Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I need help in this question. Please do it correctly and accurately and 100% 4. Tex Hardware sells many of its products overseas. The following
I need help in this question. Please do it correctly and accurately and 100%
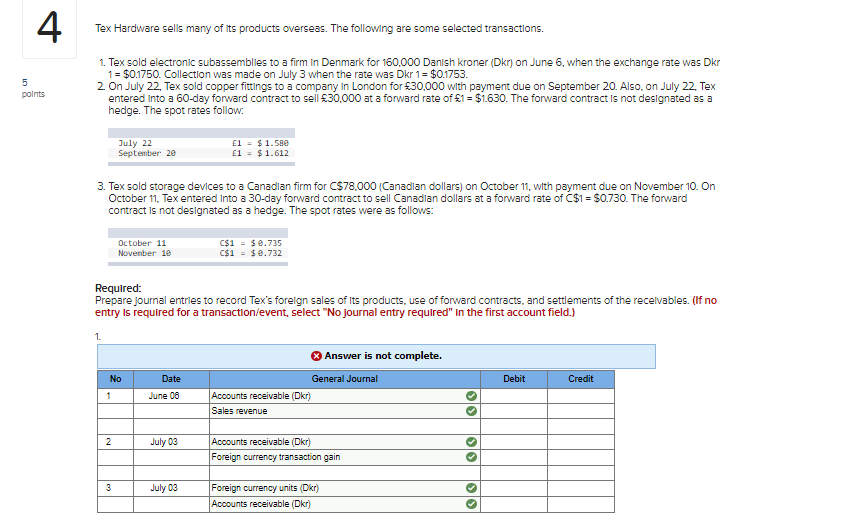
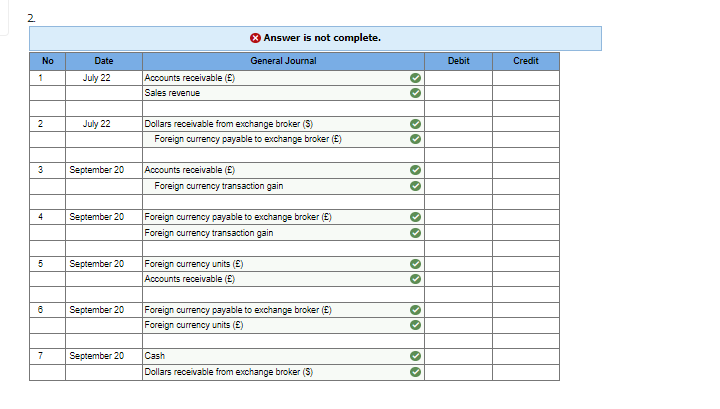
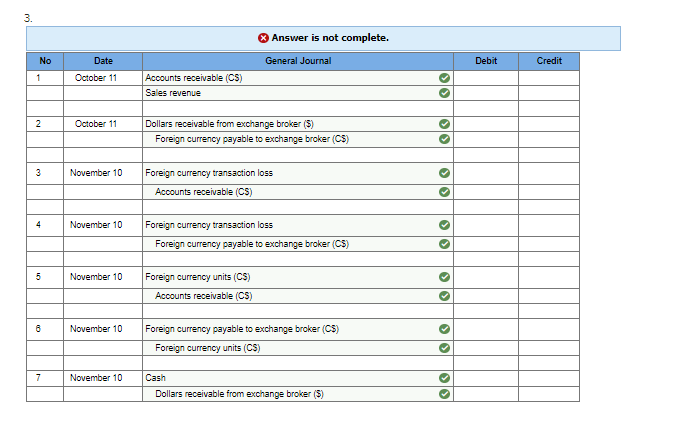
4. Tex Hardware sells many of its products overseas. The following are some selected transactions. 5 points 1. Tex sold electronic subassemblies to a firm in Denmark for 160.000 Danish kroner (Dkn on June 6, when the exchange rate was Dkr 1 = $0.1750. Collection was made on July 3 when the rate was Dkr 1 = $0.1753. 2. On July 22, Tex sold copper fittings to a company in London for 30,000 with payment due on September 20. Also on July 22. Tex entered into a 60-day forward contract to sell 30,000 at a forward rate of 1 = $1.630. The forward contract is not designated as a hedge. The spot rates follow: July 22 September 20 1 = $ 1.580 1 = $1.612 3. Tex sold storage devices to a Canadian firm for C$78.000 (Canadian dollars) on October 11, with payment due on November 10. On October 11. Tex entered into a 30-day forward contract to sell Canadian dollars at a forward rate of C$1 = $0.730. The forward contract is not designated as a hedge. The spot rates were as follows: October 11 November 10 C$1 = $ 0.735 C$1 = $0.732 Required: Prepare journal entries to record Tex's foreign sales of its products, use of forward contracts, and settlements of the recelvables. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 1. No Date Answer is not complete. General Journal Accounts receivable (Dkr) Sales revenue Debit Credit 1 June 08 OO 2 July 03 Accounts receivable (Dkr) Foreign currency transaction gain DO 3 July 03 Foreign currency units Dkr) Accounts receivable (Dkr) oo 2. Answer is not complete. No Date General Journal Debit Credit 1 July 22 Accounts receivable (E) Sales revenue 2 July 22 Dollars receivable from exchange broker (S) Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (E) OO 3 September 20 Accounts receivable (E) Foreign currency transaction gain . 4 September 20 Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (E) Foreign currency transaction gain OO 5 September 20 Foreign currency units (8) Accounts receivable (5) 6 September 20 Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (5) Foreign currency units (5) OO ol ol 7 September 20 Cash Dollars receivable from exchange broker (S) 3. Answer is not complete. No Date General Journal Debit Credit 1 October 11 Accounts receivable (CS) Sales revenue O 2 2 October 11 Dollars receivable from exchange broker (5) Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (CS) 3 November 10 Foreign currency transaction loss Accounts receivable (CS) 4 November 10 > Foreign currency transaction loss Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (CS) 5 November 10 Foreign currency units (CS) > > Accounts receivable (CS) 6 November 10 Foreign currency payable to exchange broker (CS) Foreign currency units (CS) >> 7 November 10 Cash Dollars receivable from exchange broker (5) olo
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


