I need help with the question, I would be very grateful.
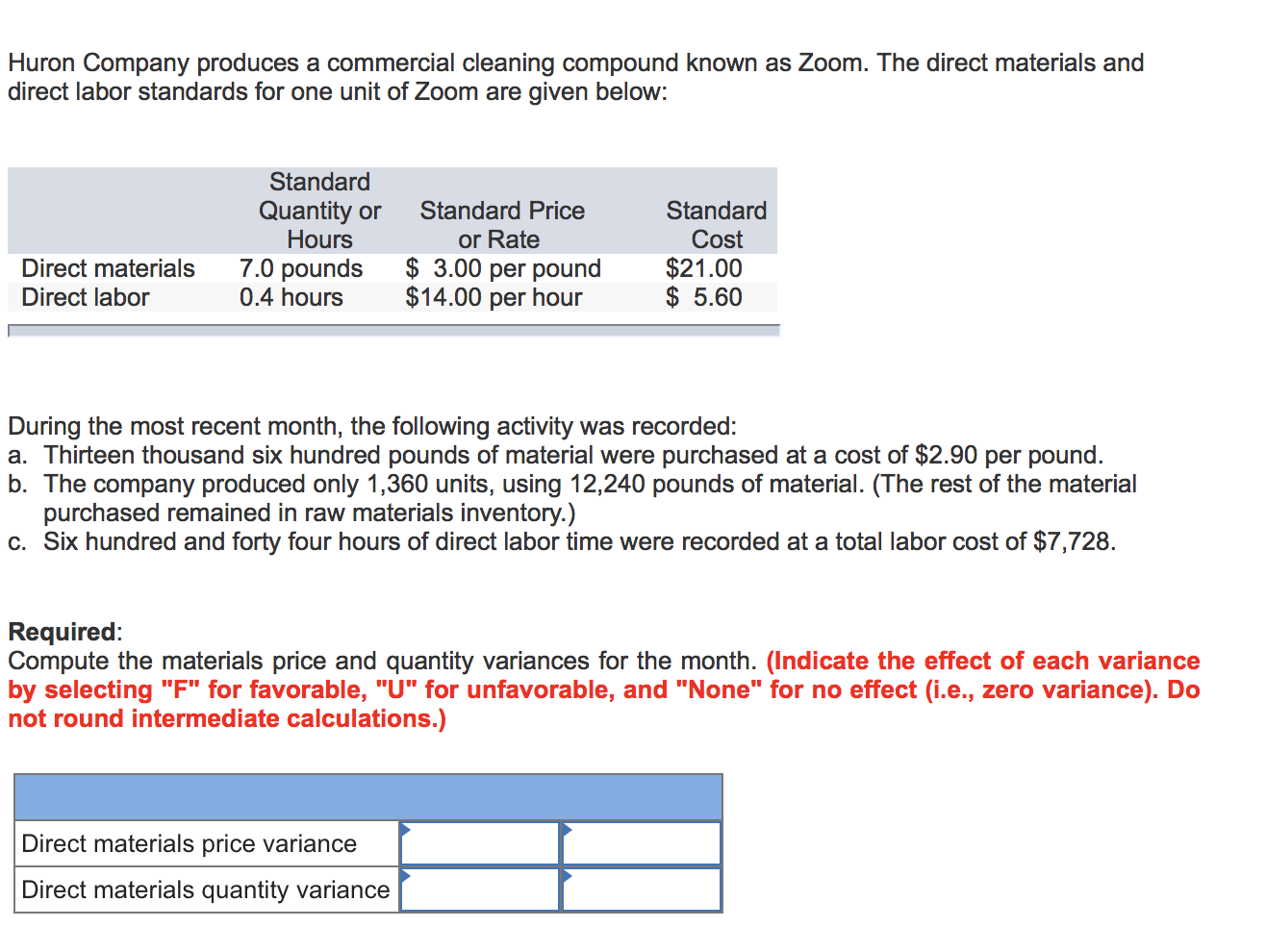
Huron Company produces a commercial cleaning compound known as Zoom. The direct materials and direct labor standards for one unit of Zoom are given below: Standard Quantity or Standard Price Standard Hours or Rate Cost Direct materials 7.0 pounds $ 3.00 per pound $21.00 Direct labor 0.4 hours $14.00 per hour $ 5.60 ' During the most recent month, the following activity was recorded: a. Thirteen thousand six hundred pounds of material were purchased at a cost of $2.90 per pound. b. The company produced only 1,360 units, using 12,240 pounds of material. (The rest of the material purchased remained in raw materials inventory.) c. Six hundred and forty four hours of direct labor time were recorded at a total labor cost of $7,728. Required: Compute the materials price and quantity variances for the month. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Do not round intermediate calculations.) Direct materials price variance - - Direct materials quantity variance - - SkyChefs, |nc., prepares in-ight meals for a number of major airlines. One of the company's products is grilled salmon in dill sauce with baby new potatoes and spring vegetables. During the most recent week, the company prepared 7,200 of these meals using 3,500 direct labor-hours. The company paid these direct labor workers a total of $31,500 for this work, or $9.00 per hour. According to the standard cost card for this meal, it should require 0.50 direct labor-hours at a cost of $8.50 per hour. Required: 1. According to the standards, what direct labor cost should have been incurred to prepare 7,200 meals? How much does this differ from the actual direct labor cost? (Round labor-hours per meal and labor cost per hour to 2 decimal places.) Total standard direct labor cost Actual cost incurred Total standard direct labor cost Total direct labor variance 2. Break down the difference computed in (1) above into a labor rate variance and a labor efficiency variance. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance\" Dawson Toys, Ltd., produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently established a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 8 microns per toy at $0.31 per micron Direct labor: 1.2 hours per toy at $7.00 per hour During July, the company produced 5,100 Maze toys. Production data for the month on the toy follow: Direct materials: 71,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.30 per micron. 20,000 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor: 6,620 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $49,650. Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Do not round intermediate calculations. Round nal answer to the nearest whole dollar.) a. The materials price and quantity variances. Material price variance - Material quantity variance - - b. The labor rate and efficiency variances. Logistics Solutions provides order fulllment services for dot.com merchants. The company maintains warehouses that stock items carried by its dot.com clients. When a client receives an order from a customer, the order is forwarded to Logistics Solutions, which pulls the item from storage, packs it, and ships it to the customer. The company uses a predetermined variable overhead rate based on direct labor- hours. In the most recent month, 150,000 items were shipped to customers using 5,900 direct labor-hours. The company incurred a total of $18,290 in variable overhead costs. According to the company's standards, 0.03 direct labor-hours are required to fulll an order for one item and the variable overhead rate is $3.15 per direct labor-hour. Required: 1. According to the standards, what variable overhead cost should have been incurred to ll the orders for the 150,000 items? How much does this differ from the actual variable overhead cost? (Round labor- hours per item and overhead cost per hour to 2 decimal places.) - - - - Total standard variable overhead cost - Actual variable overhead cost incurred - Total standard variable overhead cost - Total variable overhead variance m- 2. Break down the difference computed in (1) above into a variable overhead rate variance and a variable overhead efciency variance. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead rate variance _ _ Variable overhead efciency variance _ _