Question
**************************************If graphs are blurry, please zoom in or save to the computer. They will be clear when you do that Note: I'm sorry in advance
**************************************If graphs are blurry, please zoom in or save to the computer. They will be clear when you do that
Note: I'm sorry in advance if the picture appears small or blurry. If you right click to save the image to your computer, it will be much larger and clearer. Alternatively, you can use the "zoom" feature in Google Chrome and it will look clearer. Thanks in advance!
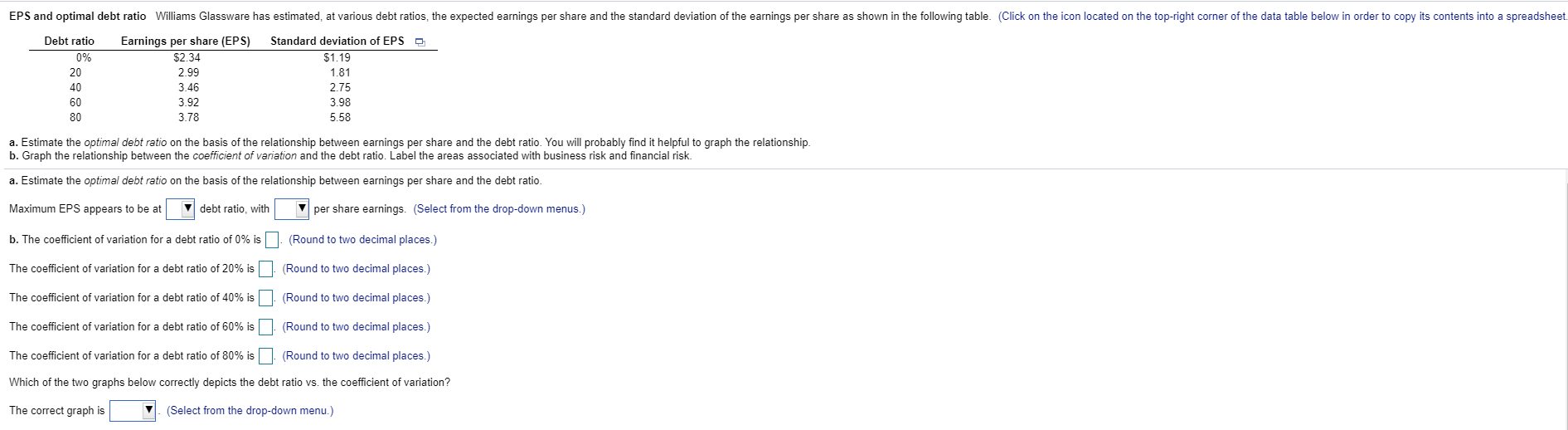
Also, the drop-down options for part A are: 0%/20%/40%/60%/80% and $2.34/$2.99/$3.46/$3.92/$3.78
The last drop down above the graphs has options: Graph 1 and Graph 2.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


