I need help with these questions asap. Will be appreciated. Thank you !!
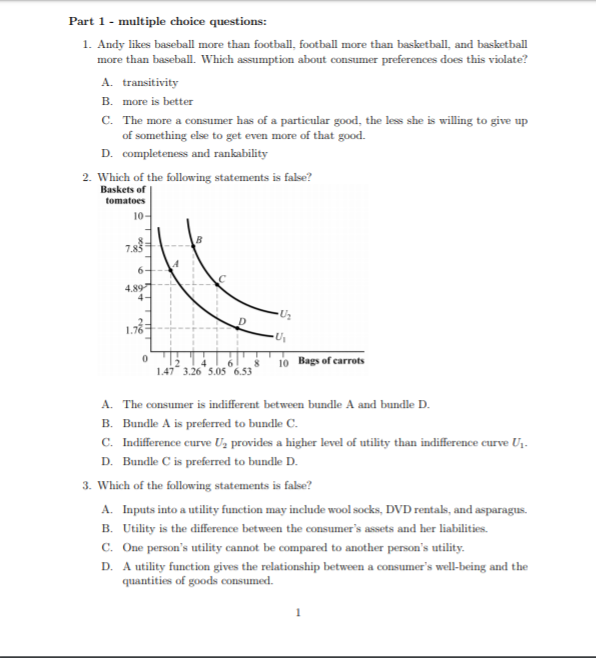
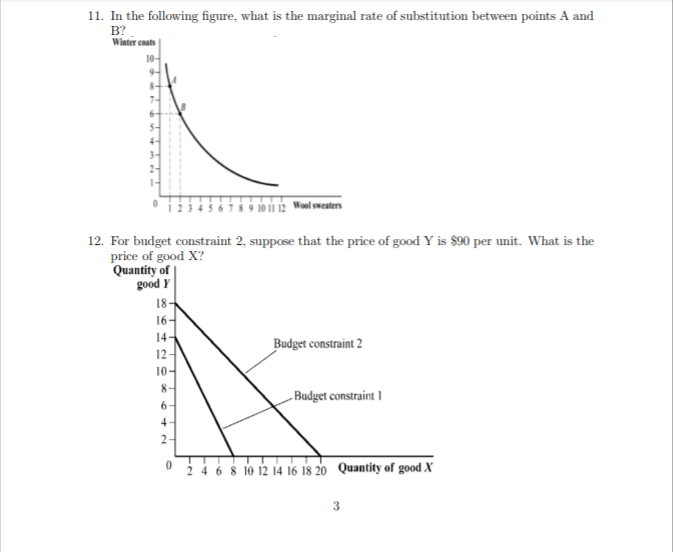
Part 1 - multiple choice questions: 1. Andy likes baseball more than football, football more than basketball, and basketball more than baseball. Which assumption about consumer preferences does this violate? A. transitivity B. more is better C. The more a consumer has of a particular good, the less she is willing to give up of something else to get even more of that good. D. completeness and rankability 2. Which of the following statements is false? Baskets of tomatoes 1.47 3.26 5.05 6.53 10 Bags of carrots A. The consumer is indifferent between bundle A and bundle D. B. Bundle A is preferred to bundle C. C. Indifference curve , provides a higher level of utility than indifference curve Uj- D. Bundle C is preferred to bundle D. 3. Which of the following statements is false? A. Inputs into a utility function may include wool socks, DVD rentals, and asparagus. B. Utility is the difference between the consumer's assets and her liabilities. C. One person's utility cannot be compared to another person's utility. D. A utility function gives the relationship between a consumer's well-being and the quantities of goods consumed.4. Which assumption(s) allow(s) us to draw indifference curves? A. that the more we have of a good, the less we are willing to give up to get even more of it B. rankability and completeness C. cardinal measurement and cardinal ranking D. free disposal and more is better 5. In the following figure, suppose the budget constraint shifted from constraint 2 to constraint 1. What could have caused this change? Quantity of good Y 18- 16- 14- 12- Budget constraint 2 10- 8- Budget constraint I 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Quantity of good X A. an increase in the price of good Y B. a decrease in income C. a decrease in income and an increase in the price of good X relative to good Y D. a decrease in the price of good X 6. Monroe consumes crab cakes and tuna. Monroe's utility increases with the consump- tion of crab cakes, but his utility neither increases nor decreases with the consumption of tuna. Assuming tuna is on the x-axis and crab cake is on the y-axis, what do Monroe's indifference curves look like? A. upward-sloping lines from the origin B. vertical lines C. downward-sloping lines D. horizontal lines7. Cher's marginal rate of substitution of necklaces (N) for earrings (E) is 5 (MRSEN = 5). This information implies that: A. Cher is willing to trade away five necklaces for one more pair of earrings, holding her utility constant. B. Cher should own five times as many necklaces as pairs of earrings. 2 C. the slope of the indifference curve is 5 and thus upward sloping. D. Cher will move to a higher indifference curve if she trades away five necklaces for one more pair of earrings. Part 2 - quantitative questions: 8. Suppose that the marginal utility of good Y = 2X- and the marginal utility of good X = 4XY. What is the slope of the indifference curve when Y = 7 and X = 2? Assume that good X is on the horizontal axis and good Y is on the vertical axis. 9. Suppose that MUx = Y and MUy = X. The prices of good X and good Y are $5 and $4, respectively. How many units of good X does the consumer buy if she has $410 of income? 10. The consumer's budget constraint is $6 = 0.50G + P, where G is packs of gum and P is bags of pretzels. The marginal utility of pretzels is AUp = GOs, and the marginal utility of gum is MUG = 0.5G P. The consumer's utility function is U = GoSP. How many packs of gum and bags of pretzels are included in the utility-maximizing bundle?11. In the following figure, what is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B? Winter coats 10- 9- 7 8 9 10 11 12 Wool sweaters 12. For budget constraint 2, suppose that the price of good Y is $90 per unit. What is the price of good X? Quantity of good Y 18- 16- 14- 12- Budget constraint 2 10 Budget constraint I 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Quantity of good X 3