Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i need help with part 2&3 - i provided part 1 as well PART 1: Review all the transactions in the next section (Part 1
i need help with part 2&3 - i provided part 1 as well 
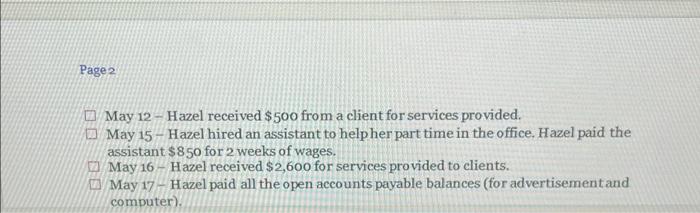



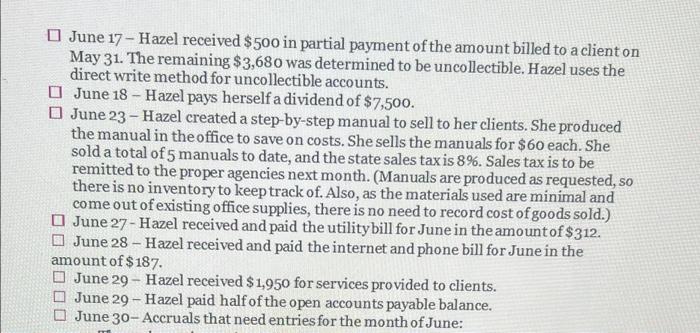


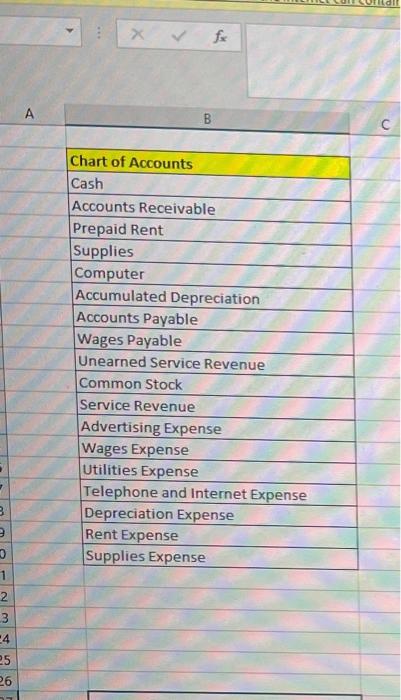
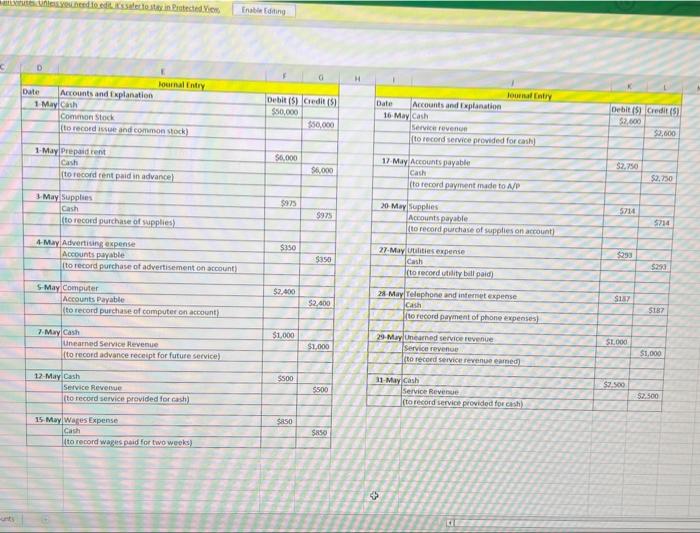
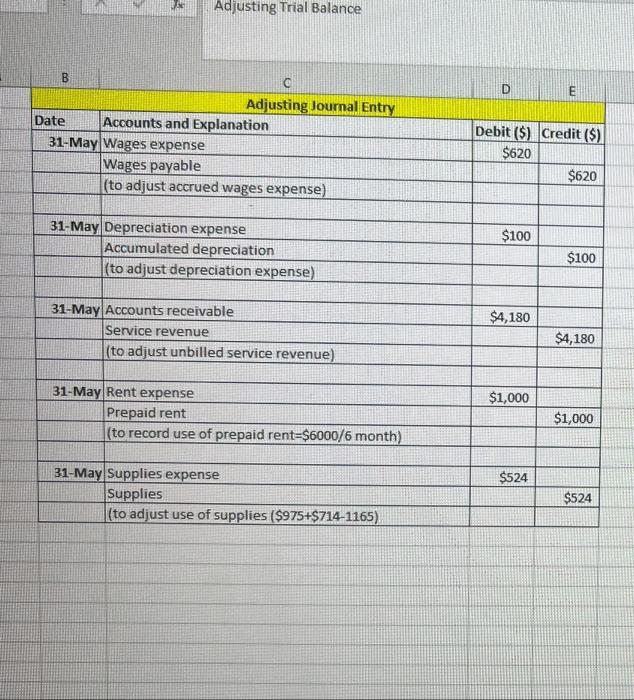
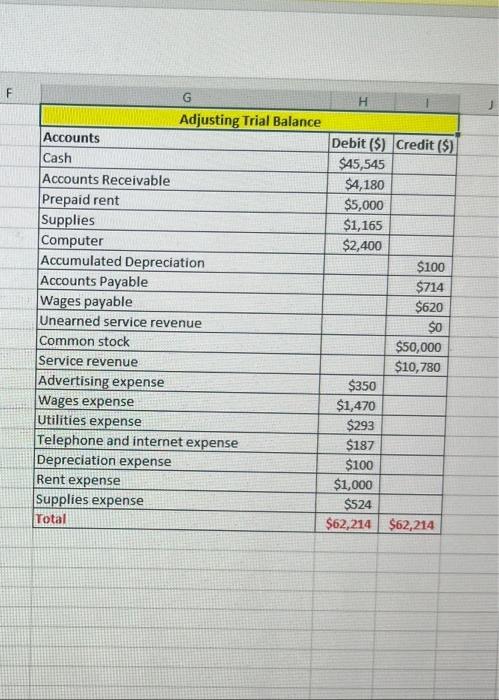
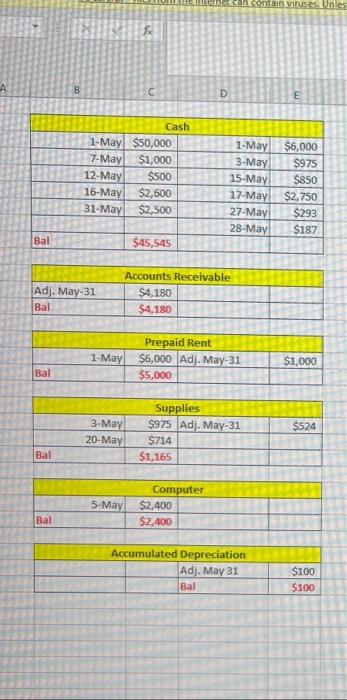
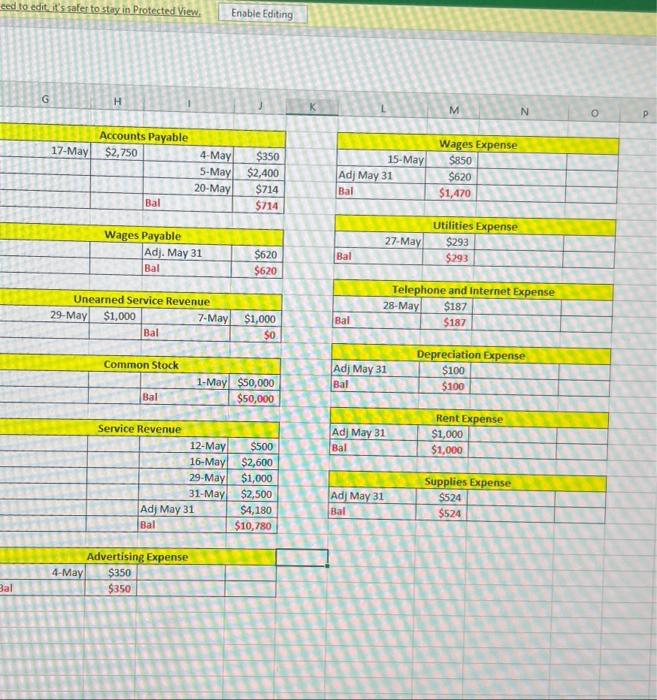
PART 1: Review all the transactions in the next section (Part 1 Transactions). Create a chart of accounts for this business. Prepare the journal entries for all the part 1 transactions (including accruals). Create T accounts for all accounts and add the part 1 transactions (including accruals). Turn in the chart of accounts, journal entries, and T accounts by the due date, either submitted in the Dropboxin D2L or turned into the instructor during class. Part 1 Transactions: 1 May 1 - Hazel invested $50,000 of her own money in the business in exchange for common stock May 1 - Hazel rented an office space for her business and paid $6,000 in advance for 6 months of rent. May 3 - Hazel purchased office supplies to use in the new office space. The supplies cost $975 and were paid for in cash. May 4 - Hazel purchased an advertisement in the local newspaper which also ran online. The ad cost $350 and was purchased on account. O May 5 - Hazel purchased a new computer for the office. The computer cost $2,400 and was purchased on account. May 7 - Hazel received $1,000 in advance for services to be completed by the end of the month. Page 2 May 12 - Hazel received $500 from a client for services provided. May 15 - Hazel hired an assistant to help her part time in the office. Hazel paid the assistant $850 for 2 weeks of wages. 22 May 16 Hazel received $2,600 for services provided to clients. May 17 - Hazel paid all the open accounts payable balances (for advertisement and computer) Page 2 May 12 - Hazel received $500 from a client for services provided. May 15 - Hazel hired an assistant to help her part time in the office. Hazel paid the assistant $850 for 2 weeks of wages. May 16 - Hazel received $2,600 for services provided to clients. May 17 - Hazel paid all the open accounts payable balances (for advertisement and computer) May 20 - Hazel purchased office supplies on account for $714. May 27 - Hazel received and paid the utility bill for May in the amount of $293. May 28 - Hazel received and paid the internet and phone bill for May in the amount of $187. May 29 - Hazel completed the work for the client who had paid in advance on May 7. May 31 - Hazel received $2,500 for services provided to clients for the second half of May. May 31 - Accruals that need entries for the month of May: The assistant is owed $620 for hours worked during the second half of May, Depreciation of $100 needs to be recorded for the month of May. Unbilled services for the month of May total $4,180. One month of prepaid rent expired. Supplies on hand at the end of the month total $1,165. PART 2: Review all the transactions in the next section (Part 2 Transactions). Prepare the journal entries for all the part 2 transactions (including accruals). Create any new Taccounts needed and add the part 2 transactions (including accruals). Prepare an adjusted trial balance for June 30, 2021. Turn in the journal entries, Taccounts, and adjusted trial balance by the due date, either submitted in the Dropbox in D2Lorturned into the instructor during class. Part 2 Transactions: June 1 - Hazel prepaid for insurance for the remaining 7 months of the year. The total premium paid was $1,680. June 1 - Hazel purchased a computer server for the office on account for $2,880. June 3 - Hazel paid $400 for an internet advertisement June 4 - Hazel paid the assistant for the amount due for May wages. June 8 - Hazel received $7,500 in advance for services to be provided to clients. June 15 - Hazel paid for the supplies purchased on May 20. June 15 - Hazel decided to create a petty cash fund for the office. The amount deposited into the petty cash account was $500. June 16 - Hazel paid her assistant $775 for wages for the first two weeks of June. June 16 - Hazel billed clients a total of $3,683 for services provided during the first half of the month June 17 - Hazel received $500 in partial payment of the amount billed to a client on May 31. The remaining $3,680 was determined to be uncollectible. Hazel uses the direct write method for uncollectible accounts. June 18 - Hazel pays herself a dividend of $7,500. June 23 - Hazel created a step-by-step manual to sell to her clients. She produced the manual in the office to save on costs. She sells the manuals for $60 each. She sold a total of 5 manuals to date, and the state sales taxis 8%. Sales tax is to be remitted to the proper agencies next month. (Manuals are produced as requested, so there is no inventory to keep track of. Also, as the materials used are minimal and come out of existing office supplies, there is no need to record cost of goods sold.) June 27 - Hazel received and paid the utility bill for June in the amountof $312. June 28 - Hazel received and paid the internet and phone bill for June in the amount of $187. June 29 - Hazel received $1,950 for services provided to clients. June 29 - Hazel paid half of the open accounts payable balance. June 30-Accruals that need entries for the month of June: June 29 - Hazel paid half of the open accounts payable balance. June 30- Accruals that need entries for the month of June: The assistant is owed $945 for hours worked during the second half of June. Depreciation of $ 100 needs to be recorded for the month of June for the computer purchased in May. The computer server is determined to have a useful life of 4 years, and a residual value of $200. Hazel decided to use the double-declining balance method for this equipment. Depreciation needs to be recorded for the one month that it was in service. (Hint: calculate the double-declining balance depreciation for the first year, then determine how much should be recorded for one month.) Unbilled services for the month of June total $1,585 One month of prepaid rent expired. One month of prepaid insurance expired. Supplies on hand at the end of the month total $265. Hazel had completed one half of the services she received prepayment foron June 8. The petty cash balance on June 30th is $327. Expenses include postage & shipping, $56; snacks and drinks for office (use supplies expense account), $82; miscellaneous expenses, $35. . . . PART 3: Prepare an income statement, statement of stockholders' equity and balance sheet for the fiscal year end, June 30, 2021. Prepare the year end closing entries. Prepare a post-closing trial balance. Turn in the financial statements, journal entries, Taccounts, and post-closing trial balance by the due date, either submitted in the Dropbox in D2Lorturned into the instructor during class. fox A B Chart of Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Prepaid Rent Supplies Computer Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Wages Payable Unearned Service Revenue Common Stock Service Revenue Advertising Expense Wages Expense Utilities Expense Telephone and Internet Expense Depreciation Expense Rent Expense Supplies Expense 3 1 2 3 -4 25 26 Used to edit safe sinteted. Entong H D lownal Entry Date Accounts and explanation 1 May Cash Common Stock to record issue and common stock) Debit(s) Credit (5) $50,000 100,000 Journal Entry Date Accounts and Explanation 16 May cash Service rovence to record service provided for cash Debitis Credit (5) 52.600 $2,600 $6,000 1. May Prepaid rent cash to recordent paid in advance! $6,000 17 May Accounts payable Cash to record payment made to AP $2.750 $2,750 3 May Supplies (cash ito record purchase of supplies) $2923 5714 $975 20 May supplies Accounts payable (to record purchase of supplies on account) 3214 $350 4-May Advertising expense Accounts payable to record purchase of advertisement on account) $350 $299 27 May Utilities expense Cash to record utility bill paid 5293 $2,400 S-May Computer Accounts Payable to record purchase of computer on account SIBY $2.400 28 May Telephone and internet expense cash to record payment of phone expenses $187 $1.000 7. May Cash uneared Service Revenue (to record advance receipt for future service) $1,000 $1,000 29 May neared service revenue Service revenue to record service revenue eamed $1,000 $500 12-May Cash Service Revenue to record service provided for cash) $500 $2.500 11-May Cash Service Revenge to record service provided for cash 52.500 $850 15. MayWars Expense (cash to record wages paid for two weeks) $850 > Adjusting Trial Balance B @ D E Adjusting Journal Entry Date Accounts and Explanation 31-May Wages expense Wages payable (to adjust accrued wages expense) Debit ($) Credit ($) $620 $620 $100 31-May Depreciation expense Accumulated depreciation (to adjust depreciation expense) $100 $4,180 31-May Accounts receivable Service revenue (to adjust unbilled service revenue) $4,180 $1,000 31-May Rent expense Prepaid rent (to record use of prepaid rent=$6000/6 month) $1,000 $524 31-May Supplies expense Supplies (to adjust use of supplies ($975+$714-1165) $524 F H G Adjusting Trial Balance Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Prepaid rent Supplies Computer Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Wages payable Unearned service revenue Common stock Service revenue Advertising expense Wages expense Utilities expense Telephone and internet expense Depreciation expense Rent expense Supplies expense Total Debit ($) Credit ($) $45,545 $4,180 $5,000 $1,165 $2,400 $100 $714 $620 $0 $50,000 $10,780 $350 $1,470 $293 $187 $100 $1,000 $524 $62,214 $62,214 et can contain viruses Unles B D E Cash 1-May $50,000 7-May $1,000 12-May $500 16-May $2,600 31-May $2,500 1-May 3-May 15-May 17-May 27-May 28-May $6,000 $975 $850 $2,750 $293 $187 Bal $45,545 Adj. May-31 Bal Accounts Receivable $4,180 $4,180 1-May Prepaid Rent $6,000 Adj. May-31 $5,000 $1,000 Bal 3-May 20-May Supplies $975 Adj. May-31 $714 $1,165 $524 Bal 5-May Computer $2,400 $2,400 Bal Accumulated Depreciation Adj. May 31 Bal $100 $100 eed to edit it's safe to stay in Protected View Enable Editing G H M N o P Accounts Payable 17-May $2,750 $350 4-May 5-May 20-May $2,400 $714 $714 Wages Expense 15-May $850 Adj May 31 $620 Bal $1,470 Bal Wages Payable Adj. May 31 Bal Utilities Expense 27-May $293 $293 Bal $620 $620 Unearned Service Revenue 29-May $1,000 7-May Bal Telephone and Internet Expense 28-May $187 $187 Bal $1,000 $0 Common Stock Depreciation Expense $100 Adj May 31 Bal 1-May $50,000 $50,000 $100 Bal Adj May 31 Bal Rent Expense $1,000 $1,000 Service Revenue 12-May $500 16-May $2,600 29-May $1,000 31-May $2,500 Adj May 31 $4,180 Bal $10,780 Adj May 31 Bal Supplies Expense $524 $524 Advertising Expense 4-May $350 $350 Bal 













Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


