Question: I really need help in writing the code for this class. I DO NOT need the whole class. I ONLY need the equals and toString
I really need help in writing the code for this class. I DO NOT need the whole class. I ONLY need the equals and toString methods in the DoublyLinkedBag class.Thank you!

The code for LinkedBag is as follows:
public class LinkedBag implements BagInterface{
private Node firstNode; // Reference to first node
private int numberOfEntries;
public LinkedBag(){
firstNode = null;
numberOfEntries = 0;
} // end default constructor
/** Sees whether this bag is empty.
* @return True if this bag is empty, or false if not.
* */
public boolean isEmpty(){
return numberOfEntries == 0;
} // end isEmpty
/** Gets the number of entries currently in this bag.
* @return The integer number of entries currently in this bag.
* */
public int getCurrentSize(){
return numberOfEntries;
} // end getCurrentSize
/** Adds a new entry to this bag.
* @param newEntry The object to be added as a new entry
* @return True if the addition is successful, or false if not.
**/
public boolean add(T newEntry) // OutOfMemoryError possible
{
// Add to beginning of chain:
Node newNode = new Node(newEntry);
newNode.next = firstNode; // Make new node reference rest of chain
// (firstNode is null if chain is empty)
firstNode = newNode; // New node is at beginning of chain
numberOfEntries++;
return true;
} // end add
/** Retrieves all entries that are in this bag.
* @return A newly allocated array of all the entries in this bag.
* */
public Object[] toArray() {
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] result = (T[])
new Object[numberOfEntries]; // Unchecked cast
int index = 0;
Node currentNode = firstNode;
while ((index
result[index] = currentNode.data;
index++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} // end while
return result;
} // end toArray
/** Counts the number of times a given entry appears in this bag.
* @param anEntry The entry to be counted.
* @return The number of times anEntry appears in this bag.
* */
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry){
int frequency = 0;
int counter = 0;
Node currentNode = firstNode;
while ((counter
if (anEntry.equals(currentNode.data)){
frequency++;
} // end if
counter++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} // end while
return frequency;
} // end getFrequencyOf
/** Tests whether this bag contains a given entry.
* @param anEntry The entry to locate.
* @return True if the bag contains anEntry, or false otherwise.
* */
public boolean contains(T anEntry){
boolean found = false;
Node currentNode = firstNode;
while (!found && (currentNode != null)){
if (anEntry.equals(currentNode.data))
found = true;
else
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} // end while
return found;
} // end contains
// Locates a given entry within this bag.
// Returns a reference to the node containing the entry, if located,
// or null otherwise.
private Node getReferenceTo(T anEntry){
boolean found = false;
Node currentNode = firstNode;
while (!found && (currentNode != null)){
if (anEntry.equals(currentNode.data))
found = true;
else
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} // end while
return currentNode;
} // end getReferenceTo
/** Removes all entries from this bag. */
public void clear(){
while (!isEmpty())remove();
} // end clear
/** Removes one unspecified entry from this bag, if possible.
* @return Either the removed entry, if the removal
* was successful, or null.
* */
public T remove(){
T result = null;
if (firstNode != null){
result = firstNode.data;
firstNode = firstNode.next; // Remove first node from chain
numberOfEntries--;
} // end if
return result;
} // end remove
/** Removes one occurrence of a given entry from this bag, if possible.
* @param anEntry The entry to be removed.
* @return True if the removal was successful, or false otherwise.
* */
public boolean remove(T anEntry) {
boolean result = false;
Node nodeN = getReferenceTo(anEntry);
if (nodeN != null){
nodeN.data = firstNode.data; // Replace located entry with entry in first node
firstNode = firstNode.next; // Remove first node
numberOfEntries--;
result = true;
} // end if
return result;
} // end remove
private class Node {
private T data; // Entry in bag
private Node next; // Link to next node
private Node(T dataPortion){
this(dataPortion, null);
} // end constructor
private Node(T dataPortion, Node nextNode){
data = dataPortion;
next = nextNode;
} // end constructor
} // end Node
public T replace(T replacement) {
T t = null;
if (!isEmpty()) {
t = firstNode.data;
firstNode.data = replacement;
}
return t;
}
public void removeEvery(T anEntry) {
Node newNode = firstNode;
while(newNode != null) {
if(newNode.data.equals(anEntry)) {
remove(anEntry);
}
newNode = newNode.next;
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
}
} // end LinkedBag
I ONLY need the equals method and the toString in the DoublyLinkedBag class. Both the methods, equals and toString are marked with //TODO
The DoublyLinkedClass is as follows:
public class DoublyLinkedBag implements BagInterface
{
private DoublyLinkedNode firstNode; // Reference to first node
private int numberOfEntries;
public DoublyLinkedBag()
{
} // end default constructor
public boolean add(T newEntry)
{
} // end add
public T[] toArray()
{
} // end toArray
public boolean isEmpty()
{
} // end isEmpty
public int getCurrentSize()
{
} // end getCurrentSize
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry)
{
} // end getFrequencyOf
public boolean contains(T anEntry)
{
} // end contains
public void clear()
{
} // end clear
public T remove()
{
} // end remove
public boolean remove(T anEntry)
{;
} // end remove
public T replace(T replacement)
{
}
public void removeEvery(T anEntry)
{
}
/**
Override the equals method of Object class so that it returns true when the contents of two DoublyLinkedBags are same. Note that two equal DoublyLinkedBags contain the same number of entries, and each entry occurs in each DoublyLinkedBag the same number of times. I.e., the elements in two do not need to be in exact same location.
Before checking the contents inside this method make sure that the passed in object is not null, is of the same runtime class, and the lengths are same. If any of these fail you can return false. Otherwise, you base your return results on contents. (At the start you can also do the quick check if both refer to the same object in memory.)
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
//TODO
}
/**
Returns String representation of the items in this bag.
For example, it would return [A, B, C] if bag had three Strings "A", "B", and "C".
@return String representation of items in this bag enclosed in square brackets, separated by comma and a single space (see example above). You can rely on the fact that items' proper toString method was implemented. In this method ONLY if you need to you can use String class's methods. Also, ONLY in this method you can use fully qualified name for StringBuffer class, and use all of its methods.
*/
@Override
public String toString()
{
//TODO
}
return "[ ]"; // this is returned in case bag is empty.
}
// A class of nodes for a chain of doubly linked nodes.
private class DoublyLinkedNode
{
private T data; // Entry in bag
private DoublyLinkedNode next; // Link to next node
private DoublyLinkedNode prev; // Link to previous node
private DoublyLinkedNode(T dataPortion)
{
this(dataPortion, null, null);
} // end constructor
private DoublyLinkedNode(T dataPortion, DoublyLinkedNode nextNode,
DoublyLinkedNode previousNode)
{
data = dataPortion;
next = nextNode;
prev = previousNode;
} // end constructor
} // end DoublyLinkedNode
} // end DoublyLinkedBag
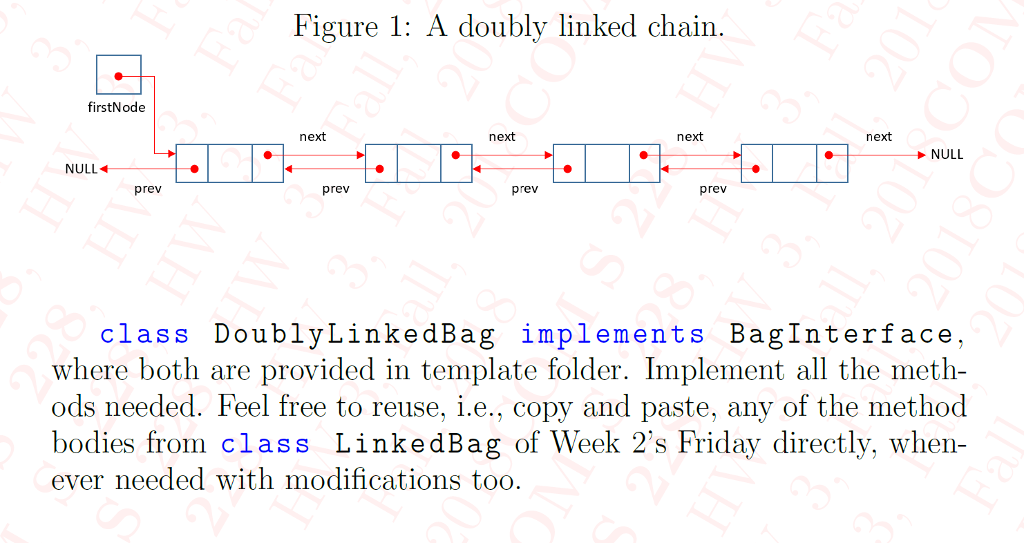
1. Part 1: Doubly Linked Chairn In a doubly linked chain, each node can reference the previous node as well as the next node. Below Figure I shows a doubly linked chain and its head reference
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


