Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i ( want it in hysis only hysis ) don ' t u waste my question Q 1 0 : Consider the problem of diffusion
i want it in hysis only hysisdont u waste my question
Q: Consider the problem of diffusion and reaction in a cylindrical pore eg in a solid catalyst where component A reacts at the walls of the cylinder according to
Where:
order reaction
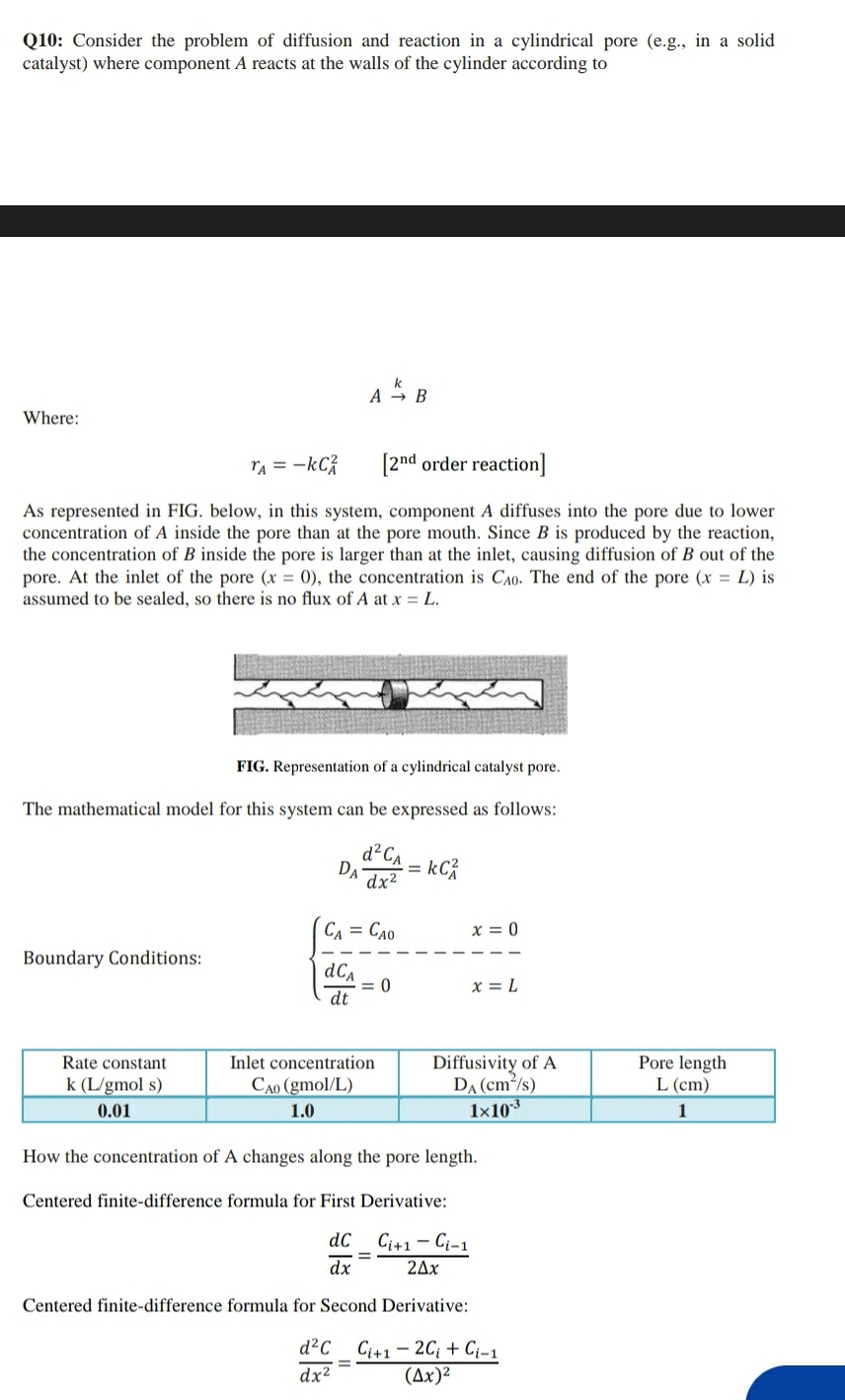
As represented in FIG. below, in this system, component A diffuses into the pore due to lower concentration of A inside the pore than at the pore mouth. Since is produced by the reaction, the concentration of inside the pore is larger than at the inlet, causing diffusion of out of the pore. At the inlet of the pore the concentration is The end of the pore is assumed to be sealed, so there is no flux of at
FIG. Representation of a cylindrical catalyst pore.
The mathematical model for this system can be expressed as follows:
Boundary Conditions:
tabletableRate constantmols
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


