Question
I will post the codes to work with at the end of the question. Use C programing globals #define RootProcess 0 int length; int length_per_process;
I will post the codes to work with at the end of the question. Use C programing
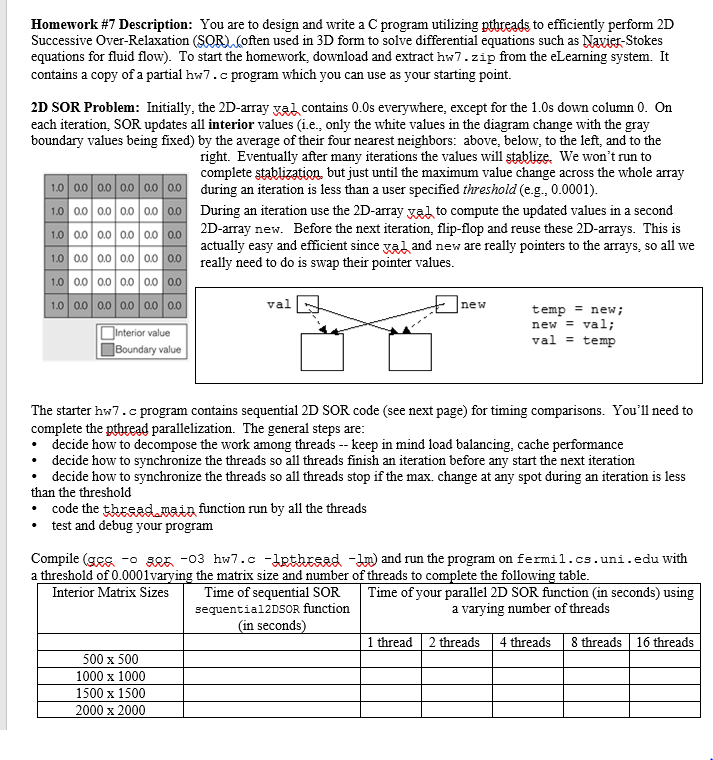

globals
#define RootProcess 0 int length; int length_per_process; int myStart; int myCount=0; int globalCount; MPI_Status status; int tag=1;
hw7.c
/* Programmer: Mark Fienup
File: hw7.c
Compiled by: gcc -o sor -O3 hw7.c -lpthread -lm
Run by: ./sor 1000 0.00001 8
Description: 2D SOR (successive over-relaxation) program written using POSIX threads.
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "timer.h"
#define MAXTHREADS 16 /* Assume max. # threads */
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define BOOL int
double ** allocate2DArray(int rows, int columns);
void print2DArray(int rows, int columns, double ** array2D);
BOOL equal2DArrays(int rows, int columns, double ** array1, double ** array2,
double tolerance);
void * thread_main(void *);
void initializeData(double ** val, int n);
void sequential2D_SOR();
/* BARRIER prototype, mutex, condition variable, if needed */
void barrier();
pthread_mutex_t update_lock;
pthread_mutex_t barrier_lock; /* mutex for the barrier */
pthread_cond_t all_here; /* condition variable for barrier */
int count=0; /* counter for barrier */
/* Global SOR variables */
int n, t;
double threshold;
double **val, **new;
double delta = 0.0;
double deltaNew = 0.0;
/* Command line args: matrix size, threshold, number of threads */
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
/* thread ids and attributes */
pthread_t tid[MAXTHREADS];
pthread_attr_t attr;
long i, j;
float myThreshold;
double startTime, endTime, seqTime, parTime;
/* set global thread attributes */
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setscope(&attr, PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM);
/* initial mutex and condition variable */
pthread_mutex_init(&update_lock, NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&barrier_lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&all_here, NULL);
/* read command line arguments */
if (argc != 4) {
printf("usage: %s
argv[0]);
exit(1);
} // end if
sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &n);
sscanf(argv[2], "%f", &myThreshold);
sscanf(argv[3], "%d", &t);
threshold = (double) myThreshold;
val = allocate2DArray(n+2, n+2);
new = allocate2DArray(n+2, n+2);
initializeData(val, n);
initializeData(new, n);
printf("InitializeData done ");
/* Time sequential SOR */
GET_TIME(startTime);
sequential2D_SOR();
GET_TIME(endTime);
printf("Sequential Time = %1.5f ", endTime-startTime);
printf("maximum difference: %e ", delta);
/* Time parallel SOR using pthreads */
initializeData(val, n);
initializeData(new, n);
GET_TIME(startTime);
for(i=0; i pthread_create(&tid[i], &attr, thread_main, (void *) i); } // end for for (i=0; i pthread_join(tid[i], NULL); } // end for GET_TIME(endTime); printf("Parallel Time with %d threads = %1.5f ", t, endTime-startTime); printf("maximum difference: %e ", delta); } // end main /*********************************************************************** * Function sequential2D_SOR - performs a sequential 2D SOR calculation * using global variables: * val - 2D array initially with all 0.0 except 1.0s along "left" column * "returns" the resulting value * new - 2D array used for storage during each iteration * n - array sizes are n x n * threshold - max. value of all elements between two iterations * delta - returned max. value after last iteration ( **********************************************************************/ void sequential2D_SOR() { double average, maxDelta, thisDelta; double ** temp; int i, j; do { maxDelta = 0.0; for (i = 1; i for (j = 1; j average = (val[i-1][j] + val[i][j+1] + val[i+1][j] + val[i][j-1])/4; thisDelta = fabs(average - val[i][j]); if (maxDelta maxDelta = thisDelta; } // end if new[i][j] = average; // store into new array } // end for j } // end for i temp = new; /* prepare for next iteration */ new = val; val = temp; // printf("maxDelta = %8.6f ", maxDelta); } while (maxDelta > threshold); // end do-while delta = maxDelta; // sets global delta } // end sequential2D_SOR void* thread_main(void * arg) { long id=(long) arg; //ADD CODE HERE FOR PTHREADS TO CALCULATE 2D SOR } // end thread_main /******************************************************************* * Function allocate2DArray dynamically allocates a 2D array of * size rows x columns, and returns it. ********************************************************************/ double ** allocate2DArray(int rows, int columns) { double ** local2DArray; int r; local2DArray = (double **) malloc(sizeof(double *)*rows); for (r=0; r local2DArray[r] = (double *) malloc(sizeof(double)*columns); } // end for return local2DArray; } // end allocate2DArray /******************************************************************* * Function initializeData initializes 2D array for SOR with 0.0 * everywhere, except 1.0s down column 0. ********************************************************************/ void initializeData(double ** array, int n) { int i, j; /* initialize to 0.0 except for 1.0s along the left boundary */ for (i = 0; i array[i][0] = 1.0; } // end for i for (i = 0; i for (j = 1; j array[i][j] = 0.0; } // end for j } // end for i } // end initializeData /******************************************************************* * Function print2DArray is passed the # rows, # columns, and the * array2D. It prints the 2D array to the screen. ********************************************************************/ void print2DArray(int rows, int columns, double ** array2D) { int r, c; for(r = 0; r for (c = 0; c printf("%10.5lf", array2D[r][c]); } // end for (c... printf(" "); } // end for(r... } // end print2DArray /******************************************************************* * Function equal2DArrays is passed the # rows, # columns, two * array2Ds, and tolerance. It returns TRUE if corresponding array * elements are equal within the specified tolerance; otherwise it * returns FALSE. ********************************************************************/ BOOL equal2DArrays(int rows, int columns, double ** array1, double ** array2, double tolerance) { int r, c; for(r = 0; r for (c = 0; c if (fabs(array1[r][c] - array2[r][c]) > tolerance) { return FALSE; } // end if } // end for (c... } // end for(r... return TRUE; } // end equal2DArray /******************************************************************* * Function barrier passed the thread id for debugging purposes. * Implements barrier synchronization using global variables: * count - # of thread that have arrived at the barrier * t - # of threads we are synchronizing * barrier_lock - the mutex ensuring mutual exclusion * all_here - the condition variable where threads wait for all to arrive ********************************************************************/ void barrier(long id) { pthread_mutex_lock(&barrier_lock); count++; // printf("count %d, id %d ", count, id); if (count == t) { count = 0; pthread_cond_broadcast(&all_here); } else { while(pthread_cond_wait(&all_here, &barrier_lock) != 0); } // end if pthread_mutex_unlock(&barrier_lock); } // end barrier seq2DSOR.c /* Programmer: Mark Fienup File: seq2DSOR.c Compiled by: gcc -o seq2DSOR seq2DSOR.c -lpthread -lm Run by: seq2DSOR 5 0.01 Run by: seq2DSOR Description: Sequential 2D over-relaxation program. */ #include #include #include #include #include #include "timer.h" /* Prototypes */ void InitializeData(); void perform2D_SOR(); void printVal(); int n, t; double threshold, delta; double **val, **new; /* Command line args: matrix size, threshold */ int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { long i, j; float myThreshold; double startTime, endTime; /* read command line arguments */ if (argc != 3) { printf("usage: %s argv[0]); exit(1); } // end if sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &n); sscanf(argv[2], "%f", &myThreshold); threshold = (double) myThreshold; InitializeData(); printf("Initialize Data done "); GET_TIME(startTime) /* Use global variables like the pthread verision */ perform2D_SOR(); GET_TIME(endTime); printf("Time = %1.5f ", endTime-startTime); printf("maximum difference: %8.6f ", delta); } // end main void perform2D_SOR() { double average, maxDelta; double thisDelta; double **temp; int i, j; do { maxDelta = 0.0; /* printVal(aaa); */ for (i = 1; i for (j = 1; j average = (val[i-1][j] + val[i][j+1] + val[i+1][j] + val[i][j-1])/4; thisDelta = fabs(average - val[i][j]); if (maxDelta maxDelta = thisDelta; } // end if // store into new array new[i][j] = average; } // end for j } // end for i temp = new; /* prepare for next iteration */ new = val; val = temp; /* printf("maxDelta = %8.6f ", maxDelta); */ } while (maxDelta > threshold); // end do-while delta = maxDelta; // sets global } // end perform2D_SOR void printVal() { int i,j; printf(" *2222********************************************** "); for (i = 0; i for (j = 0; j printf("%7.3f ", val[i][j]); } // end for j printf(" "); } // end for i } // end printVal void InitializeData() { int i, j; new = (double **) malloc((n+2)*sizeof(double *)); val = (double **) malloc((n+2)*sizeof(double *)); for (i = 0; i new[i] = (double *) malloc((n+2)*sizeof(double)); val[i] = (double *) malloc((n+2)*sizeof(double)); } // end for i /* initialize to 0.0 except to 1.0 along the left boundary */ for (i = 0; i val[i][0] = 1.0; new[i][0] = 1.0; } // end for i for (i = 0; i for (j = 1; j val[i][j] = 0.0; new[i][j] = 0.0; } // end for j } // end for i } // end InitializeData timer /* File: timer.h * * Purpose: Define a macro that returns the number of seconds that * have elapsed since some point in the past. The timer * should return times with microsecond accuracy. * * Note: The argument passed to the GET_TIME macro should be * a double, *not* a pointer to a double. * * Example: * #include "timer.h" * . . . * double start, finish, elapsed; * . . . * GET_TIME(start); * . . . * Code to be timed * . . . * GET_TIME(finish); * elapsed = finish - start; * printf("The code to be timed took %e seconds ", elapsed); * * IPP: Section 3.6.1 (pp. 121 and ff.) and Section 6.1.2 (pp. 273 and ff.) */ #ifndef _TIMER_H_ #define _TIMER_H_ #include /* The argument now should be a double (not a pointer to a double) */ #define GET_TIME(now) { \ struct timeval t; \ gettimeofday(&t, NULL); \ now = t.tv_sec + t.tv_usec/1000000.0; \ } #endif
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


