I need the excel solution for #6 and #7 for the Case Problem: Portfolio Optimization with Transaction Costs (Hauck Financial Services),Thank you


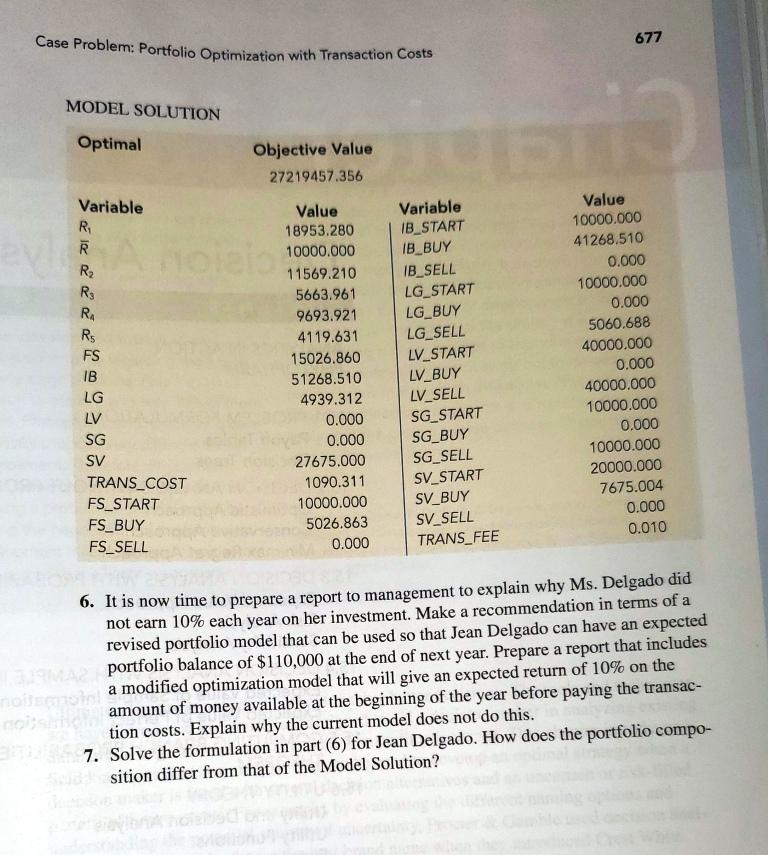
Hauck Financial Services has a number of passive, buy-and-hold clients. For these clients, Hauck offers an investment account whereby clients agree to put their money into a portfolio of mutual funds that is rebalanced once a year. When the rebalancing occurs, Hauck determines Case Problem: Portfolio Optimization with Transaction Costs 675 WITH TRANSACTION COSTS. or sold. CASE PROBLEM PORTFOLIO OPTIMIZATION interpreted as the proportion of the portfolio invested in the asset represented by the variable. portfolio model that incorporates transaction costs. Investors are charged a small transaction the mix of mutual funds in each investor's portfolio by solving an extension of the Markowita cost for the annual rebalancing of their portfolio. For simplicity, assume the following: At the beginning of the time period (in this case one year), the portfolio is rebalanced by buying and selling Hauck mutual funds. The transaction costs associated with buying and selling mutual funds are paid at the beginning of the period when the portfolio is rebalanced, which, in effect, reduces the amount of money available to reinvest. No further transactions are made until the end of the time period, at which point the new value of the portfolio is observed. The transaction cost is a linear function of the dollar amount of mutual funds bought Jean Delgado is one of Hauck's buy-and-hold clients. We briefly describe the model as it is used by Hauck for rebalancing her portfolio. The mix of mutual funds that are being con Asidered for her portfolio are a foreign stock fund (FS), an intermediate-term bond fund (IB),a GOLOB large-cap growth fund (LG), a large-cap value fund (LV), a small-cap growth fund (SG), and a small-cap value fund (SV). In the traditional Markowitz model, the variables are usually For example, FS is the proportion of the portfolio invested in the foreign stock fund. How- ever, it is equally correct to interpret FS as the dollar amount invested in the foreign stock fund. Then FS = 25,000 implies that $25,000 is invested in the foreign stock fund. Based on these assumptions, the initial portfolio value must equal the amount of money spent on trans- action costs plus the amount invested in all the assets after rebalancing; that is. Initial portfolio value = amount invested in all assets after rebalancing + transaction costs The extension of the Markowitz model that Hauck uses for rebalancing portfolios requires a balance constraint for each mutual fund. This balance constraint is U Amount invested in fund i = initial holding of fund i + amount of fund i purchased - amount of fund i sold Using this balance constraint requires three additional variables for each fund: one for the amount invested prior to rebalancing, one for the amount sold, and one for the amount purchased. For instance, the balance constraint for the foreign stock fund is FS = FS_START + FS_BUY - FS_ SELL Jean Delgado has $100,000 in her account prior to the annual rebalancing, and she has specified a minimum acceptable return of 10%. Hauck plans to use the following model to rebalance Ms. Delgado's portfolio. The complete model with transaction costs is Min (R, - R2 s.t. 0.1006F5 + 0.17641B + 0.3241LG + 0.3236LV + 0,3344SG + 0.2456SV = R, 0.1312FS + 3.25001B + 0.1871LG + 0.2061LV + 0.1940SG + 0.25325V = R, 0.1347FS + 0.07511B + 0.3328LG + 0.1293LV + 0.3850SG - 0.0670SV = R 0.4542FS - 0.01331B + 0.4146LG + 0.07062V + 0.58685G + 0.05438V = R. -0.2193FS + 0,07361B 0.2326LG - 0.0537LV 0.0902SG + 0.17315V = R Chapter 14 Nonlinear Optimization Models R 10.000 FS + B + LG + LV + SG + SV + TRANS_COST = 100,000 FS_START + FS_BUY - FS_SELL = FS IB_START + 1B_BUY - IB_SELL = IB LG_START + LG_BUY - LG_SELL = LG LV_START + LV_BUY - LV_SELL = LV SG_START + SG_BUY-SG_SELL = SG SV_START + SV_BUY - SV_SELL = SV TRANS_FEE * (FS_BUY + FS_SELL + IB_BUY + IB_SELL + LG_BUY + LG_SELL + LV_BUY + LV_SELL + SG_BUY + SG_SELL + SV_BUY + SV_SELL) = TRANS_COST FS_START = 10,000 IB_START = 10,000 LG START = 10,000 LV_START = 40,000 SG_START = 10,000 SV_START = 20,000 TRANS_FEE = 0.01 FS, IB, LG, LV, SG, SV > 0 Notice that the transaction fee is set at 1% in the model (the last constraint) and that the transaction cost for buying and selling shares of the mutual funds is a linear function of the amount bought and sold. With this model, the transaction costs are deducted from the cli- ent's account at the time of rebalancing and thus reduce the amount of money invested. The solution for Ms. Delgado's rebalancing problem is shown as part of the Managerial Report Managerial Report Assume that you are a financial analytics specialist newly hired by Hauck Financial Services. One of your first tasks is to review the portfolio rebalancing model in order to resolve a dispute with Jean Delgado. Ms. Delgado has had one of the Hauck passively managed portfolios for the past five years and has complained that she is not getting the rate of return of 10% that she specified. After reviewing her annual statements for the past five years, she feels that she is actually getting less than 10% on average. 1. According to the following Model Solution, IB_BUY = $41,268.51. How much in transaction costs did Ms. Delgado pay for purchasing additional shares of the inter- mediate-term bond fund? 2. Based on the Model Solution, what is the total transaction cost associated with rebalancing Ms. Delgado's portfolio? 3. After paying transactions costs, how much did Ms. Delgado have invested in mutual funds after her portfolio was rebalanced? 4. According to the Model Solution, IB = $51,268.51. How much can Ms. Delgado expect to have in the intermediate-term bond fund at the end of the year? 5. According to the Model Solution, the expected return of the portfolio is $10,000. What is the expected dollar amount in Ms. Delgado's portfolio at the end of the year? Can she expect to earn 10% on the $100,000 she had at the beginning of the year? Case Problem: Portfolio Optimization with Transaction Costs 677 MODEL SOLUTION Optimal Objective Value 27219457.356 Variable R R R2 RE RA RS FS IB LG LV SG SV TRANS_COST FS_START FS_BUY FS_SELL Value 18953.280 10000.000 11569.210 5663.961 9693.921 4119.631 15026.860 51268.510 4939.312 0.000 0.000 27675.000 1090.311 10000.000 5026.863 0.000 Variable IB_START IB_BUY IB_SELL LG_START LG_BUY LG_SELL LV_START LV_BUY LV_SELL SG_START SG_BUY SG_SELL SV_START SV_BUY SV_SELL TRANS_FEE Value 10000.000 41268.510 0.000 10000.000 0.000 5060.688 40000.000 0.000 40000.000 10000.000 0.000 10000.000 20000.000 7675.004 0.000 0.010 6. It is now time to prepare a report to management to explain why Ms. Delgado did not earn 10% each year on her investment. Make a recommendation in terms of a revised portfolio model that can be used so that Jean Delgado can have an expected portfolio balance of $110,000 at the end of next year. Prepare a report that includes a modified optimization model that will give an expected return of 10% on the amount of money available at the beginning of the year before paying the transac- tion costs. Explain why the current model does not do this. 7. Solve the formulation in part (6) for Jean Delgado. How does the portfolio compo- sition differ from that of the Model Solution? Hauck Financial Services has a number of passive, buy-and-hold clients. For these clients, Hauck offers an investment account whereby clients agree to put their money into a portfolio of mutual funds that is rebalanced once a year. When the rebalancing occurs, Hauck determines Case Problem: Portfolio Optimization with Transaction Costs 675 WITH TRANSACTION COSTS. or sold. CASE PROBLEM PORTFOLIO OPTIMIZATION interpreted as the proportion of the portfolio invested in the asset represented by the variable. portfolio model that incorporates transaction costs. Investors are charged a small transaction the mix of mutual funds in each investor's portfolio by solving an extension of the Markowita cost for the annual rebalancing of their portfolio. For simplicity, assume the following: At the beginning of the time period (in this case one year), the portfolio is rebalanced by buying and selling Hauck mutual funds. The transaction costs associated with buying and selling mutual funds are paid at the beginning of the period when the portfolio is rebalanced, which, in effect, reduces the amount of money available to reinvest. No further transactions are made until the end of the time period, at which point the new value of the portfolio is observed. The transaction cost is a linear function of the dollar amount of mutual funds bought Jean Delgado is one of Hauck's buy-and-hold clients. We briefly describe the model as it is used by Hauck for rebalancing her portfolio. The mix of mutual funds that are being con Asidered for her portfolio are a foreign stock fund (FS), an intermediate-term bond fund (IB),a GOLOB large-cap growth fund (LG), a large-cap value fund (LV), a small-cap growth fund (SG), and a small-cap value fund (SV). In the traditional Markowitz model, the variables are usually For example, FS is the proportion of the portfolio invested in the foreign stock fund. How- ever, it is equally correct to interpret FS as the dollar amount invested in the foreign stock fund. Then FS = 25,000 implies that $25,000 is invested in the foreign stock fund. Based on these assumptions, the initial portfolio value must equal the amount of money spent on trans- action costs plus the amount invested in all the assets after rebalancing; that is. Initial portfolio value = amount invested in all assets after rebalancing + transaction costs The extension of the Markowitz model that Hauck uses for rebalancing portfolios requires a balance constraint for each mutual fund. This balance constraint is U Amount invested in fund i = initial holding of fund i + amount of fund i purchased - amount of fund i sold Using this balance constraint requires three additional variables for each fund: one for the amount invested prior to rebalancing, one for the amount sold, and one for the amount purchased. For instance, the balance constraint for the foreign stock fund is FS = FS_START + FS_BUY - FS_ SELL Jean Delgado has $100,000 in her account prior to the annual rebalancing, and she has specified a minimum acceptable return of 10%. Hauck plans to use the following model to rebalance Ms. Delgado's portfolio. The complete model with transaction costs is Min (R, - R2 s.t. 0.1006F5 + 0.17641B + 0.3241LG + 0.3236LV + 0,3344SG + 0.2456SV = R, 0.1312FS + 3.25001B + 0.1871LG + 0.2061LV + 0.1940SG + 0.25325V = R, 0.1347FS + 0.07511B + 0.3328LG + 0.1293LV + 0.3850SG - 0.0670SV = R 0.4542FS - 0.01331B + 0.4146LG + 0.07062V + 0.58685G + 0.05438V = R. -0.2193FS + 0,07361B 0.2326LG - 0.0537LV 0.0902SG + 0.17315V = R Chapter 14 Nonlinear Optimization Models R 10.000 FS + B + LG + LV + SG + SV + TRANS_COST = 100,000 FS_START + FS_BUY - FS_SELL = FS IB_START + 1B_BUY - IB_SELL = IB LG_START + LG_BUY - LG_SELL = LG LV_START + LV_BUY - LV_SELL = LV SG_START + SG_BUY-SG_SELL = SG SV_START + SV_BUY - SV_SELL = SV TRANS_FEE * (FS_BUY + FS_SELL + IB_BUY + IB_SELL + LG_BUY + LG_SELL + LV_BUY + LV_SELL + SG_BUY + SG_SELL + SV_BUY + SV_SELL) = TRANS_COST FS_START = 10,000 IB_START = 10,000 LG START = 10,000 LV_START = 40,000 SG_START = 10,000 SV_START = 20,000 TRANS_FEE = 0.01 FS, IB, LG, LV, SG, SV > 0 Notice that the transaction fee is set at 1% in the model (the last constraint) and that the transaction cost for buying and selling shares of the mutual funds is a linear function of the amount bought and sold. With this model, the transaction costs are deducted from the cli- ent's account at the time of rebalancing and thus reduce the amount of money invested. The solution for Ms. Delgado's rebalancing problem is shown as part of the Managerial Report Managerial Report Assume that you are a financial analytics specialist newly hired by Hauck Financial Services. One of your first tasks is to review the portfolio rebalancing model in order to resolve a dispute with Jean Delgado. Ms. Delgado has had one of the Hauck passively managed portfolios for the past five years and has complained that she is not getting the rate of return of 10% that she specified. After reviewing her annual statements for the past five years, she feels that she is actually getting less than 10% on average. 1. According to the following Model Solution, IB_BUY = $41,268.51. How much in transaction costs did Ms. Delgado pay for purchasing additional shares of the inter- mediate-term bond fund? 2. Based on the Model Solution, what is the total transaction cost associated with rebalancing Ms. Delgado's portfolio? 3. After paying transactions costs, how much did Ms. Delgado have invested in mutual funds after her portfolio was rebalanced? 4. According to the Model Solution, IB = $51,268.51. How much can Ms. Delgado expect to have in the intermediate-term bond fund at the end of the year? 5. According to the Model Solution, the expected return of the portfolio is $10,000. What is the expected dollar amount in Ms. Delgado's portfolio at the end of the year? Can she expect to earn 10% on the $100,000 she had at the beginning of the year? Case Problem: Portfolio Optimization with Transaction Costs 677 MODEL SOLUTION Optimal Objective Value 27219457.356 Variable R R R2 RE RA RS FS IB LG LV SG SV TRANS_COST FS_START FS_BUY FS_SELL Value 18953.280 10000.000 11569.210 5663.961 9693.921 4119.631 15026.860 51268.510 4939.312 0.000 0.000 27675.000 1090.311 10000.000 5026.863 0.000 Variable IB_START IB_BUY IB_SELL LG_START LG_BUY LG_SELL LV_START LV_BUY LV_SELL SG_START SG_BUY SG_SELL SV_START SV_BUY SV_SELL TRANS_FEE Value 10000.000 41268.510 0.000 10000.000 0.000 5060.688 40000.000 0.000 40000.000 10000.000 0.000 10000.000 20000.000 7675.004 0.000 0.010 6. It is now time to prepare a report to management to explain why Ms. Delgado did not earn 10% each year on her investment. Make a recommendation in terms of a revised portfolio model that can be used so that Jean Delgado can have an expected portfolio balance of $110,000 at the end of next year. Prepare a report that includes a modified optimization model that will give an expected return of 10% on the amount of money available at the beginning of the year before paying the transac- tion costs. Explain why the current model does not do this. 7. Solve the formulation in part (6) for Jean Delgado. How does the portfolio compo- sition differ from that of the Model Solution









