Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I want the solution very quickly, but I do not have time because it is due to the exam Part 2. Select 3 (three) of


I want the solution very quickly, but I do not have time because it is due to the exam
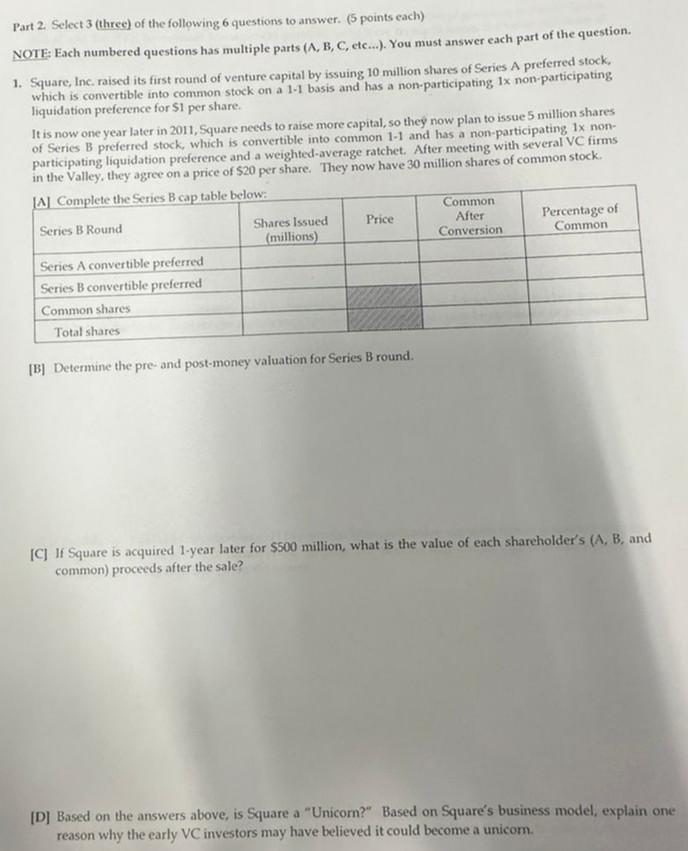
Part 2. Select 3 (three) of the following 6 questions to answer. (5 points each) NOTE: Each numbered questions has multiple parts ( A,B,C, etc...). You must answer each part of the question. 1. Square, Inc, raised its first round of venture capital by issuing 10 million shares of Series A preferred stock, which is convertible into common stock on a 1.1 basis and has a non-participating 1 non-participating liquidation preference for $1 per share. It is now one year later in 2011 , Square needs to raise more capital, so they now plan to issue 5 million shares of Series B preferred stock, which is convertible into common 1-1 and has a non-participating 1 nonparticipating liquidation preference and a weighted-average ratchet. After meeting with several VC firms in the Valley, they agree on a price of $20 per share. They now have 30 million shares of common stock. [B] Determine the pre- and post-money valuation for Series B round. [C] If Square is acquired 1-year later for $500 million, what is the value of each sharcholder's (A, B, and common) proceeds after the sale? [D] Based on the answers above, is Square a "Unicom?" Based on Square's business model, explain one reason why the early VC investors may have believed it could become a unicom. 5. In class, a valuation model for The We Company ahead of its planned IPO was developed. [A] WeWork was described as "tech company that happens to have some real estate on the balance sheet." [A1] Explain one reason that WeWork's business model is similar to a real estate investment trust (REIT). Explain one reason that WeWork's business model is different than a REIT. [A2] Explain one reason that WeWork's business model is similar to a software-as-a-service (SaaS) startup. Explain one reason that WeWork's business model is different from a SaaS firm. [B] In the S-1 offering prospectus, The We Company provided calculations of historical "contribution margins" to help investors forecast future percent profit margins. Explain one reason why this measure may be misleading. [C] In the S-1 offering prospectus, The We Company provided guidance to help investors forecast the total available market (TAM). Explain one reason why their TAM measurement may be misleading. 4. Goodyear eventually offered $54.50 per share to acquire Cooper in a merger. Before the initial announcement, Cooper stock was trading for $40.50 and there were 80 million shares outstanding. In the case study, several reasons were provided by Goodyear to justify this premium. [A] Based on the information in the case, explain how one of the cost synergies was expected to be realized. Explain exactly how this reason can be incorporated into a DCF model. [B] Based on the information in the case, explain how one of the revenue synergies was expected to be realized. Explain exactly how this reason can be incorporated into a DCF model. [C] Based on the information in the case, explain how one of the tax synergies was expected to be realized. Explain exactly how this reason can be incorporated into a DCF model. [D] Based on the information in the case, explain how one of the working capital synergies was expected to be realized. Explain exactly how this reason can be incorporated into a DCF model. [E] Why was the CEO of Cooper willing to be acquired by Goodyear, even though he would lose his job as CEO which paid him over $6 million per yearStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


