Question: I need your help to answer these MCQs Pls. 11. The TVC of producing 2 units of output is $16. The TVC of producing 3
I need your help to answer these MCQs Pls.

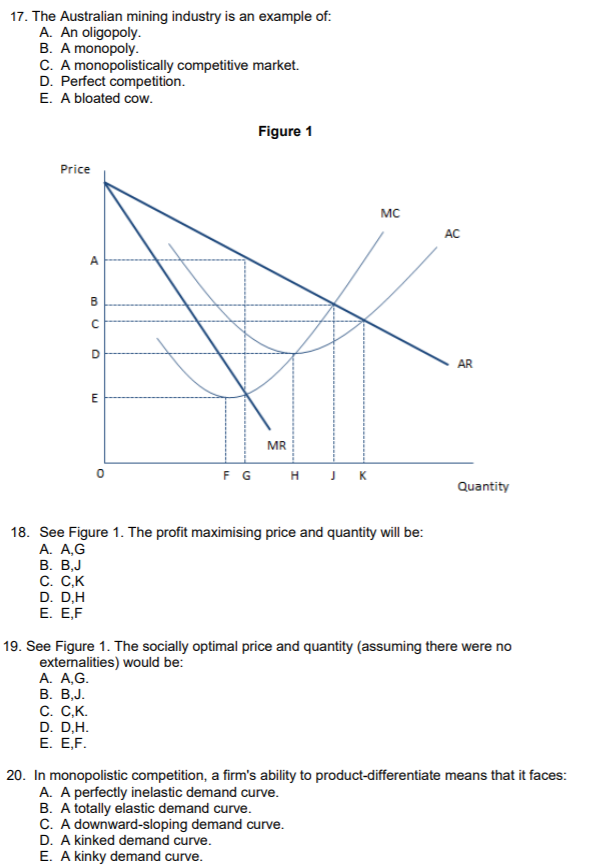



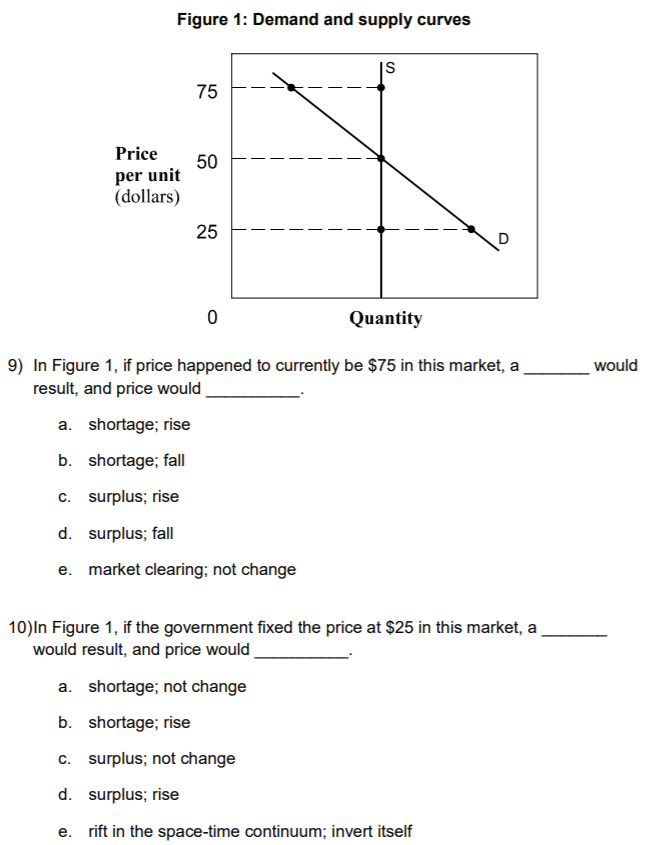



11. The TVC of producing 2 units of output is $16. The TVC of producing 3 units of output is $20. The TVC of producing 4 units of output is $25. The MC of the third unit of output is: A. $36. B. $20. C. $5. D. $4. E. Impossible to calculate because TC is unknown. 12. If a firm has total revenue of $100 zillion, explicit costs of $60 zillion and implicit costs of $10 zillion, its accounting profit is: A. $0. B. $10 zillion. C. $30 zillion. D. $40 zillion. E. $60 zillion. 13. Which of the following is true of a firm seeking to maximize profit immediately? It will seek to produce at the point where: A. MR=AC. B. MR=AR. C. MR=MRS. D. MR=MISS. E. MR=MC. 14. When substitutes exist, a monopolist has power to raise price. A. No; infinite. B. More; more. C. Fewer; less. D. More; less. E. More? Less? 15. A monopoly can result because of: A. The exclusive ownership of a vital resource. B. A legal patent over a good is shared with another large firm. C. Government regulations preventing new competitors entering the market. D. Substantial economies of scale. E. A, B, C and D. 16.A natural monopoly describes the situation where: A. Average cost is lower when there is one producer than when there are two or more competitors. B. A single firm produces a natural health-care product that has no good substitutes. C. There are legal barriers to entry. D. An established firm can prevent new firms entering by starting a price war. E. A Lannister always pays his debts.17. The Australian mining industry is an example of: A. An oligopoly. B. A monopoly. C. A monopolistically competitive market. D. Perfect competition. E. A bloated cow. Figure 1 Price MC AC A D AR E MR 0 F G H K Quantity 18. See Figure 1. The profit maximising price and quantity will be: A. A,G B. B,J C. C.K D. D,H E. E,F 19. See Figure 1. The socially optimal price and quantity (assuming there were no externalities) would be: A. A,G. B. B, J. C. C,K. D. D,H. E. E,F. 20. In monopolistic competition, a firm's ability to product-differentiate means that it faces: A. A perfectly inelastic demand curve. B. A totally elastic demand curve. C. A downward-sloping demand curve. D. A kinked demand curve. E. A kinky demand curve.1) What type of economic analysis is limited to non-moral and non-prescriptive claims? a. Macroeconomics. b. Entrepreneurial economics. c. Positive economics. d. Normative economics. e. Microeconomics 2) Macroeconomics deals with the analysis of all of the following questions except: a. why do national economies grow. b. what determines a nation's savings and investments. c. how does a central bank inuence ination. d. why does a country experience recessions. e. how does Microsoft price its software packages. 3) The opportunity cost of your university education is: a. c and d. b. d and e. c. the actual dollar cost of your education. d. your best alternative use of the money you spend for an education. e. money you could have earned working instead of going to university. 4) Sami decides to work at a supermarket five hours the night before her economics exam. She earns an extra $75, but her exam score is 10 points lower than it would have been had she stayed home and studied. Her opportunity cost of working at the supermarket is the: a. five hours she worked. b. $75 she earned. c. 10 points she lost on her exam. d. time she could have spent watching television. e. guilt she undoubtedly feels about neglecting her economics studies. 5) Assuming that rugby league and rugby union football give very similar experiences to spectators, an increase in the ticket price for rugby league football, other things being equal, will: a. increase the demand for rugby union football tickets. b. decrease the demand for rugby union football tickets. c. not change the demand for rugby union football tickets. d. decrease the demand for rugby league football tickets. e. increase the demand for chess match tickets in Thailand. 6) Two goods, X and Y, are complementary goods if the demand for X a. increases when the price of Y increases. b. increases when income increases. c. decreases when the price of Y increases. d. increases as the price of its substitute good increases. e. decreases as the price of its substitute good decreases.7) if consumer incomes go up and Harley Davidson motorcycles are a normal good, the effect on the demand for these motorcycles, ceteris paribus, will be a (an): a. upward movement along the demand curve for Harley Davidsons. b. downward movement along the demand curve for Harley Davidsons. c. rightward shill? in the demand curve for Harley Davidsons. d. leftward shift in demand for Sons of Anarchy DVDs- e. leftward shift in the demand curve for Harley Davidsons. 8) It is widely reported that the price of houses in Sydney will increase signicantly over the next six months. Assuming this is the only factor which has changed in the housing market, one would predict that: a. house prices will rise because demand will decrease and supply will decrease. b. house prices will fall because demand will increase and supply will decrease. c. house prices will move chaotically because the future is unknowable. d. house prices will rise because demand will increase and supply will decrease. e. house prices will fall because demand will increase and supply will increase. Figure 1: Demand and supply curves S 75 Price per unit 50 (dollars) 25 0 Quantity 9) In Figure 1, if price happened to currently be $75 in this market, a would result, and price would a. shortage; rise b. shortage; fall c. surplus; rise d. surplus; fall e. market clearing; not change 10) In Figure 1, if the government fixed the price at $25 in this market, a would result, and price would a. shortage; not change b. shortage; rise c. surplus; not change d. surplus; rise e. rift in the space-time continuum; invert itself11)lf the demand price elasticity coefficient {in absolute terms) equals 2, this implies that consumers would: a. buy twice as much of the product if the price drops 10 percent. b. require a 2 percent drop in price to increase their purchases by 1 percent. c. buy 2 percent more of the product in response to a 1 percent drop in d. require at least a $2 increase in price before showing an}!r response. e. buy twice as much of the product if the price drops 1 percent. 12}An economist left her $100,000-a-year teaching position to work full-time in her own consulting business. In the rst year, she had total revenue of $200,000 and business expenses of $100,000. She made a (an): a. economic prot. b. economic loss. c. implicit prot. d. accounting loss but not an economic loss. e. zero economic prot. 13)During the course of a week, McDonald's has enough time to hire or layoff workers, but it does not have enough time to expand its kitchen or add an additional seating area. In this situation, McDonald's: a. has no fixed costs. b. is doomed to bankruptcy in the long run. c. suffers an economic loss. d. earns a large prot. e. is in the short mn. 14) If the marginal cost of a firm rises in the short run, this is because of: a. the law of diminishing marginal utility. b. the Galilean law of fall. c. the law of supply and demand. d. the law of diminishing marginal returns to variable inputs. e. the long run. 15) In the long run, total fixed cost: a. falls. b. rises. C. is constant. d. does not exist. e. falls then rises in a U shape. 16) Market structure describes which of the following characteristics? a. The ease of entry into the market. b. The ease of exit from the market. C. The similarity of the product sold. d. The number of firms in each industry. e. All of the above are true. 17)Which of the following is always true for a pure monopolist? a. The firm has a perfectly elastic demand curve. b. The firm will always earn an economic profit. C. The demand curve is above the marginal revenue curve. d. The firm will be regulated by the government. e. None of the above.18) Bunnings hardware stores buy their goods in 'bulk' quantities and therefore at lower prices than otherwise. Also, Bunnings usually locates its stores outside of the community business district on large, relatively cheap blocks of land. Many customers shop at Bunnings because of low prices and free parking. Local small hardware stores have slowly gone out of business because they have lost customers to Bunnings. This story demonstrates that: a. consumers are boycotting local hardware stores. b. Bunnings engages in illegal acts of monopolization. c. there are substantial diseconomies of scale in this industry. d. Bunnings is taking advantage of economies of scale. e. Bunnings is managed by unusually ruthless business people. 19) The cafe industry in Sydney is an illustration of: a. perfect competition. b. monopoly. c. monopolistic competition. d. oligopoly. e. olimonisty. 20)Product differentiation: a. refers to the attempt of firms to make their products look like those of the other firms in the industry. b. refers to the attempt of firms to make essentially substitutable products look different in the minds of the consumers. C. refers to the advantage big firms have in research and development. d. is a common characteristic of a perfectly competitive market structure. e. is only employed in a monopoly market structure
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


