted prints: 25,000 print capacity (16,000 steel: 9,000 wood) Once the $129,000 of the third activity was allocated across the two broad product categories, the number of prints at operating capacity was used as the cost driver. Note that operating capacity was used instead of expected units sold. The overhead costs related to website optimization are relatively fixed because the employees are salaried. If a fixed cost is allocated using a value that varies from period to period (like expected sales), then the cost per unit will vary from period to period. When allocating fixed costs it is better to use a base that does not vary as much, such as operating capacity. The advantage of using operating capacity as the base is that it keeps the fixed costs per unit stable over time. case 2 Cases for Management Decision Making Greetings CA-9 The final activity is framing and matting. The expected overhead costs related to framing and matting are $123.900. None of this overhead cost should be allo cated to unframed prints. The costs related to framing and matting are relatively fixed because the costs relate to equipment and other costs that do not vary with sales volume. As a consequence, like website optimization, you chose to base the cost driver on levels at operating capacity, rather than at the expected sales level. The cost driver is the number of components. Steel-framed prints have two com- ponents (the print and frame), and wood-framed prints have three components (the print, mat, and frame). The total components at operating capacity would be steel frame 32,000 (or 16,000 x 2) and wood frame 27,000 (or 9,000 X 3,000). Estimated Overhead $123.900 Illustration CA 2-4 Information for activity 4 Activity Framing and matting cost (equipment insurance, rent and supervisory labor) Cost Driver Number of components at capacity Expected Use of Cost Driver Print and frame: 16,000 x 2 - 32,000 components at capacity Print, mat, and frame: 9,000 3 -27.000 components at capacity Total = 59,000 components To summarize, the overhead costs and cost drivers used for each product are expected to be: Steel Wood- Framed, Framed, illustration CA 2-5 Summary of overhead costs and cost drivers No with Overhead Cost Unframed Matting Matting Total 80,000 15,000 7.000 102.000 $ 30,600 Cost Activity Driver 1. Picking Number of prints prints 2. Inventory Number of selection and components management 3. Website Number of optimization prints at capacity 4. Framing and Number of matting components at capacity 30.000 30.000 100,000 21.000 131,000 100,000 91.700 25,800 16,000 9,000 25,000 103.200 na 32.000 27.000 59,000 123.900 $375,200 Instructions Answer the following questions 1. Identify two reasons why an activity-based costing system may be appropriate for Wall Decor 2. Compute the activity-based overhead rates for each of the four activities 3. Discuss the implications of using operating capacity as the cost driver rather than the expected units sold when allocating fixed overhead costs. 4. (a) Allocate the overhead to the three product categories (unframed prints, steel framed prints, and wood-Framed prints with matting), assuming that the estimate of the expected units sold is correct and the actual amount of overhead incurred equaled the estimated amount of $375,200. (b) Calculate the total amount of overhead allocated. Explain why the total overhead of $375,200 was not allocated, even though the estimate of sales was correct. What are the implications of this for management? Instructions Answer the following questions. 1. Identify two reasons why an activity-based costing system may be appropriate for Wall Dcor. 2. Compute the activity-based overhead rates for each of the four activities. 3. Discuss the implications of using operating capacity as the cost driver rather than the expected units sold when allocating fixed overhead costs. 4. (a) Allocate the overhead to the three product categories (unframed prints, steel- framed prints, and wood-framed prints with matting), assuming that the estimate of the expected units sold is correct and the actual amount of overhead incurred equaled the estimated amount of $375,200. (b) Calculate the total amount of overhead allocated. Explain why the total overhead of $375,200 was not allocated, even though the estimate of sales was correct. What are the implications of this for management 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


