I need help on these 2 stats questions:
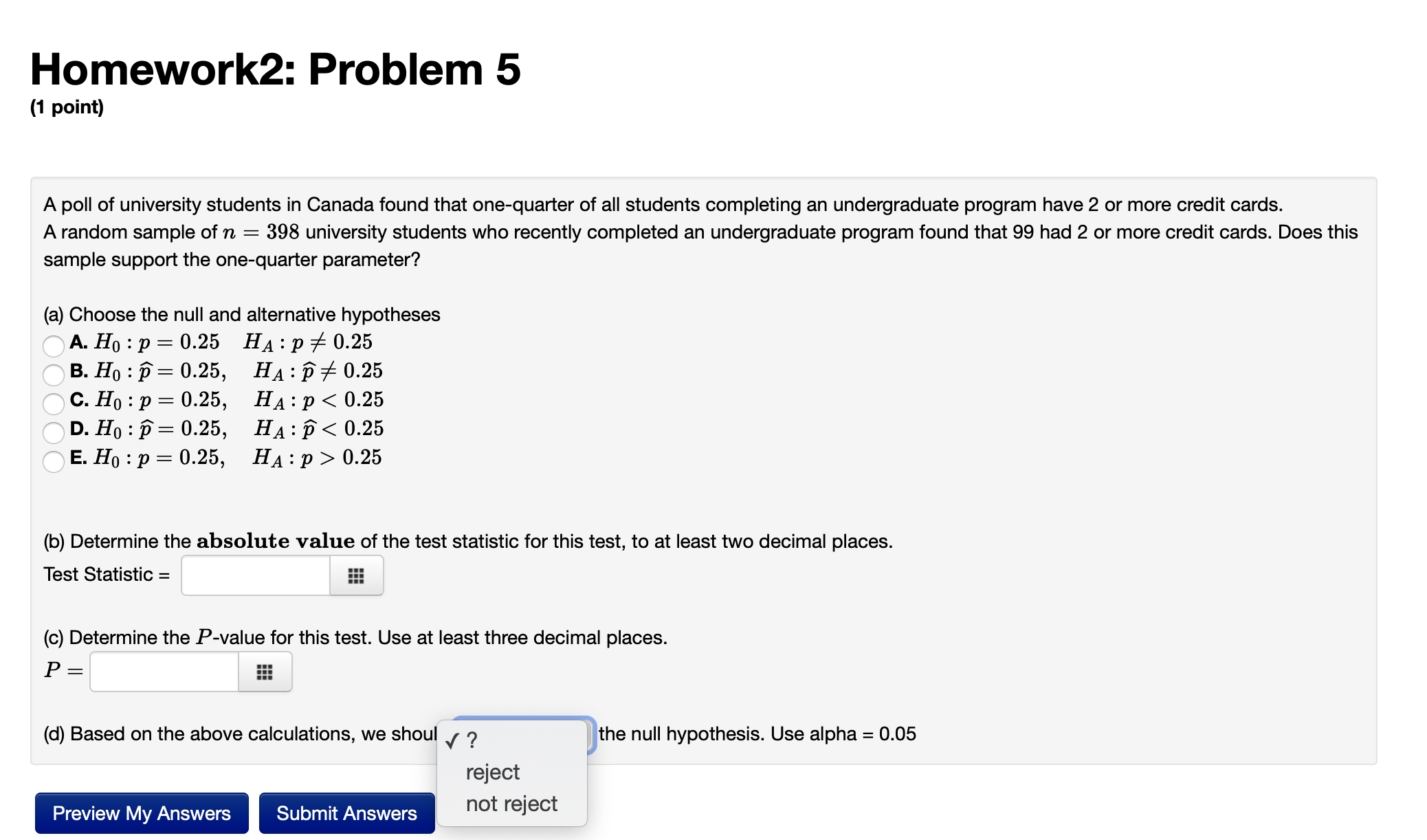
Homework2: Problem 6 (1 point) The editor of a magazine knows that 40.2% of all people who subscribe to the magazine do not renew their subscriptions. In an attempt to decrease this percentage, current subscribers are offered a renewal offer - one that offers current subscribers to renew their subscription at a substantially reduced price. After a period of six-months, the magazine editor wishes to investigate if this renewal offer does decrease the percentage of subscribers who do not renew subscriptions, or p. (a) Choose the correct statistical hypotheses. AA. H0 :17 = 0.402 HA :1) 0.402 A F. H0 :1) = 0.402 HA :1) 0.402 (b) The null hypothesis is to be tested from a random sample of n = 200 magazine subscribers whose subscriptions were to be renewed in the past six months. If statistical testing is to be carried out at P(Type I Error) 2 0.05. what is the maximum number of subscribers out of 200 who did not renew their subscription in order to determine that the renewal offer does decrease the percentage of subscribers who do not renew. Enter your answer as an appropriate integer. a (c) The sample of 200 subscribers who were offered the renewal offer was taken, of which 67 didn't renew their magazine subscription in the past six months. The P-value of this result was 0.0266. What type of error could be made from this sample? .A. A. Type II Error A B. Power of a Test A. c. Type | Error (d) How powerful is the statistical test outlined in (b) if the percentage of all subscribers who do not renew their subscription, p, drops by 5 percentage points ? Enter your answer to three decimals. Power = E Homework2: Problem 5 (1 point) A poll of university students in Canada found that one-quarter of all students completing an undergraduate program have 2 or more credit cards. A random sample of n = 398 university students who recently completed an undergraduate program found that 99 had 2 or more credit cards. Does this sample support the one-quarter parameter? (a) Choose the null and alternative hypotheses (TA. H0 :1) = 0.25 HA : p 7e 0.25 63.11.):5: 0.25, HA : 575 0.25 A c. H : p = 0.25, HA : p 0.25 (b) Determine the absolute value of the test statistic for this test, to at least two decimal places. Test Statistic = m (c) Determine the P-value for this test. Use at least three decimal places. P = m (d) Based on the above calculations, we shou J ? the null hypothesis. Use alpha = 0.05 reject Preview My Answers Submit Answers m