Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I will provide the code of the Vertex Coloring Algorithm and i need description of high level design with FSM diagrams and FSM table.And either
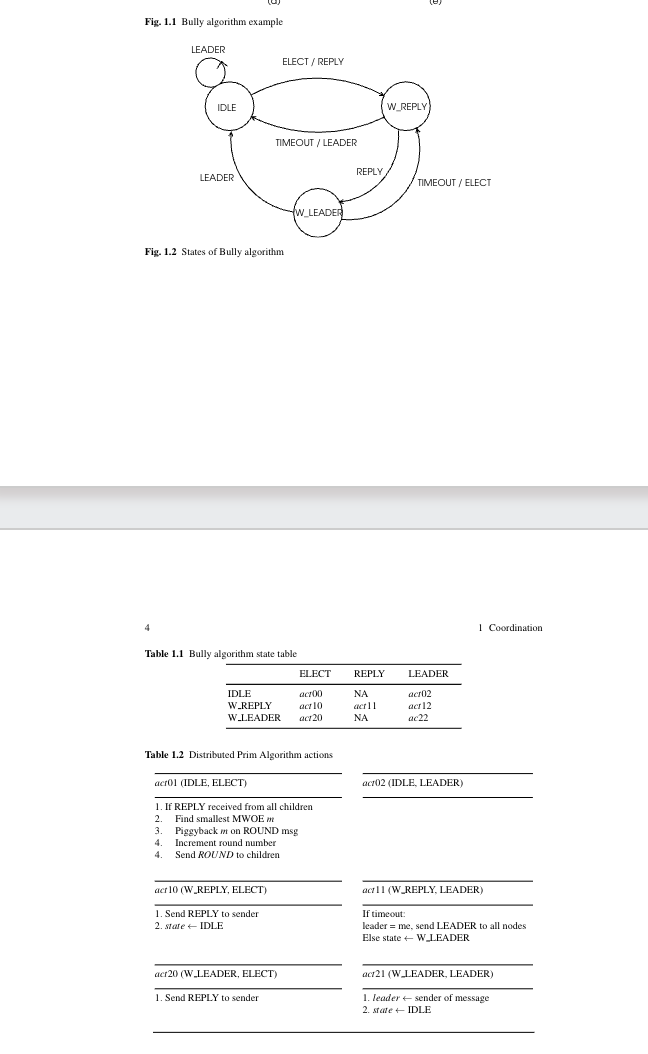
I will provide the code of the Vertex Coloring Algorithm and i need description of high level design with FSM diagrams and FSM table.And either give the pseudocode of actions or the pseudocode of the whole algorithm.The pictures are about Bully Algorithm. What i want is the same version of the FSM and FSM table of Vertex Coloring Algorithm that i will provide.
from mpipy import MPI
import numpy as np
# MPI setup
comm MPI.COMMWORLD
rank comm.Getrank
n comm.Getsize
# Message types
IDLE
COLORED
TERMINATE
ROUND
UPDATE
ACK
DISCARD
ROVER
TERMINATE
# Spanning tree of graph
ROOT
A nparray
dtypeint
children
parents
# Process state and communication variables
state IDLE
parent parentsrank
childs setchildrenrank
neighs indicesset seti for i value in enumerateArank if value
nneighs neighs.copy
neighsreceived set
roversreceived set
roundreceived False
color
bannedcolors set
msg None # sender type, data
round False # round number, round over
# Function to find the smallest available color
def findsmallestavailablecolor:
global bannedcolors
candidatecolor
while candidatecolor in bannedcolors:
candidatecolor
return candidatecolor
# Function to check if the process has the highest degree in not colored neighbors
def highestdegreeinnotcoloredneighbors:
global nneighs
return not nneighs or rank maxnneighs
while state TERMINATE:
round False
neighsreceived.clear
roversreceived.clear
roundreceived False
if rank :
if state COLORED:
termmsg msgcopy
termmsg termmsg rank, TERMINATE
comm.sendobjtermmsg destROOT, tagTERMINATE
else:
round
roundmsg msgcopy
roundmsg roundmsg roundmsg rank, ROUND, round
comm.sendobjroundmsg destROOT, tagROUND
while not round:
sendertype, data comm.recv
if type ROUND:
round data
roundmsg msgcopy
roundmsg roundmsg roundmsg rank, ROUND, data
for child in childs:
comm.sendobjroundmsg destchild, tagROUND
if state COLORED:
discardmsg msgcopy
discardmsg discardmsg rank, DISCARD
for neigh in neighs:
comm.sendobjdiscardmsg destneigh, tagDISCARD
else:
if highestdegreeinnotcoloredneighbors:
color findsmallestavailablecolor
state COLORED
updatemsg msgcopy
updatemsg updatemsg updatemsg rank, UPDATE, color for neigh in nneighs:
comm.sendobjupdatemsg destneigh, tagUPDATE
else:
discardmsg msgcopy
discardmsg discardmsg rank, DISCARD
for neigh in neighs:
comm.sendobjdiscardmsg destneigh, tagDISCARD
roundreceived True
elif type UPDATE:
neighsreceived.addsender
ackmsg msgcopy
ackmsg ackmsg rank, ACK
comm.sendobjackmsg destsender tagACK
if state COLORED:
nneighs.removesender
bannedcolors.adddata
elif type DISCARD:
neighsreceived.addsender
elif type ACK:
neighsreceived.addsender
elif type ROVER:
roversreceived.addsender
elif type TERMINATE:
if childs:
for child in childs:
termmsg msgcopy
termmsg termmsg rank, TERMINATE
state TERMINATE
break
# Check conditions for round completion
if roundreceived and neighs.issubsetneighsreceived and lenchilds lenroversreceived:
rovermsg msgcopy
rovermsg rovermsg rank, ROVER
comm.sendobjrovermsg destparent, tagROVER
round True
printfI am rank rank and my color colorFig Bully algorithm example
I
Table Bully algorithm state table
Table Distributed Prim Algo
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


