Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I need more information for an answer. Please write down a 'T' when the statement is correct, and an 'F' when the statement is incorrect.
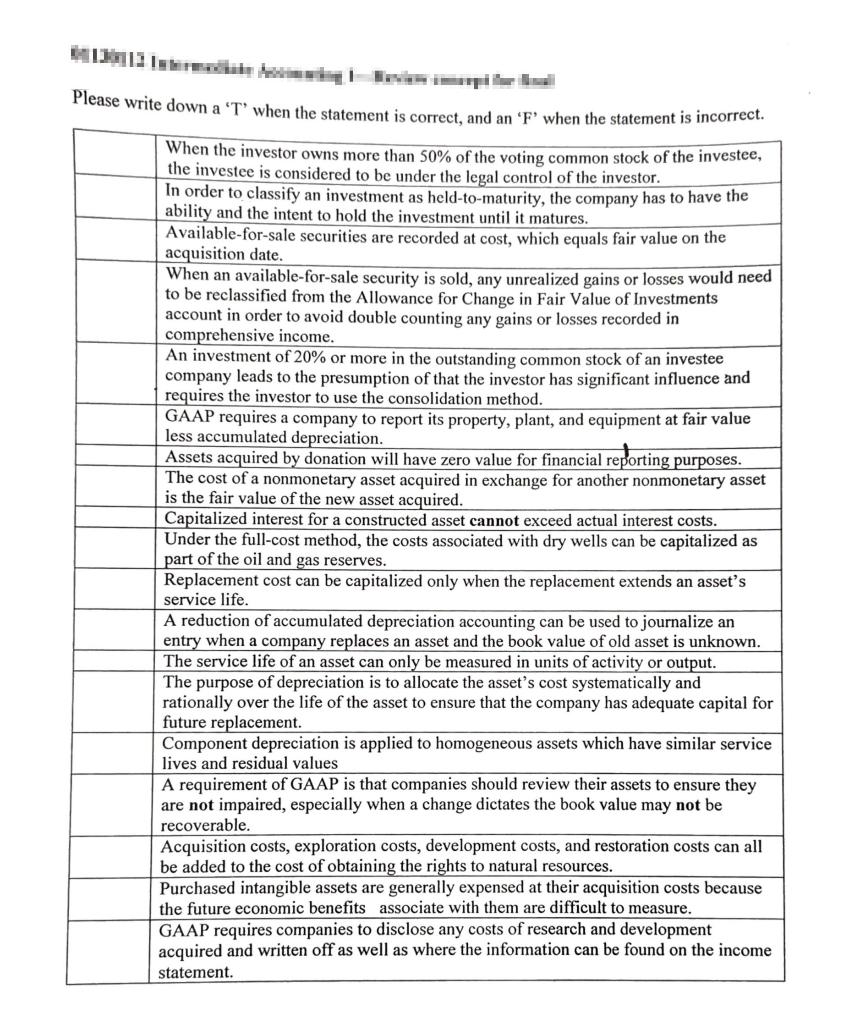
I need more information for an answer.
Please write down a 'T' when the statement is correct, and an 'F' when the statement is incorrect. When the investor owns more than 50% of the voting common stock of the investee, the investee is considered to be under the legal control of the investor. In order to classify an investment as held-to-maturity, the company has to have the ability and the intent to hold the investment until it matures. Available-for-sale securities are recorded at cost, which equals fair value on the acquisition date. When an available-for-sale security is sold, any unrealized gains or losses would need to be reclassified from the Allowance for Change in Fair Value of Investments account in order to avoid double counting any gains or losses recorded in comprehensive income. An investment of 20% or more in the outstanding common stock of an investee company leads to the presumption of that the investor has significant influence and requires the investor to use the consolidation method. GAAP requires a company to report its property, plant, and equipment at fair value less accumulated depreciation. Assets acquired by donation will have zero value for financial reporting purposes. The cost of a nonmonetary asset acquired in exchange for another nonmonetary asset is the fair value of the new asset acquired. Capitalized interest for a constructed asset cannot exceed actual interest costs. Under the full-cost method, the costs associated with dry wells can be capitalized as part of the oil and gas reserves. Replacement cost can be capitalized only when the replacement extends an asset's service life. A reduction of accumulated depreciation accounting can be used to journalize an entry when a company replaces an asset and the book value of old asset is unknown. The service life of an asset can only be measured in units of activity or output. The purpose of depreciation is to allocate the asset's cost systematically and rationally over the life of the asset to ensure that the company has adequate capital for future replacement. Component depreciation is applied to homogeneous assets which have similar service lives and residual values A requirement of GAAP is that companies should review their assets to ensure they are not impaired, especially when a change dictates the book value may not be recoverable. Acquisition costs, exploration costs, development costs, and restoration costs can all be added to the cost of obtaining the rights to natural resources. Purchased intangible assets are generally expensed at their acquisition costs because the future economic benefits associate with them are difficult to measure. GAAP requires companies to disclose any costs of research and development acquired and written off as well as where the information can be found on the income statementStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


