Question: I NEED HELP PLEASE. I have attached the article below please refer to the article for the last question. Thank you in advance ;) In
I NEED HELP PLEASE. I have attached the article below please refer to the article for the last question. Thank you in advance ;)



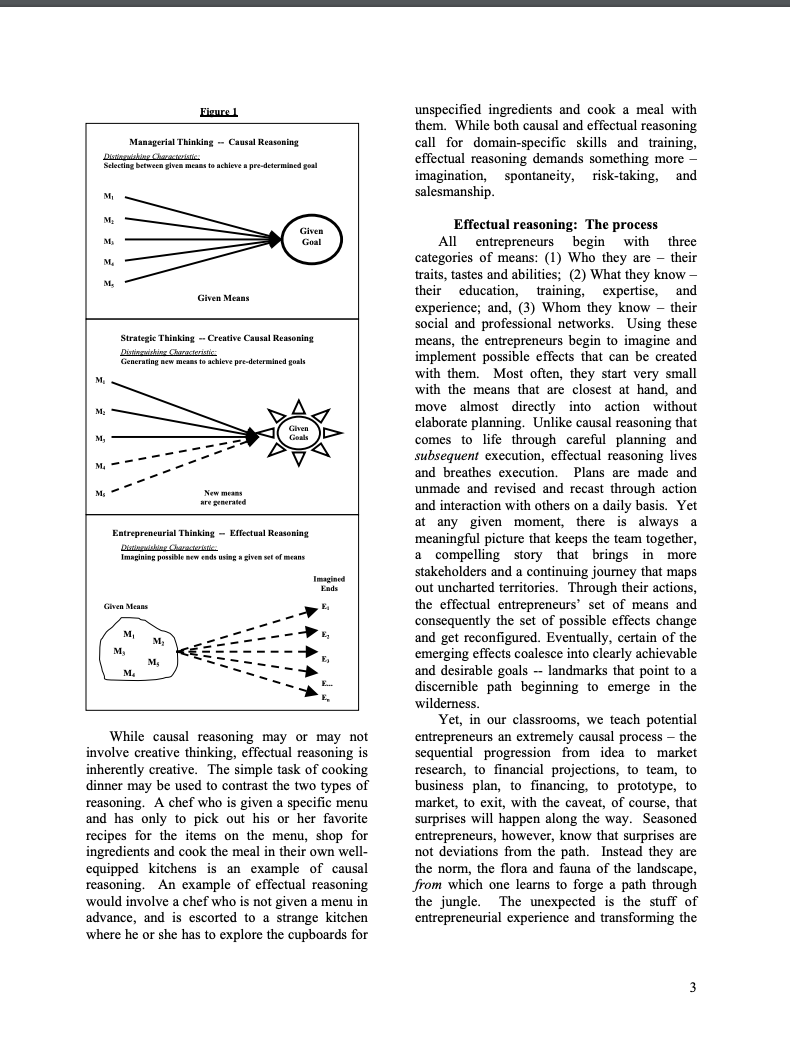
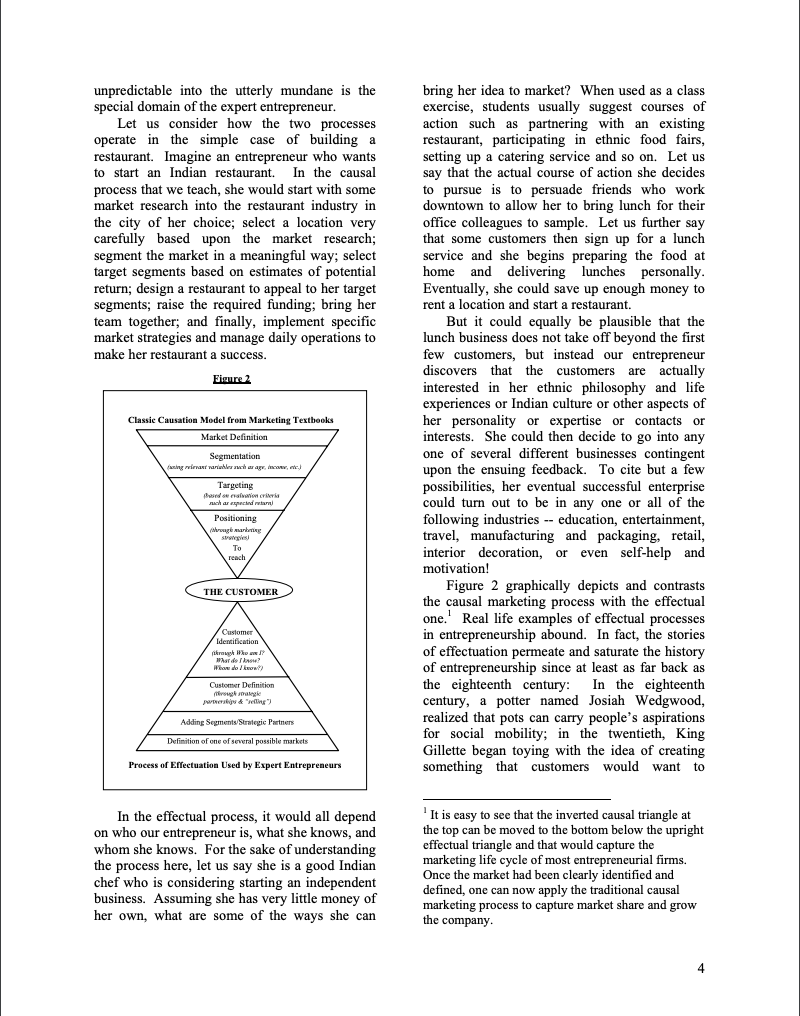


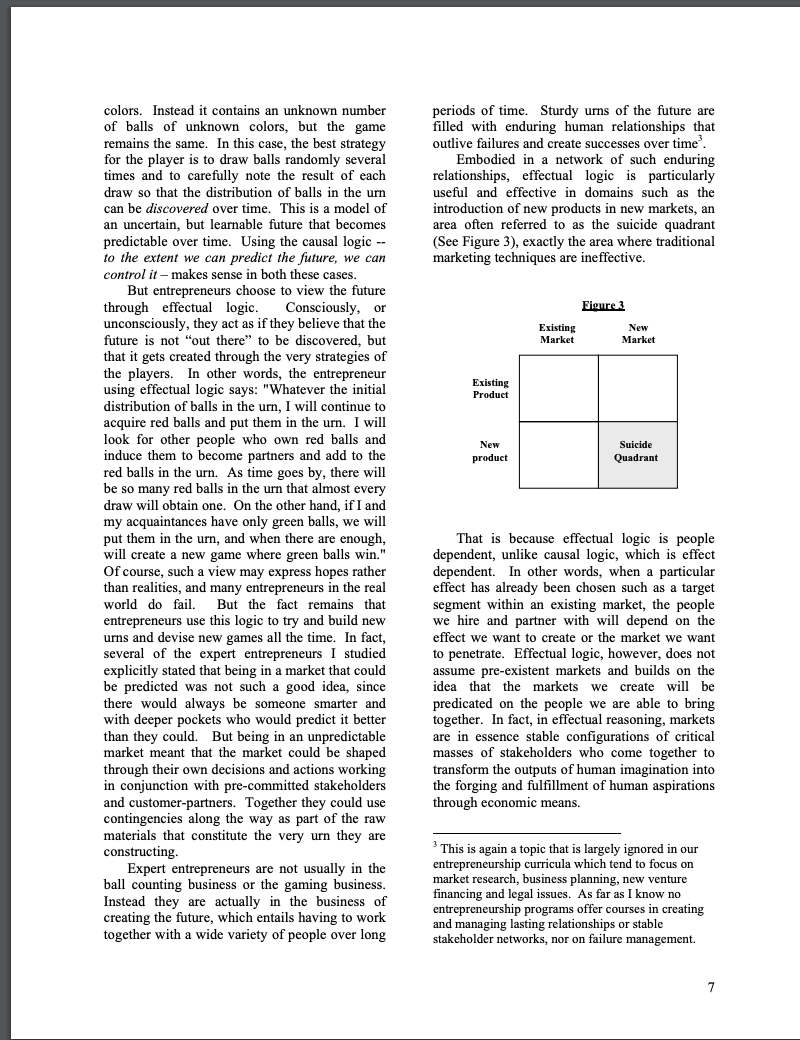


In 1927, Conrad M. Gentry and Don F. Kenworthy founded Mayflower Transit Co. in Indianapolis, IN as an alternative to railroads for customers who were interested in moving their belongings across the country on the expanding network of paved roads. During and after World War II Mayflower operated 24 hours a day 7 days a week moving thousands of families. Imagine that you are 29-year-old Leonard "Sam" Shoen, mid-level manager for Mayflower in 1945. Your brother, who was discharged from the Navy that summer complained to you about trying to rent a utility vehicle to move his (and his family's) possessions from Los Angeles to Portland, Ore. It couldn't be done. They had to take only what they could fit in the car. Your brother noticed, however, that small luggage-type passenger automobile vehicles were being rented from 'rental lots' in Los Angeles. Each lot had from 20 to 40 units which were rented locally for approximately $2 per day. You begin wondering why people could not simply rent moving vehicles "here" in LA that you could leave off "there" in Portland. You begin to think that this could make an exciting new business - one-way rentals of moving vans where the customers would drive (and move) themselves from anywhere to anywhere within the continental United States. As a new 'Founder', begin to develop answers to the following questions for your new business: 1. How many vehicles would you need? 2. How many locations? 3. How would you go about building this venture? What would your first steps be? Note: Do your calculations in today's dollars, but make assumptions and other inputs to your new business as if it were 1945. 4. According to your reading of Sarasvathy's 'What Makes ..., is your strategy effectual or causal? Explain your reasoning. What makes entrepreneurs entrepreneurial? Saras D. Sarasvathy Associate Professor The Darden Graduate School of Business Administration University of Virginia Professionals who work closely with them clear in the next section, I have termed this type and researchers who study them have often of rationality "effectual reasoning". speculated about what makes entrepreneurs "entrepreneurial". Of course, entrepreneurs also Effectual reasoning: The problem love to hold forth on this topic. But while there The word "effectual" is the inverse of are as many war stories and pet theories as there "causal". In general, in MBA programs across are entrepreneurs and researchers, gathering the world, students are taught causal or together a coherent theory of entrepreneurial predictive reasoning - in every functional area expertise has thus far eluded academics and of business. Causal rationality begins with a practitioners alike. pre-determined goal and a given set of means, What are the characteristics, habits, and and seeks to identify the optimal - fastest, behaviors of the species entrepreneur? Is there cheapest, most efficient, etc. - alternative to a learnable and teachable "core" to achieve the given goal. The make-vs.-buy entrepreneurship? In other words, what can decision in production, or choosing the target today's entrepreneurs such as Rob Glaser and market with the highest potential return in Jeff Bezos learn from old stalwarts such as marketing, or picking a portfolio with the lowest Josiah Wedgwood and Leonard Shoen? Or even risk in finance, or even hiring the best person for within the same period in history, what are the the job in human resources management, are all common elements that entrepreneurs across a examples of problems of causal reasoning. A wide variety of industries share with each other? more interesting variation of causal reasoning In sum, is there such a thing as "entrepreneurial involves the creation of additional alternatives to thinking" that can be applied across space, time achieve the given goal. This form of creative and technology? causal reasoning is often used in strategic In 1997, I set out on a rather perilous but thinking. exhilarating journey to investigate this question. Effectual reasoning, however, does not Traveling across 17 states in the US over several begin with a specific goal. Instead, it begins with months, I met with 30 founders of companies a given set of means and allows goals to emerge ranging in size from $200M to $6.5B and contingently over time from the varied spanning a variety of industries from steel and imagination and diverse aspirations of the railroad to teddy bears and semiconductors and founders and the people they interact with. bio-tech. The idea behind the study was not While causal thinkers are like great generals merely to interview these founders, but to get seeking to conquer fertile lands (Genghis Khan behind their stories and understand how they conquering two thirds of the known world), reason about specific problems in transforming effectual thinkers are like explorers setting out an idea into an enduring firm. The entrepreneurs on voyages into uncharted waters (Columbus worked their way through a 17-page problem set discovering the new world). It is important to over two hours, talking aloud continuously as point out though that the same person can use they each solved exactly the same ten decision both causal and effectual reasoning at different problems to build a company starting with times depending on what the circumstances call exactly the same product idea. Rigorous for. In fact, the best entrepreneurs are capable of analyses of the transcribed tapes led to rather both and do use both modes well. But they surprising but eminently teachable principles. prefer effectual reasoning over causal reasoning This set of principles, when put together, rested in the early stages of a new venture, and on a coherent logic that clearly established the arguably, most entrepreneurs do not transition existence of a distinct form of rationality that we well into latter stages requiring more causal have all long recognized intuitively as reasoning. Figure 1 graphically depicts the "entrepreneurial". For reasons that will become different forms of reasoning discussed above. unspecified ingredients and cook a meal with them. While both causal and effectual reasoning call for domain-specific skills and training, effectual reasoning demands something more imagination, spontaneity, risk-taking, and salesmanship. Effectual reasoning: The process All entrepreneurs begin with three categories of means: (1) Who they are - their traits, tastes and abilities; (2) What they know their education, training, expertise, and experience; and, (3) Whom they know - their social and professional networks. Using these means, the entrepreneurs begin to imagine and implement possible effects that can be created with them. Most often, they start very small with the means that are closest at hand, and move almost directly into action without elaborate planning. Unlike causal reasoning that comes to life through careful planning and subsequent execution, effectual reasoning lives and breathes execution. Plans are made and unmade and revised and recast through action and interaction with others on a daily basis. Yet at any given moment, there is always a meaningful picture that keeps the team together, a compelling story that brings in more stakeholders and a continuing journey that maps out uncharted territories. Through their actions, the effectual entrepreneurs' set of means and consequently the set of possible effects change and get reconfigured. Eventually, certain of the emerging effects coalesce into clearly achievable and desirable goals - landmarks that point to a discernible path beginning to emerge in the wilderness. Yet, in our classrooms, we teach potential While causal reasoning may or may not entrepreneurs an extremely causal process - the involve creative thinking, effectual reasoning is sequential progression from idea to market inherently creative. The simple task of cooking research, to financial projections, to team, to dinner may be used to contrast the two types of business plan, to financing, to prototype, to reasoning. A chef who is given a specific menu market, to exit, with the caveat, of course, that and has only to pick out his or her favorite surprises will happen along the way. Seasoned recipes for the items on the menu, shop for entrepreneurs, however, know that surprises are ingredients and cook the meal in their own well- not deviations from the path. Instead they are equipped kitchens is an example of causal the norm, the flora and fauna of the landscape, reasoning. An example of effectual reasoning from which one learns to forge a path through would involve a chef who is not given a menu in the jungle. The unexpected is the stuff of advance, and is escorted to a strange kitchen entrepreneurial experience and transforming the where he or she has to explore the cupboards for unpredictable into the utterly mundane is the bring her idea to market? When used as a class special domain of the expert entrepreneur. exercise, students usually suggest courses of Let us consider how the two processes action such as partnering with an existing operate in the simple case of building a restaurant, participating in ethnic food fairs, restaurant. Imagine an entrepreneur who wants setting up a catering service and so on. Let us to start an Indian restaurant. In the causal say that the actual course of action she decides process that we teach, she would start with some to pursue is to persuade friends who work market research into the restaurant industry in downtown to allow her to bring lunch for their the city of her choice; select a location very office colleagues to sample. Let us further say carefully based upon the market research; that some customers then sign up for a lunch segment the market in a meaningful way; select service and she begins preparing the food at target segments based on estimates of potential home and delivering lunches personally. return; design a restaurant to appeal to her target Eventually, she could save up enough money to segments; raise the required funding; bring her rent a location and start a restaurant. team together; and finally, implement specific But it could equally be plausible that the market strategies and manage daily operations to lunch business does not take off beyond the first make her restaurant a success. few customers, but instead our entrepreneur discovers that the customers are actually interested in her ethnic philosophy and life experiences or Indian culture or other aspects of her personality or expertise or contacts or interests. She could then decide to go into any one of several different businesses contingent upon the ensuing feedback. To cite but a few possibilities, her eventual successful enterprise could turn out to be in any one or all of the following industries - education, entertainment, travel, manufacturing and packaging, retail, interior decoration, or even self-help and motivation! Figure 2 graphically depicts and contrasts the causal marketing process with the effectual one. 1 Real life examples of effectual processes in entrepreneurship abound. In fact, the stories of effectuation permeate and saturate the history of entrepreneurship since at least as far back as the eighteenth century: In the eighteenth century, a potter named Josiah Wedgwood, realized that pots can carry people's aspirations for social mobility; in the twentieth, King Gillette began toying with the idea of creating something that customers would want to In the effectual process, it would all depend 1 It is easy to see that the inverted causal triangle at on who our entrepreneur is, what she knows, and the top can be moved to the bottom below the upright whom she knows. For the sake of understanding effectual triangle and that would capture the the process here, let us say she is a good Indian marketing life cycle of most entrepreneurial firms. chef who is considering starting an independent Once the market had been clearly identified and business. Assuming she has very little money of defined, one can now apply the traditional causal her own, what are some of the ways she can larketing proces repeatedly re-purchase and while shaving one get me and my buddies - or I would go out morning, hit upon disposable razors as a and start selling. I'd learn a lot you know.. possibility; Tom Fatjo, a respectable which people.. what were the obstacles.. what professional in Houston, practically got dared were the questions.. which prices work better into founding the garbage giant BFI during a and just DO it. Just try to take it out and sell it. suburban subdivision meeting to solve the Even before I have the machine. I'd just go try community's garbage disposal problems; and to sell it. Even before I started production. So closer to the twenty-first century, while trying to my market research would actually be hands on build an interactive cable channel with actual selling. Hard work, but I think much progressive content, an ex-Microsoft executive better than trying to do market research". named Rob Glaser fell in love with Mosaic, and In finding the first customer within their set out to give voice to the mute Web in the form immediate vicinity, whether within their of RealNetworks; and so it goes. geographic vicinity, within their social network, or within their area of professional expertise, Effectual reasoning: The principles entrepreneurs do not tie themselves to any Does all this mean, though, that we are once theorized or pre-conceived "market" or strategic again resorting to tales by the campfire? It turns universe for their idea. Instead, they open out that all these stories have some common themselves to surprises as to which market or principles of reasoning that invert their markets they will eventually end up building counterparts in causal reasoning. Moreover, their business in or even which new markets these principles tie together into a coherent logic they will end up creating. Starting with exactly that demonstrates that this is indeed a the same product, the entrepreneurs in the study convincing alternative to causal rationality: ended up creating companies in 18 completely - While causal reasoning focuses on expected disparate industries! return, effectual reasoning emphasizes affordable loss; The strategic partnerships principle - While causal reasoning depends upon Another key principle of effectual reasoning competitive analyses, effectual reasoning is is the focus on building partnerships rather than built upon strategic partnerships; and, on doing a systematic competitive analysis. - While causal reasoning urges the Since entrepreneurs tend to start the process exploitation of pre-existing knowledge and without assuming the existence of a preprediction, effectual reasoning stresses the determined market for their idea, detailed leveraging of contingencies. competitive analyses do not seem to make any sense to them at the startup phase. As one of the The affordable loss principle subjects explained, "At one time in our While managers are taught to analyze the company, I ordered people not to think about market and choose target segments with the competitors. Just do your job. Think only of highest potential return, entrepreneurs tend to your work."2 Instead entrepreneurs focus on find ways to reach the market with minimum building partnerships right from the start. In expenditure of resources such as time, effort, fact, the ideal beginning for a successful startup and money. In the extreme case, the affordable seemed to be the induction of customers into loss principle translates into the zero resources strategic partnerships. Again, to hear it from the to market principle. Several of the expert entrepreneurs I studied insisted that they would not do any traditional market research, but 2 He went on to add, "Now that isn't entirely would take the product to the nearest possible possible, we do a lot of competitive research now." potential customer even before it was built. To At the time of the study, his company was a 3 Billion quote but one of them, "I think I'd start by just... dollar company. The evidence shows that as an going... instead of asking all the questions I'd go _ entrepreneurial company grows beyond a critical and say... effectual reasoning has to be supplemented with and say.. try and make some sale. I'd make and even replaced at times by causal modes of some... just judgments about where I was going thinking. horse's mouth, "Traditional market research IBM had written a different type of a contract or says, you do very broad based information if Gary Kildahl had not been out flying his gathering, possibly using mailings. I wouldn't airplane the day IBM came calling. Yet, it is not do that. I would literally, target, as I said the contingencies themselves that shaped the initially, key companies who I would call companies in the foregoing examples. It is how flagship, do a frontal lobotomy on them.... The the entrepreneurs leveraged the contingencies challenge then is really to pick your partners, that came upon them that has to form the core of and package yourself early on before you have models of effectual reasoning. The realization to put a lot of capital out" that not all surprises are bad and that surprises, In fact, the strategic partnerships principle whether good or bad, can be used as inputs into dovetails very well with the affordable loss the new venture creation process differentiates principle to bring the entrepreneurs' idea to effectual reasoning from causal reasoning which market at really low levels of capital outlay. tends to focus on the avoidance of surprises as Furthermore, obtaining pre-commitments from far as possible. key stakeholders helps reduce uncertainty in the early stages of creating an enterprise. Finally, Effectual reasoning: The logic since the entrepreneur is not wedded to any Underlying all the principles of effectual particular market for their idea, the expanding reasoning is a coherent logic that rests on a network of strategic partnerships determines to a fundamentally different assumption about the great extent which market or markets the future than causal reasoning. Causal reasoning company will eventually end up in. is based on the logic, To the extent that we can predict the future, we can control it. That is The leveraging contingencies principle why both academics and practitioners in The third principle of effectual reasoning is business today spend enormous amounts of the heart of entrepreneurial expertise - the brainpower and resources on developing ability to turn the unexpected into the profitable. predictive models. Effectual reasoning, As one of the subjects in the study put it, "I however, is based on the logic, To the extent that always live by the motto of Ready-fire-aim. I we can control the future, we do not need to think if you spend too much time doing ready- predict it. aim-aim-aim-aim, you're never gonna see all the How does one control an unpredictable good things that would happen if you actually future? The answer to this question depends on start doing it and then aim. And find out where our beliefs about where the future comes from. your target is." Is the future largely a continuation of the past? Great entrepreneurial firms are products of To what extent can human action actually contingencies. Their structure, culture, core change its course? While the future is always competence, and endurance are all residuals of uncertain, not all uncertainties are the same. In particular human beings striving to forge and fact, the simplest way we can model the fulfil particular aspirations through interactions different types of uncertainties is through the with the space, time and technologies they live classic statistical model of the future as an urn in. For example, we could speculate whether containing different colored balls wherein the Wedgwood pottery would have been possible if drawing of (say) a red ball, results in a reward the potter Josiah Wedgwood had not met the (of say, \$50). Assume the first urn contains 10 gentleman philosopher Thomas Bentley and red balls and 10 green balls. In this case, the wooed him into a partnership that created a player can calculate the odds as an expected brand and a great company that has lasted over return of $25 on every draw since there is a 50 two centuries. The key to the Wedgwood 50 chance of winning $50. This is the model of fortune was the realization that people put their a risky, but predictable, future. Entrepreneurs, money where their aspirations are and that pots as well as most human beings in the real world, and vases could become vehicles of social however, usually have to operate without such mobility. Similarly, in our time, researchers predictability. The urn they have to deal with speculate what Microsoft would have been if does not have a given number of balls of known colors. Instead it contains an unknown number periods of time. Sturdy urns of the future are of balls of unknown colors, but the game filled with enduring human relationships that remains the same. In this case, the best strategy outlive failures and create successes over time 3. for the player is to draw balls randomly several Embodied in a network of such enduring times and to carefully note the result of each relationships, effectual logic is particularly draw so that the distribution of balls in the urn useful and effective in domains such as the can be discovered over time. This is a model of introduction of new products in new markets, an an uncertain, but learnable future that becomes area often referred to as the suicide quadrant predictable over time. Using the causal logic - (See Figure 3), exactly the area where traditional to the extent we can predict the future, we can marketing techniques are ineffective. control it-makes sense in both these cases. But entrepreneurs choose to view the future through effectual logic. Consciously, or unconsciously, they act as if they believe that the future is not "out there" to be discovered, but that it gets created through the very strategies of the players. In other words, the entrepreneur using effectual logic says: "Whatever the initial distribution of balls in the urn, I will continue to acquire red balls and put them in the urn. I will look for other people who own red balls and induce them to become partners and add to the red balls in the urn. As time goes by, there will be so many red balls in the urn that almost every draw will obtain one. On the other hand, if I and my acquaintances have only green balls, we will put them in the urn, and when there are enough, That is because effectual logic is people will create a new game where green balls win." dependent, unlike causal logic, which is effect Of course, such a view may express hopes rather dependent. In other words, when a particular than realities, and many entrepreneurs in the real effect has already been chosen such as a target world do fail. But the fact remains that segment within an existing market, the people entrepreneurs use this logic to try and build new we hire and partner with will depend on the urns and devise new games all the time. In fact, effect we want to create or the market we want several of the expert entrepreneurs I studied to penetrate. Effectual logic, however, does not explicitly stated that being in a market that could assume pre-existent markets and builds on the be predicted was not such a good idea, since idea that the markets we create will be there would always be someone smarter and predicated on the people we are able to bring with deeper pockets who would predict it better together. In fact, in effectual reasoning, markets than they could. But being in an unpredictable are in essence stable configurations of critical market meant that the market could be shaped masses of stakeholders who come together to through their own decisions and actions working transform the outputs of human imagination into in conjunction with pre-committed stakeholders the forging and fulfillment of human aspirations and customer-partners. Together they could use through economic means. contingencies along the way as part of the raw materials that constitute the very urn they are constructing. Expert entrepreneurs are not usually in the entrepreneurship curricula which tend to focus on ball counting business or the gaming business. market research, business planning, new venture Instead they are actually in the business of financing and legal issues. As far as I know no creating the future, which entails having to work entrepreneurship programs offer courses in creating together with a wide variety of people over long and managing lasting relationships or stable stakeholder networks, nor on failure management. Experienced professionals in the The creation of U-Haul: entrepreneurial arena, whether they are bankers, An exemplar of effectual logic lawyers, VCs or other investors have always In 1945, newly married, and with barely agreed with successful entrepreneurs that finding $5,000, Leonard Shoen set out on his effectual and leading the right people is the key to journey that led to the creation of U-Haul. By creating an enduring venture. These the end of 1949, it was possible to rent a trailer entrepreneurs know that such "right" people are one-way from city to city throughout most of the not on the job market waiting for the jobs and United States. When we examine his journey, incentives the entrepreneurs can offer them. we find that this feat could not have been Instead the "right" people need emotional accomplished except through the use of effectual ownership in the goals and objectives of the reasoning. When students today set out to write endeavor and can only be incentivized by the a business plan for this venture (using causal belief that the effects they create will embody processes), they conclude that the plan is their deepest passions and aspirations while financially infeasible, or even psychologically enabling them to achieve their best potential. infeasible, since it requires a large and risky But great entrepreneurs realize something capital outlay, most of which gets locked up in more about the central role of people in shaping relatively worthless assets such as trucks and the urn. Using effectual logic, they understand location rental. Moreover, the logistics of that they too cannot wait around to find the starting the business at a much smaller scale and "right" people all the time. Besides continually growing it as fast as Shoen did overwhelms the striving to attract the "right" people, they learn analytical prowess of the best of causal thinkers. also to nurture and grow them in their own The final nail in the coffin usually is the backyards. As Josiah Wedgwood wrote, "We complete lack of any entry barriers to imitators have to make artists of mere men." And more with deep pockets after the concept is proved on recently, the founders of AES Corp., a multi- a smaller scale. billion dollar electric power company with Shoen, however, did not do elaborate market operations in dozens of countries around the research or detailed forecasting and fund-raising world say, "[AES] is fun because the people in the sense in which we use the terms today. who work here are fully engaged. They have Instead, using effectual means, (who he was, total responsibility for decisions. They are what he knew, and whom he knew), he plunged accountable for results. What they do every day into action, creating the market as he grew the matters to the company, and it matters to the business. In his own words, "Since my fortune communities we operate in." was just about enough to make the down There is, however, a dark corollary to the payment on a home and furnish it, and knowing use of effectual logic in entrepreneurial activity. that if I did this we would be sunk, we started Since they do not assume specific pre-existent the life of nomads by putting our belongings in a goals or effects and let these effects emerge trailer and living between in-laws and parents through the process, in using effectual logic to for the next six months. I barbered part time and create products and markets, entrepreneurs and bought trailers of the kind I thought we needed their partners may also end up creating harmful to rent from anybody who happened to have one and problematic effects for the society they live at the price I thought was right. By the fall of in. The effects they create may reflect the 1945, I was in so deep into the trailer rental deal ignorance and cupidity as well as the will and economically that it was either make it or lose aspirations of the people who participate in the the whole thing." creation of new urns and games of the future. At that time he moved with his wife Anna But our awareness of the existence of effectual Mary Carty Shoen and their young child to the reasoning should alert us more sharply to the Carty ranch in Ridgefield, Washington. There, role of entrepreneurs and the market system in with the help of the Carty family, the Shoens shaping our future as a species, not merely as built the first trailers in the fall of 1945, painted contributors to GDP. in striking orange with the evocative name U Haul on the sides, using the ranch's automobile garage (and milk house) as the first entrepreneurial ventures. Effectual reasoning manufacturing plant. Shoen then practically may not necessarily increase the probability of gave away the initial trailers to renters so they success of new enterprises, but it reduces the could establish dealerships in cities they moved costs of failure by enabling the failure to occur to. He would also purchase trailers and trucks earlier and at lower levels of investment. and sell them to employees, family members, friends, and investors who would then lease So, what makes entrepreneurs them back to AMERCO, the parent company of entrepreneurial? U-Haul. He contracted with national gas station Entrepreneurs are entrepreneurial, as chains to utilize their unused space for parking differentiated from managerial or strategic, and to manage the paperwork. Together, this because they think effectually; they believe in a vast network of stakeholders formed a yet-to-be-made future that can substantially be substantial entry barrier to any imitator who shaped by human action; and they realize that to would have to risk a large capital outlay to the extent that this human action can control the compete. Advertising was entirely limited to future, they need not expend energies trying to Yellow Pages and to the sudden and startling predict it. In fact, to the extent that the future is sight of growing numbers of distinctively shaped by human action, it is not much use painted vans being driven along the freeways of trying to predict it - it is much more useful to the country. understand and work with the people who are At any given moment, U-Haul could have engaged in the decisions and actions that bring it failed, but the resulting financial fall-out would into existence. not have been a disaster since the investments were spread across so many stakeholders. This brings us to the key implication of effectual reasoning for the success or failure of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


