Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i need Q8 answers in 50 mins i will give you thumb up Here is a more realistic scenario. This scenario in various forms happens
i need Q8 answers in 50 mins i will give you thumb up
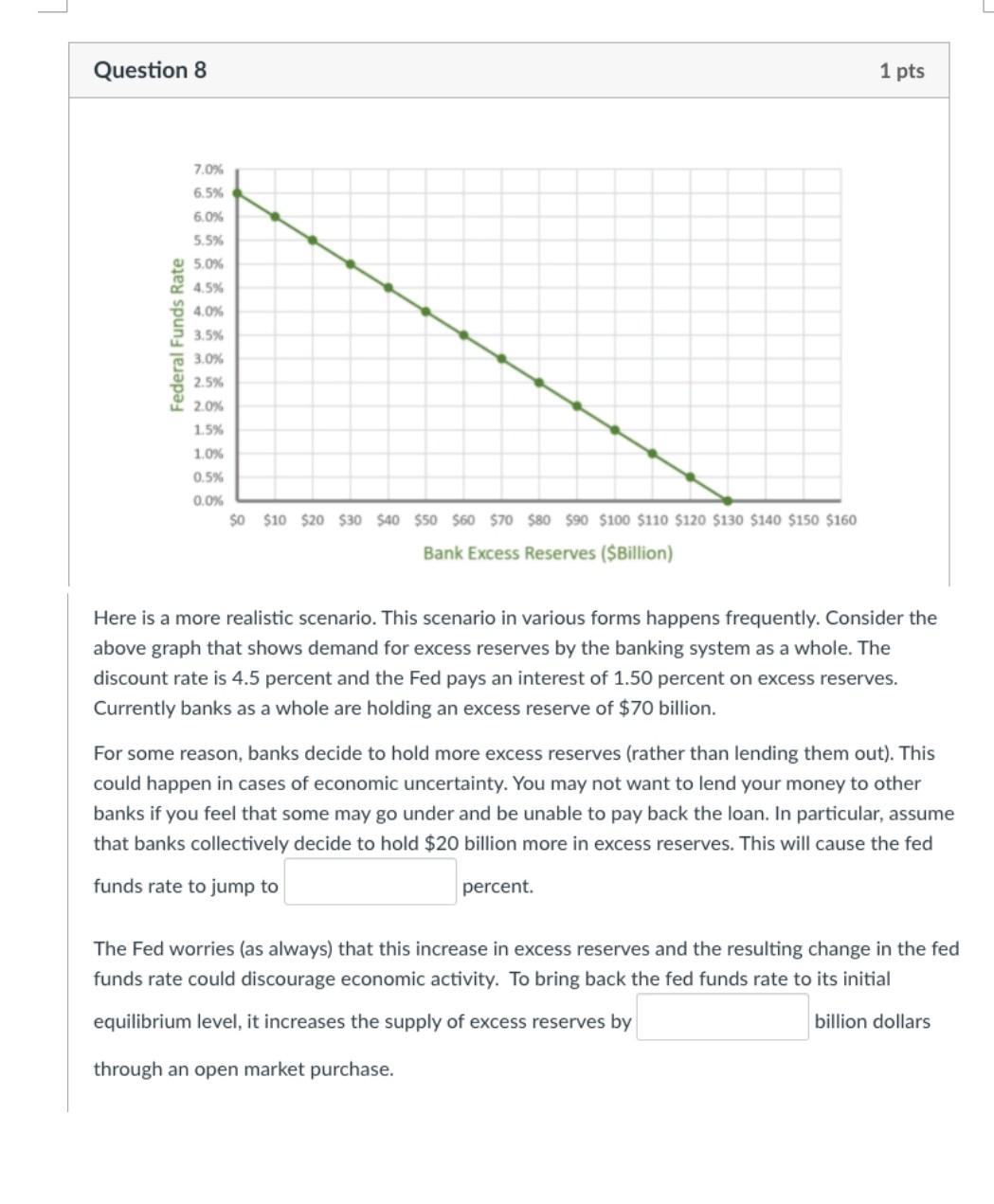
Here is a more realistic scenario. This scenario in various forms happens frequently. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves by the banking system as a whole. The discount rate is 4.5 percent and the Fed pays an interest of 1.50 percent on excess reserves. Currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. For some reason, banks decide to hold more excess reserves (rather than lending them out). This could happen in cases of economic uncertainty. You may not want to lend your money to other banks if you feel that some may go under and be unable to pay back the loan. In particular, assume that banks collectively decide to hold $20 billion more in excess reserves. This will cause the fed funds rate to jump to percent. The Fed worries (as always) that this increase in excess reserves and the resulting change in the fed funds rate could discourage economic activity. To bring back the fed funds rate to its initial equilibrium level, it increases the supply of excess reserves by billion dollars through an open market purchase. Here is a more realistic scenario. This scenario in various forms happens frequently. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves by the banking system as a whole. The discount rate is 4.5 percent and the Fed pays an interest of 1.50 percent on excess reserves. Currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. For some reason, banks decide to hold more excess reserves (rather than lending them out). This could happen in cases of economic uncertainty. You may not want to lend your money to other banks if you feel that some may go under and be unable to pay back the loan. In particular, assume that banks collectively decide to hold $20 billion more in excess reserves. This will cause the fed funds rate to jump to percent. The Fed worries (as always) that this increase in excess reserves and the resulting change in the fed funds rate could discourage economic activity. To bring back the fed funds rate to its initial equilibrium level, it increases the supply of excess reserves by billion dollars through an open market purchaseStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


