i need help with a multiple step income statement, post closing trial, and statement of retained earnings.
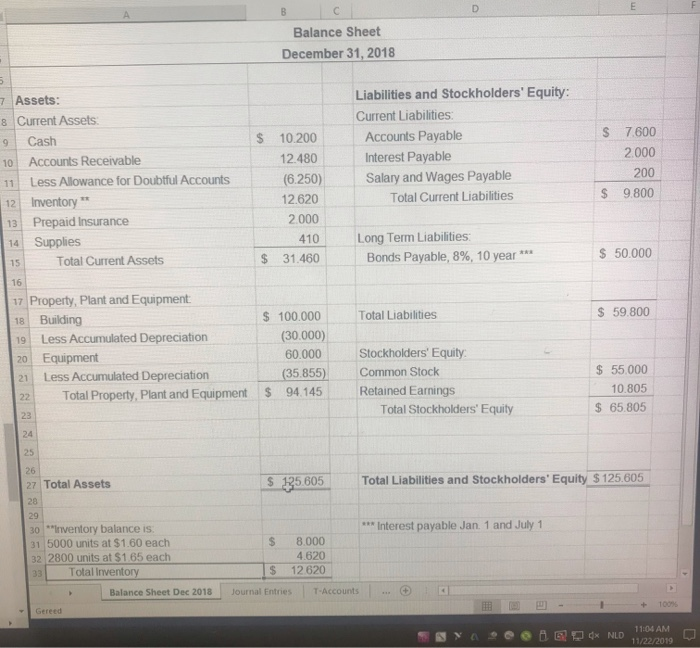
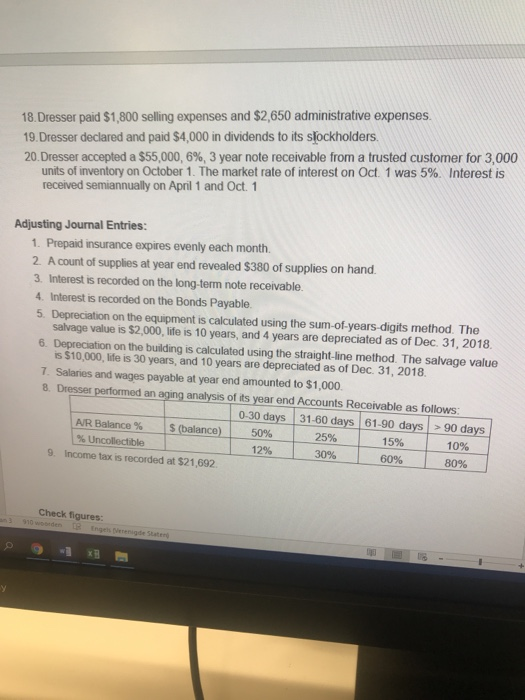
Balance Sheet December 31, 2018 $ $ Assets: 8 Current Assets 9 Cash 10 Accounts Receivable 11 Less Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 12 Inventory 13 Prepaid Insurance 14 Supplies Total Current Assets 10.200 12.480 (6.250) 12.620 2.000 410 31.460 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity: Current Liabilities: Accounts Payable Interest Payable Salary and Wages Payable Total Current Liabilities 7.600 2000 200 9.800 $ Long Term Liabilities: Bonds Payable, 8%, 10 year *** $ $ 50.000 Total Liabilities $ 59.800 17 Property, Plant and Equipment 18 Building 19 Less Accumulated Depreciation 20 Equipment 21 Less Accumulated Depreciation Total Property, Plant and Equipment $ 100.000 (30.000) 60.000 (35.855) S 94.145 Stockholders' Equity Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Equity $ 55.000 10.805 $ 65.805 27 Total Assets $ 125.605 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $ 125.605 *** Interest payable Jan 1 and July 1 $ 30 **inventory balance is 31 5000 units at $1.60 each 32 2800 units at $1 65 each 33 Total Inventory Balance Sheet Dec 2018 8.000 4.620 12620 $ Journal Entries Accounts Gereed Ya9oOBX NLD 1104 AM 11/22/2019 Journal Entries: 1. Dresser paid the interest due on the Bonds Payable on January 1. 2. Dresser paid $750 of salaries and wages, which includes the amount accrued as of December 31, 2018 3. Dresser sold 4,000 units of inventory for $13.00 each 4. Dresser purchased supplies on account for $1,200. 5. Dresser purchased 3,000 units of inventory for $1.70 each. 6. Dresser sold 2,800 units of inventory for $14.00 each. 7. Dresser wrote off as uncollectible the accounts of Barker Corporation ($3,200) and Elm Company ($2,500) 8. Dresser paid the interest due on the Bonds Payable on July 1. 9. Dresser purchased 1,500 units of inventory for $1.72 each. 10. Dresser collected $1,000 from Elm Company, part of the balance previously written off. 11. Dresser paid salaries and wages of $64,000. 12. Dresser paid $7,200 for insurance coverage from May 1, 2019 thru April 30, 2020. 13. Dresser sold 2,500 units of inventory for $15.00 each. 14. Dresser collected $98,900 from customers on account 15. Dresser purchased 3,800 units of inventory for $1.75 each. 16. Dresser paid $12,300 on accounts payable. 17. Dresser sold 600 units of inventory for $14.50 each as a cash sale. 18. Dresser paid $1,800 selling expenses and $2,650 administrative expenses. 19. Dresser declared and paid $4,000 in dividends to its stockholders. 20. Dresser accepted a $55,000, 6%, 3 year note receivable from a trusted customer for 3,000 units of inventory on October 1. The market rate of interest on Oct. 1 was 5%. Interest is received semiannually on April 1 and Oct. 1 Adjusting Journal Entries: 1. Prepaid insurance expires evenly each month. 2. A count of supplies at year end revealed $380 of supplies on hand. 3. Interest is recorded on the long-term note receivable. 4. Interest is recorded on the Bonds Payable. 5. Depreciation on the equipment is calculated using the sum-of-years-digits method. The salvage value is $2,000, life is 10 years, and 4 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018. 6. Depreciation on the building is calculated using the straight-line method. The salvage value is $10,000, life is 30 years, and 10 years are depreciated as of Dec 31, 2018 7. Salaries and wages payable at year end amounted to $1,000 8. Dresser performed an aging analysis of its year end Accounts Receivable as follows: 0-30 days 31-60 days 61-90 days > 90 days AJR Balance % S (balance) 50% 25% 15% 10% 18. Dresser paid $1,800 selling expenses and $2,650 administrative expenses. 19. Dresser declared and paid $4,000 in dividends to its stockholders 20. Dresser accepted a $55,000, 6%, 3 year note receivable from a trusted customer for 3,000 units of inventory on October 1. The market rate of interest on Oct. 1 was 5%. Interest is received semiannually on April 1 and Oct. 1 Adjusting Journal Entries: 1. Prepaid insurance expires evenly each month. 2. A count of supplies at year end revealed $380 of supplies on hand. 3. Interest is recorded on the long-term note receivable 4. Interest is recorded on the Bonds Payable 5. Depreciation on the equipment is calculated using the sum-of-years-digits method. The salvage value is $2,000, life is 10 years, and 4 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018 6. Depreciation on the building is calculated using the straight-line method. The salvage value is $10,000, life is 30 years, and 10 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018 7. Salaries and wages payable at year end amounted to $1,000 8. Dresser performed an aging analysis of its year end Accounts Receivable as follows: 0-30 days 31-60 days 61-90 days > 90 days AJR Balance % $ (balance) 50% 25% 15% 10% % Uncollectible | 12% 30% 60% 80% 9. Income tax is recorded at $21,692 Check figures: Balance Sheet December 31, 2018 $ $ Assets: 8 Current Assets 9 Cash 10 Accounts Receivable 11 Less Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 12 Inventory 13 Prepaid Insurance 14 Supplies Total Current Assets 10.200 12.480 (6.250) 12.620 2.000 410 31.460 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity: Current Liabilities: Accounts Payable Interest Payable Salary and Wages Payable Total Current Liabilities 7.600 2000 200 9.800 $ Long Term Liabilities: Bonds Payable, 8%, 10 year *** $ $ 50.000 Total Liabilities $ 59.800 17 Property, Plant and Equipment 18 Building 19 Less Accumulated Depreciation 20 Equipment 21 Less Accumulated Depreciation Total Property, Plant and Equipment $ 100.000 (30.000) 60.000 (35.855) S 94.145 Stockholders' Equity Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Equity $ 55.000 10.805 $ 65.805 27 Total Assets $ 125.605 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $ 125.605 *** Interest payable Jan 1 and July 1 $ 30 **inventory balance is 31 5000 units at $1.60 each 32 2800 units at $1 65 each 33 Total Inventory Balance Sheet Dec 2018 8.000 4.620 12620 $ Journal Entries Accounts Gereed Ya9oOBX NLD 1104 AM 11/22/2019 Journal Entries: 1. Dresser paid the interest due on the Bonds Payable on January 1. 2. Dresser paid $750 of salaries and wages, which includes the amount accrued as of December 31, 2018 3. Dresser sold 4,000 units of inventory for $13.00 each 4. Dresser purchased supplies on account for $1,200. 5. Dresser purchased 3,000 units of inventory for $1.70 each. 6. Dresser sold 2,800 units of inventory for $14.00 each. 7. Dresser wrote off as uncollectible the accounts of Barker Corporation ($3,200) and Elm Company ($2,500) 8. Dresser paid the interest due on the Bonds Payable on July 1. 9. Dresser purchased 1,500 units of inventory for $1.72 each. 10. Dresser collected $1,000 from Elm Company, part of the balance previously written off. 11. Dresser paid salaries and wages of $64,000. 12. Dresser paid $7,200 for insurance coverage from May 1, 2019 thru April 30, 2020. 13. Dresser sold 2,500 units of inventory for $15.00 each. 14. Dresser collected $98,900 from customers on account 15. Dresser purchased 3,800 units of inventory for $1.75 each. 16. Dresser paid $12,300 on accounts payable. 17. Dresser sold 600 units of inventory for $14.50 each as a cash sale. 18. Dresser paid $1,800 selling expenses and $2,650 administrative expenses. 19. Dresser declared and paid $4,000 in dividends to its stockholders. 20. Dresser accepted a $55,000, 6%, 3 year note receivable from a trusted customer for 3,000 units of inventory on October 1. The market rate of interest on Oct. 1 was 5%. Interest is received semiannually on April 1 and Oct. 1 Adjusting Journal Entries: 1. Prepaid insurance expires evenly each month. 2. A count of supplies at year end revealed $380 of supplies on hand. 3. Interest is recorded on the long-term note receivable. 4. Interest is recorded on the Bonds Payable. 5. Depreciation on the equipment is calculated using the sum-of-years-digits method. The salvage value is $2,000, life is 10 years, and 4 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018. 6. Depreciation on the building is calculated using the straight-line method. The salvage value is $10,000, life is 30 years, and 10 years are depreciated as of Dec 31, 2018 7. Salaries and wages payable at year end amounted to $1,000 8. Dresser performed an aging analysis of its year end Accounts Receivable as follows: 0-30 days 31-60 days 61-90 days > 90 days AJR Balance % S (balance) 50% 25% 15% 10% 18. Dresser paid $1,800 selling expenses and $2,650 administrative expenses. 19. Dresser declared and paid $4,000 in dividends to its stockholders 20. Dresser accepted a $55,000, 6%, 3 year note receivable from a trusted customer for 3,000 units of inventory on October 1. The market rate of interest on Oct. 1 was 5%. Interest is received semiannually on April 1 and Oct. 1 Adjusting Journal Entries: 1. Prepaid insurance expires evenly each month. 2. A count of supplies at year end revealed $380 of supplies on hand. 3. Interest is recorded on the long-term note receivable 4. Interest is recorded on the Bonds Payable 5. Depreciation on the equipment is calculated using the sum-of-years-digits method. The salvage value is $2,000, life is 10 years, and 4 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018 6. Depreciation on the building is calculated using the straight-line method. The salvage value is $10,000, life is 30 years, and 10 years are depreciated as of Dec. 31, 2018 7. Salaries and wages payable at year end amounted to $1,000 8. Dresser performed an aging analysis of its year end Accounts Receivable as follows: 0-30 days 31-60 days 61-90 days > 90 days AJR Balance % $ (balance) 50% 25% 15% 10% % Uncollectible | 12% 30% 60% 80% 9. Income tax is recorded at $21,692 Check figures