Read the case and follow instructions to complete the assignment. Windward manufactures one product. The table below displays the weekly production costs. The managerial
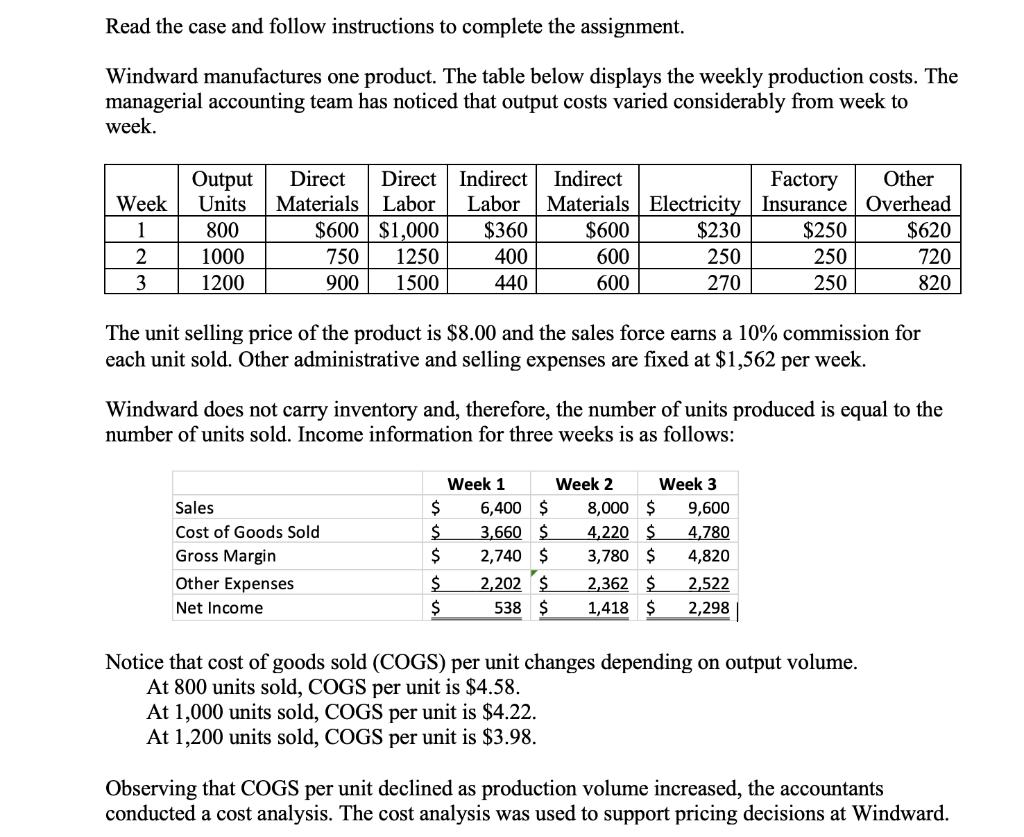



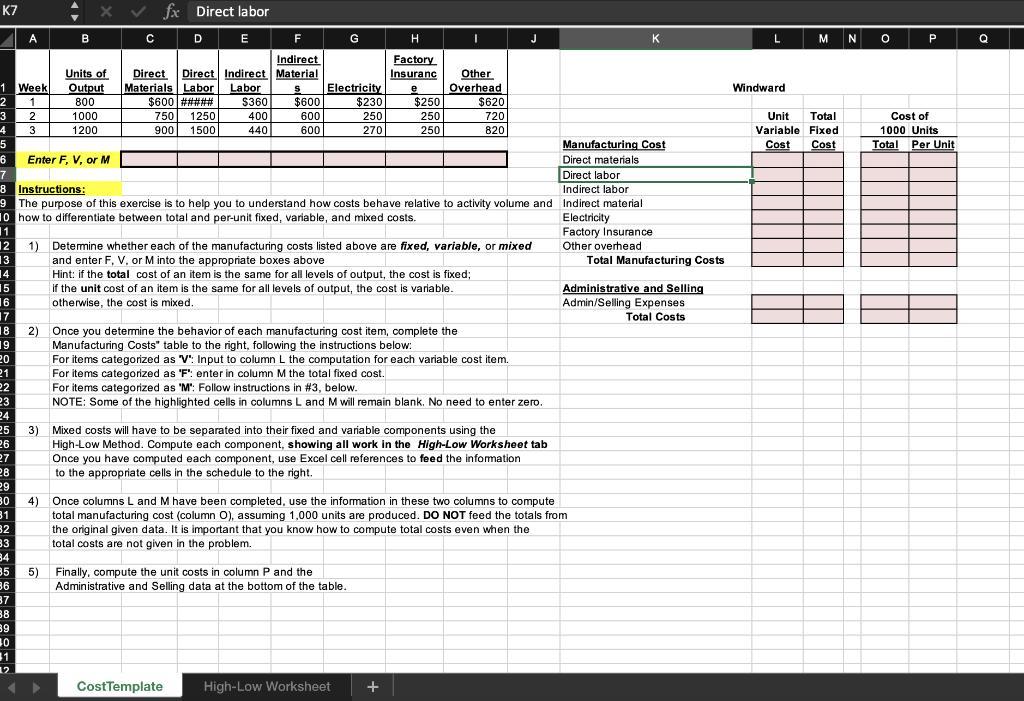
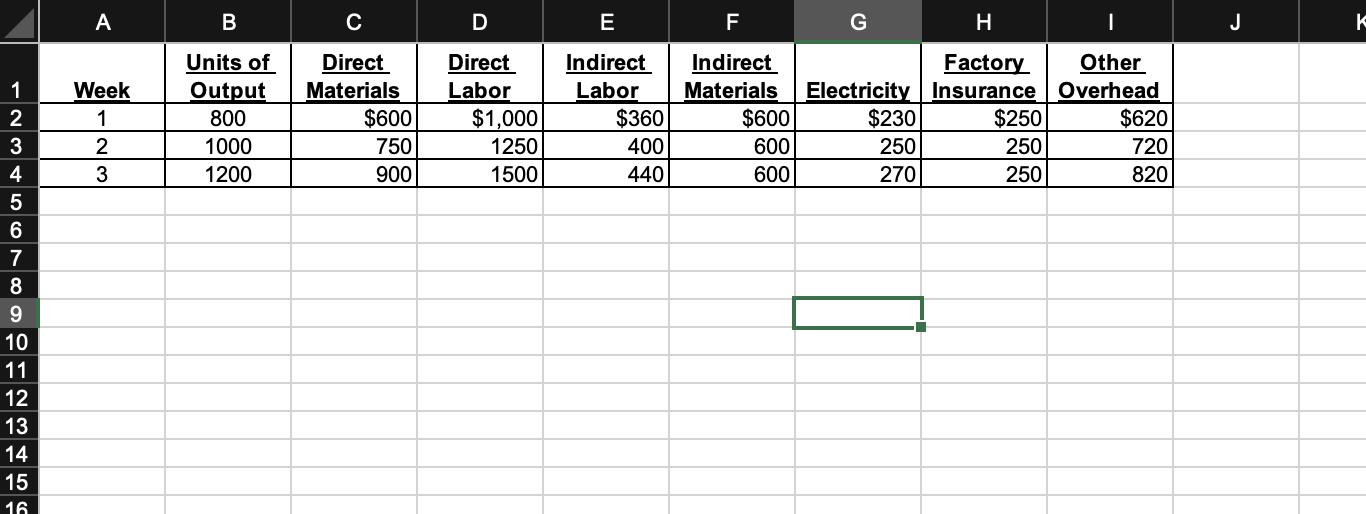
Read the case and follow instructions to complete the assignment. Windward manufactures one product. The table below displays the weekly production costs. The managerial accounting team has noticed that output costs varied considerably from week to week. Output Direct Direct Indirect Indirect Factory Other Week Units Materials Labor Labor Materials Electricity Insurance Overhead 1 800 $600 $1,000 $360 2 1000 1250 400 750 900 1500 3 1200 440 Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Margin Other Expenses Net Income $ $ $ The unit selling price of the product is $8.00 and the sales force earns a 10% commission for each unit sold. Other administrative and selling expenses are fixed at $1,562 per week. $ $ Windward does not carry inventory and, therefore, the number of units produced is equal to the number of units sold. Income information for three weeks is as follows: Week 1 $600 600 600 6,400 $ 3,660 $ 2,740 $ 2,202 $ 538 $ Week 2 $230 250 270 8,000 $ 4,220 $ 3,780 $ 2,362 $ 1,418 $ Week 3 9,600 $250 250 250 4,780 4,820 2,522 2,298 $620 720 820 Notice that cost of goods sold (COGS) per unit changes depending on output volume. At 800 units sold, COGS per unit is $4.58. At 1,000 units sold, COGS per unit is $4.22. At 1,200 units sold, COGS per unit is $3.98. Observing that COGS per unit declined as production volume increased, the accountants conducted a cost analysis. The cost analysis was used to support pricing decisions at Windward. An average production volume over the three weeks was used to determine the cost of production, which was $6.58 per unit. The per-unit cost was also assumed to be the break-even cost, which was used to create guidelines for the sales force. -2- Instructions: 1. Complete the highlighted items in the Excel Template, following the directions provided in the worksheet. Use Excel formulas to compute your answers. Credit cannot be awarded if the formulas are not included. 2. Use the amounts you computed in the Excel Template to complete items (a) through (h): a) The variable manufacturing cost per unit for this product is b) The total variable cost per unit for this product is c) The total fixed manufacturing cost for this product is d) The total fixed cost for this product is e) The total manufacturing cost when 1,000 units are produced is f) The total cost when 1,000 units are produced is g) The manufacturing cost per unit when 1,000 units are produced is h) The total cost per unit when 1,000 units are produced is Answer each of the following questions (show your computations and formulas directly under each question): 3. How many units does Windward need to sell to break even? Show the formula to compute break-even and show all your computations. 4. Assume the office manager received a call from a customer who wanted to purchase 100 units of product (no sales commission on this order). What is the per-unit profit contributed by the sale of these additional 100 units (assume break-even point has already been reached by the sales team)? Show your computations and explain your answer. 5. Suppose a loyal customer requested to place a special order to buy 100 units at $5.50 per unit. This is a one-time only order, Windward has the capacity to fill this order, and by filling the order no other regular order will go unfilled. No sales commission on special order; assume BEP has already been met. a) What would be the per-unit profit or loss associated with this order? Show your computations. b) Is there an opportunity cost associated with accepting this order? Explain. c) Would you fill this order if you were the manager? Why? 6. Describe each team member's contribution to the case analysis. 7. What did you learn about relevant costs for decision making from completing this case? (Each member of the team must contribute a paragraph to this answer. Include your name at the end of your paragraph.) K7 1 Week 2 1 3 4 5 6 27 28 29 30 31 32 83 34 35 36 37 A 38 39 2 3 30 31 12 B Enter F, V, or M Units of Output 800 1000 1200 4) fx Direct labor DE 5) C F Indirect Direct Direct Indirect Material Materials Labor Labor $600 ##### $360 400 750 1250 900 1500 440 Manufacturing Cost Direct materials 7 Direct labor Indirect labor 8 Instructions: 9 The purpose of this exercise is to help you to understand how costs behave relative to activity volume and Indirect material 10 how to differentiate between total and per-unit fixed, variable, and mixed costs. Electricity Factory Insurance Other overhead 1 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 3) Mixed costs will have to be separated into their fixed and variable components using the 26 S Electricity $600 600 600 G $230 250 270 H Factory Insuranc Other e 1) Determine whether each of the manufacturing costs listed above are fixed, variable, or mixed and enter F, V, or M into the appropriate boxes above Hint: if the total cost of an item is the same for all levels of output, the cost is fixed; $250 250 250 Finally, compute the unit costs in column P and the Administrative and Selling data at the bottom of the table. CostTemplate I if the unit cost of an item is the same for all levels of output, the cost is variable. otherwise, the cost is mixed. 2) Once you determine the behavior of each manufacturing cost item, complete the Manufacturing Costs" table to the right, following the instructions below: For items categorized as "V": Input to column L the computation for each variable cost item. For items categorized as 'F': enter in column M the total fixed cost. For items categorized as "M": Follow instructions in #3, below. NOTE: Some of the highlighted cells in columns L and M will remain blank. No need to enter zero. Overhead $620 720 820 High-Low Worksheet J High-Low Method. Compute each component, showing all work in the High-Low Worksheet tab Once you have computed each component, use Excel cell references to feed the information to the appropriate cells in the schedule to the right. + Once columns L and M have been completed, use the information in these two columns to compute total manufacturing cost (column O), assuming 1,000 units are produced. DO NOT feed the totals from the original given data. It is important that you know how to compute total costs even when the total costs are not given in the problem. K Total Manufacturing Costs Administrative and Selling Admin/Selling Expenses Total Costs L M N O Windward Unit Total Variable Fixed Cost Cost P Cost of 1000 Units Total Per Unit Q INSSON SHEE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 A Week 1 2 3 B Units of Output 800 1000 1200 C Direct Materials $600 750 900 D Direct Labor $1,000 1250 1500 E Indirect Labor $360 400 440 F H | Indirect Factory Other Materials Electricity Insurance Overhead $600 600 600 G $230 250 270 $250 250 250 $620 720 820 J k
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


