Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i need help with part 2 and 3, somebody has solved part 1 The Nature of Crystals Lab Crystalline solids are solids in which the
i need help with part 2 and 3, somebody has solved part 1 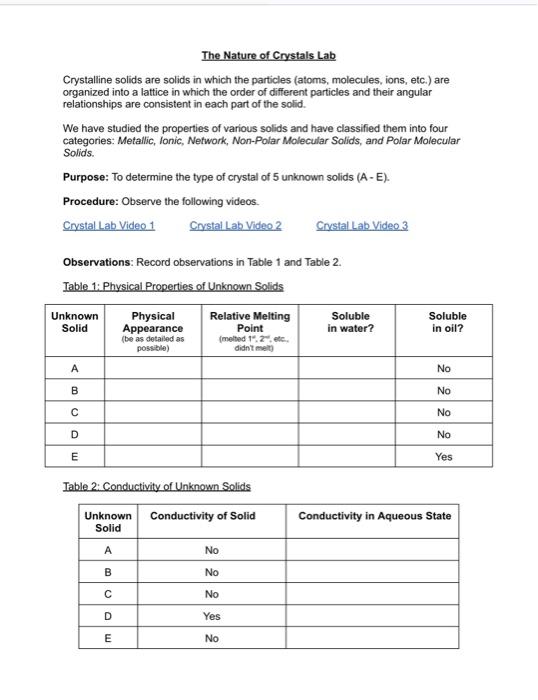



The Nature of Crystals Lab Crystalline solids are solids in which the particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) are organized into a lattice in which the order of different particles and their angular relationships are consistent in each part of the solid. We have studied the properties of various solids and have classified them into four categories: Metallic, Ionic, Network, Non-Polar Molecular Solids, and Polar Molecular Solids. Purpose: To determine the type of crystal of 5 unknown solids (A-E). Procedure: Observe the following videos. Observations: Record observations in Table 1 and Table 2. Table 1: Physical Properties of Unknown Solids Table 2: Conductivity of Unknown Solids Conclusion: Identify the type of crystal for each unknown solid (AE). Extension Questions: 1. Describe and explain the intramolecular and intermolecular forces in crystal D. ] 2. Explain the apparent solubility of the unknown sample D with reference to crystal type and forces. 3. Identify the source of error in the method used to test conductivity of the crystals' aqueous solutions. What steps (or missing steps) resulted in potential errors in the recorded observation? Expert Q&A Firstly, types of crystals: A - Polar Molecular Solids EXPLANATION Because, these are water soluble but insoluble in oil and bad conductor of electricity in both states. These are water soluble due to polar interactions. Solids have low melting points. B - Non-Polar Solids EXPLANATION Because, these are insoluble in both types of solvents and bad conductor of electricity. C. Ionic Solids EXPLANATION Because, these are only water soluble and good conductor of electricity in aqueous state. In aqueous state, molecules become free to move and show conductivity. D - Metallic Solids EXPLANATION Because, these are good conductor in both solid and aqueous state. E - Network Solids EXPLANATION Because, of their solubility in oil. Solids have high melting points. Because, of their solubility in oil. Solids have high melting points. Explanation Please refer to solution in this step. Step 2/3 The molecules in crystal A are held together with dipole-dipole interactions. The polar molecular solids have dipole-dipole type of intramolecular and intermolecular forces. Explanation Please refer to solution in this step. The A-type solids are soluble in water because of their polar nature. So, due to their intermolecular and intramolecular dipole interaction have solubility in water. Explanation Please refer to solution in this step. Answers only 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


