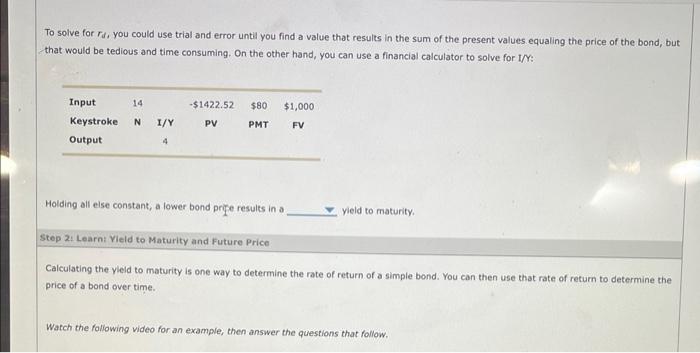
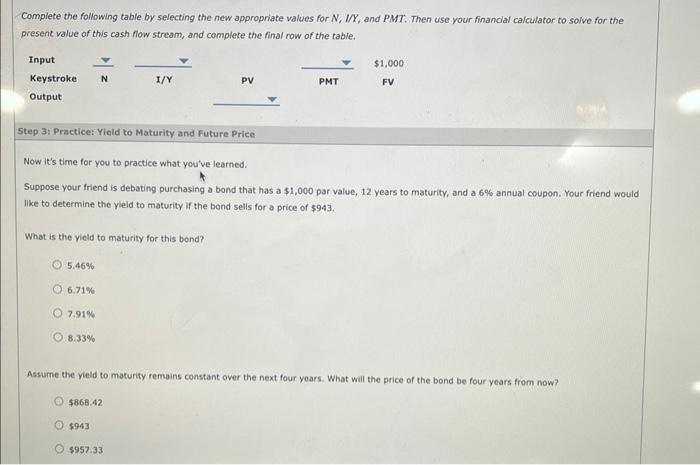
If the terms of a bond do not allow the issuer to buy the bond back early, you can use the to estimate the bond's rate of returt. Suppose you were offered a 14-year, 8% annual coupon, $1,000 par value bond at a price of $1,422.52. If you bought the bond, heid it to maturity, and received the promised intentst payments and maturity value, the rate of interest you would earn is called the bond's yield to maturity (YTM). The yield to maturity is the value for rd that solves the following equation: Where: VM : the bond's value or price rd : the market rate of interest on the bond N: the number of years before the bond matures INT: the dollars of interest paid each year, which equals the coupon rate times the par value of the bond M: par, or maturity, value of the bond If the terms of a bond do not allow the issuer to buy the bond back early, you can use the to estimate the bond's rate of returt. Suppose you were offered a 14-year, 8% annual coupon, $1,000 par value bond at a price of $1,422.52. If you bought the bond, heid it to maturity, and received the promised intentst payments and maturity value, the rate of interest you would earn is called the bond's yield to maturity (YTM). The yield to maturity is the value for rd that solves the following equation: Where: VM : the bond's value or price rd : the market rate of interest on the bond N: the number of years before the bond matures INT: the dollars of interest paid each year, which equals the coupon rate times the par value of the bond M: par, or maturity, value of the bond To solve for rd, you could use trial and error until you find a value that results in the sum of the present values equaling the price of the bond, but that would be tedious and time consuming. On the other hand, you can use a financial calculator to solve for I/r: Holding all else constant, a lower bond pripe results in a yield to maturity. Step 2: Learn: Yield to Maturity and Future Price Calculating the yleld to maturity is one way to determine the rate of return of a simple bond. You can then use that rate of return to determine the price of a bond over time. Watch the following video for an example, then answer the questions that follow. Suppose your friend is debating purchasing a bond that has a $1,000 par value, 15 years to maturity, and a 9% annual coupon. Your friend would like to determine the yield to maturity if the bond sells for a price of $865. In order to use your financial calculator to solve for the rate of return on this bond, you need to know the following information: Complete the following table by selecting the appropriate values for N, PV and PMTT. Then use your financial calculator to solve for the rate of return, and complete the final row of the table. Suppose your friend wants to know what price the bond will be in three years assuming the yield to maturity remains constent. To calculate what the bond price will be three years from now, the new value for N is years. Because this bond is trading at a , you should expect that the bond price three years from now will be Complete the following table by selecting the new appropriate values for N,IK, and PMT. Then use your financlal calculator to solve for the present value of this cash flow stream, and complete the final row of the table. Step 3: Practice: Yield to Maturity and Future Price Now it's time for you to practice what you've learned. Suppose your friend is debating purchasing a bond that has a $1,000 par value, 12 years to maturity, and a 6% annual coupon. Your friend would Ilke to determine the yield to maturity if the bond sells for a price of $943. What is the yield to maturity for this bend? 5.46% 6.71% 7.91% 8.33\% Assume the yield to maturity remains constant over the next four years. What will the price of the bond be four years from now? $868,42 $943 $957.33 Assume the yield to maturity remains constant over the next four years. What will the price of the bond be four years from now? $868.42 5943 5957.33 $1,060