I need help with question 13 and 14 please.
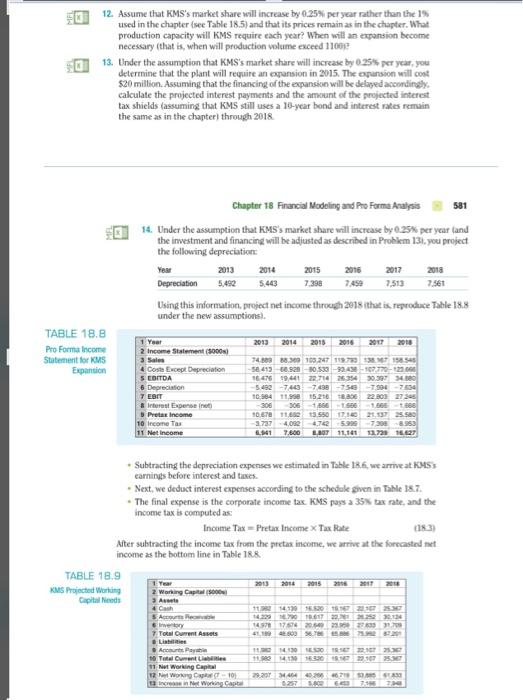
FD 12. Assume that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year rather than the 1% used in the chapter (see Table 18.5) and that its prices remain as in the chapter. What production capacity will KMS require each year? When will an expansion become necessary that is, when will production volume exceed 110012 13. Under the assumption that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year, you determine that the plant will require an expansion in 2015. The apansion will cost $20 million. Assuming that the financing of the expansion will be delayed accordingly. calculate the projected interest payments and the amount of the projected interest tax shields (assuming that KMS still uses a 10-year bond and interest rates remain the same as in the chapter through 2018 Chapter 18 Financial Modeling and Pro Forme Analysis 581 14. Under the assumption that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year and the investment and financing will be adjusted as described in Problem 131. you project the following depreciation You 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Depreciation 5.492 5.443 7.398 7.513 7.561 Using this information, project net income through 2013 that is reproduce Table 18.8 under the new assumptions) 2013 2014 2015 2017 TABLE 18.8 Pro Forma Income Statement for KMS Expansion 2 Income Statement (5000) Costa Except Depreciation 5 EBITDA 5 Depreciation 7 EBIT Interest Expense Pret Income 10 Income Tax 11 Net Income 74.00 88.00 10.247199707158546 58.419.92 -130530-99.430107770-2200 1676 19.441 22.714 26.354 30.37 -743 7.438 -750 -7.50 -7.896 10 964 11.9 15.210 TE 22.803 27245 -306 300 -1860 16 SET 11 13.50 2017 25.50 4.76 72988950 7.600 LOT 11.141 12.72 16.622 Subtracting the depreciation expenses we estimated in Table 18.6, we arrive at KMS carnings before interest and taxes Next, we deduct interest expenses according to the schedule given in Table 18.7 The final expense is the corporate income tax KMS pays a 35% bax rate, and the income tax is computed as: Income Tax = Pretax Income Tax Rate (183) After subtracting the income tax from the pretax income, we arrive at the forecasted net income as the bottom line in Table 188 TABLE 18.9 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 KMS Projected Working 2 Working Capital (9000 Capital de 1182141015.62015161207 14.223.01.17 22.125230.136 sy 149211754 20.09.2002 7 Total Current Assets ACP 10 Total Centres 11 Not Working Capital 12 Wong 101 Li 11 14116320 122107 Working Capta 29:20746442567 S. FD 12. Assume that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year rather than the 1% used in the chapter (see Table 18.5) and that its prices remain as in the chapter. What production capacity will KMS require each year? When will an expansion become necessary that is, when will production volume exceed 110012 13. Under the assumption that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year, you determine that the plant will require an expansion in 2015. The apansion will cost $20 million. Assuming that the financing of the expansion will be delayed accordingly. calculate the projected interest payments and the amount of the projected interest tax shields (assuming that KMS still uses a 10-year bond and interest rates remain the same as in the chapter through 2018 Chapter 18 Financial Modeling and Pro Forme Analysis 581 14. Under the assumption that KMS's market share will increase by 0.25% per year and the investment and financing will be adjusted as described in Problem 131. you project the following depreciation You 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Depreciation 5.492 5.443 7.398 7.513 7.561 Using this information, project net income through 2013 that is reproduce Table 18.8 under the new assumptions) 2013 2014 2015 2017 TABLE 18.8 Pro Forma Income Statement for KMS Expansion 2 Income Statement (5000) Costa Except Depreciation 5 EBITDA 5 Depreciation 7 EBIT Interest Expense Pret Income 10 Income Tax 11 Net Income 74.00 88.00 10.247199707158546 58.419.92 -130530-99.430107770-2200 1676 19.441 22.714 26.354 30.37 -743 7.438 -750 -7.50 -7.896 10 964 11.9 15.210 TE 22.803 27245 -306 300 -1860 16 SET 11 13.50 2017 25.50 4.76 72988950 7.600 LOT 11.141 12.72 16.622 Subtracting the depreciation expenses we estimated in Table 18.6, we arrive at KMS carnings before interest and taxes Next, we deduct interest expenses according to the schedule given in Table 18.7 The final expense is the corporate income tax KMS pays a 35% bax rate, and the income tax is computed as: Income Tax = Pretax Income Tax Rate (183) After subtracting the income tax from the pretax income, we arrive at the forecasted net income as the bottom line in Table 188 TABLE 18.9 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 KMS Projected Working 2 Working Capital (9000 Capital de 1182141015.62015161207 14.223.01.17 22.125230.136 sy 149211754 20.09.2002 7 Total Current Assets ACP 10 Total Centres 11 Not Working Capital 12 Wong 101 Li 11 14116320 122107 Working Capta 29:20746442567 S








