Question: I need help with this question. You have to use the image above to answer the 3 questions Review this inode structure inode structure.pdf and

 I need help with this question. You have to use the image above to answer the 3 questions
I need help with this question. You have to use the image above to answer the 3 questions
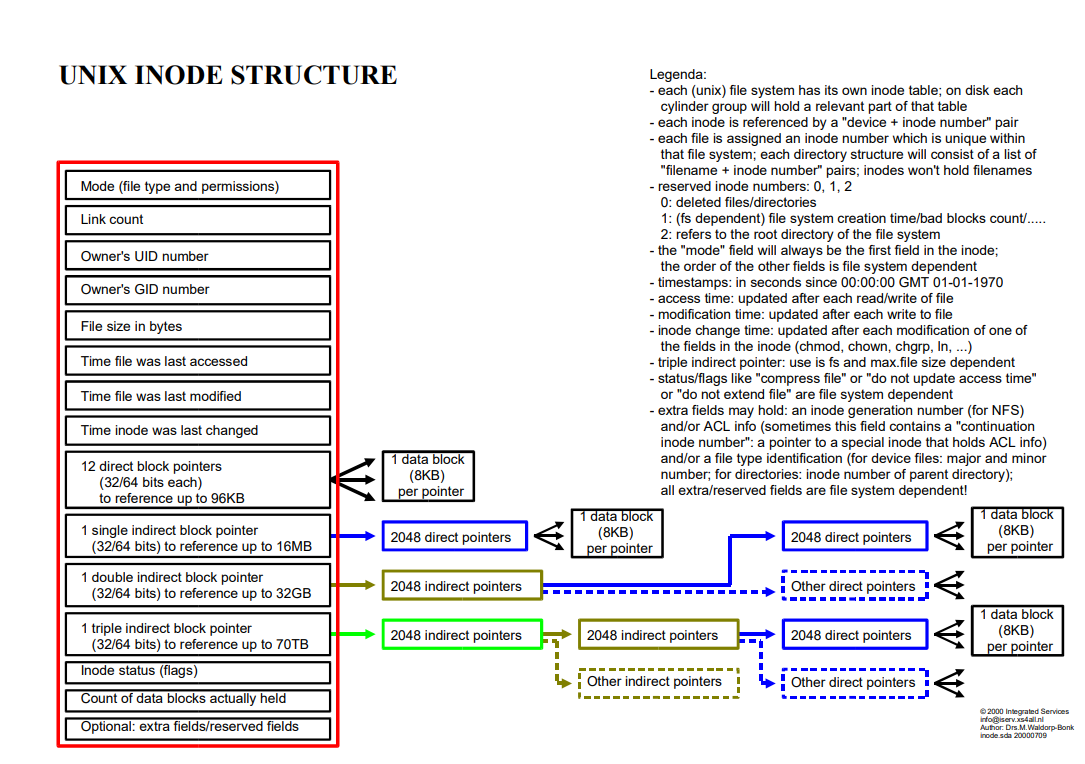
Review this inode structure inode structure.pdf and answer the following questions. Don't forget to include the indirect blocks if needed, but no need to consider the space required for additional inode. Note that 1MB is 1024KB and 1GB is 1024MB. Each disk block can be a data block o indirect block. # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100KB: # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100MB: # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100GB: - each file "filename + name + inode 2: refers - modification time the fields ---------- UNIX INODE STRUCTURE Legenda: - each (unix) file system has its own inode table, on disk each cylinder group will hold a relevant part of that table - each inode is referenced by a "device + inode number" pair is assigned an inode number which is unique within thot file that file system; each directory structure will consist of a list of number" pairs; inodes won't hold filenames Mode (file type and permissions) - reserved inode numbers: 0, 1, 2 0: deleted files/directories Link count 1: (fs dependent) file system creation time/bad blocks count/.... . to the root directory of the file system the "mode" field will always be the first field in the inode; Owner's UID number the order of the other fields is file system dependent Owner's GID number timestamps:in seconds since 00:00:00 GMT 01-01-1970 - access time: updated after each read/write of file time: updated after each write to file File size in bytes in the inode (chmod, chown, chgrp, In, ...) Time file was last accessed triple indirect pointer: use is fs and max.file size dependent - status/flags like "compress file" or "do not update access time" Time file was last modified or " - extra fields may hold: an inode generation number (for NFS) Time inode was last changed and/or (sometimest this field contains a "continuation inode number": a pointer to a special inode that holds ACL info) 12 direct block pointers 1 data block and/or a file type identification (for device files: major and minor (32/64 bits each) (8KB) number; for directories: inode number of parent directory); to reference up to 96KB per pointer all extra/reserved fields are file system dependent! data block 1 data block 1 single indirect block pointer 2048 direct pointers (8KB) 2048 direct pointers (32/64 bits) to reference up to 16MB per pointer per pointer 1 double indirect block pointer 2048 indirect pointers Other direct pointers (32/64 bits) to reference up to 32GB 1 data block 1 triple indirect block pointer 2048 indirect pointers 2048 indirect pointers 2048 direct pointers (8KB) (32/64 bits) to reference up to 70TB per pointer Inode status (flags) Other indirect pointers HOther direct pointers Count of data blocks actually held Optional: extra fields/reserved fields file" are are file svetlo dependent systema andler ACL info (BKB) 1 2000 Integrated Services intoiserv.xs4all.nl Author: Drs. M.Waldorp-Bonk inode sda 20000700 Review this inode structure inode structure.pdf and answer the following questions. Don't forget to include the indirect blocks if needed, but no need to consider the space required for additional inode. Note that 1MB is 1024KB and 1GB is 1024MB. Each disk block can be a data block o indirect block. # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100KB: # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100MB: # of disk blocks needed to store a file of size 100GB: - each file "filename + name + inode 2: refers - modification time the fields ---------- UNIX INODE STRUCTURE Legenda: - each (unix) file system has its own inode table, on disk each cylinder group will hold a relevant part of that table - each inode is referenced by a "device + inode number" pair is assigned an inode number which is unique within thot file that file system; each directory structure will consist of a list of number" pairs; inodes won't hold filenames Mode (file type and permissions) - reserved inode numbers: 0, 1, 2 0: deleted files/directories Link count 1: (fs dependent) file system creation time/bad blocks count/.... . to the root directory of the file system the "mode" field will always be the first field in the inode; Owner's UID number the order of the other fields is file system dependent Owner's GID number timestamps:in seconds since 00:00:00 GMT 01-01-1970 - access time: updated after each read/write of file time: updated after each write to file File size in bytes in the inode (chmod, chown, chgrp, In, ...) Time file was last accessed triple indirect pointer: use is fs and max.file size dependent - status/flags like "compress file" or "do not update access time" Time file was last modified or " - extra fields may hold: an inode generation number (for NFS) Time inode was last changed and/or (sometimest this field contains a "continuation inode number": a pointer to a special inode that holds ACL info) 12 direct block pointers 1 data block and/or a file type identification (for device files: major and minor (32/64 bits each) (8KB) number; for directories: inode number of parent directory); to reference up to 96KB per pointer all extra/reserved fields are file system dependent! data block 1 data block 1 single indirect block pointer 2048 direct pointers (8KB) 2048 direct pointers (32/64 bits) to reference up to 16MB per pointer per pointer 1 double indirect block pointer 2048 indirect pointers Other direct pointers (32/64 bits) to reference up to 32GB 1 data block 1 triple indirect block pointer 2048 indirect pointers 2048 indirect pointers 2048 direct pointers (8KB) (32/64 bits) to reference up to 70TB per pointer Inode status (flags) Other indirect pointers HOther direct pointers Count of data blocks actually held Optional: extra fields/reserved fields file" are are file svetlo dependent systema andler ACL info (BKB) 1 2000 Integrated Services intoiserv.xs4all.nl Author: Drs. M.Waldorp-Bonk inode sda 20000700
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


