Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ignore the first 5 photos i posted the wrong pictures that's why they are blurry LL Tante Sales June an tres, Teymur 200 women t.com
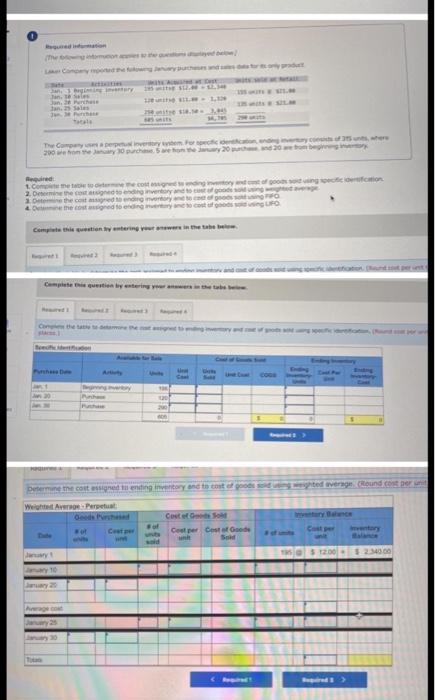

ignore the first 5 photos i posted the wrong pictures that's why they are blurry
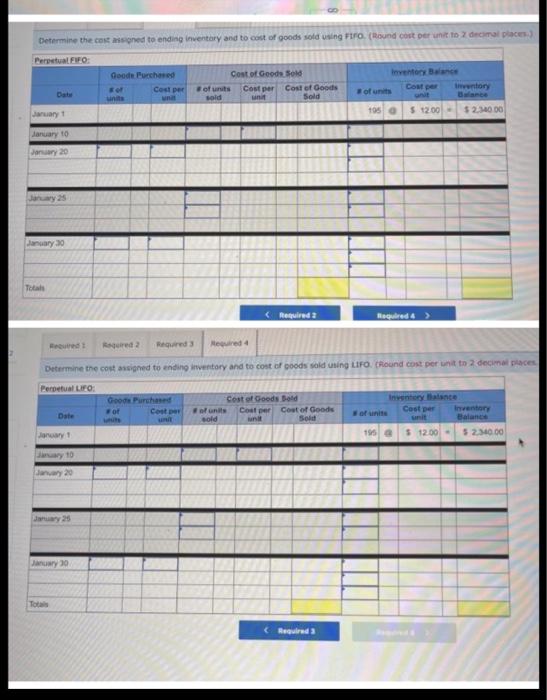
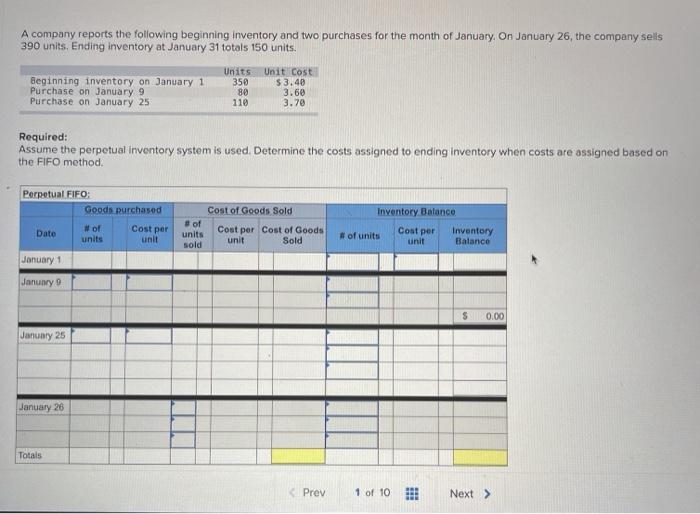
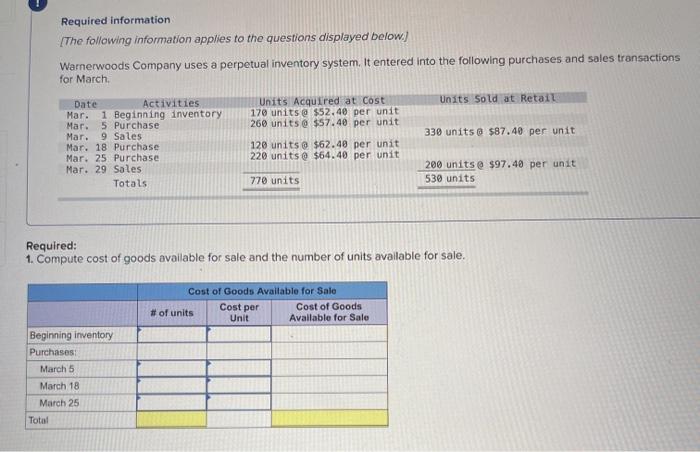
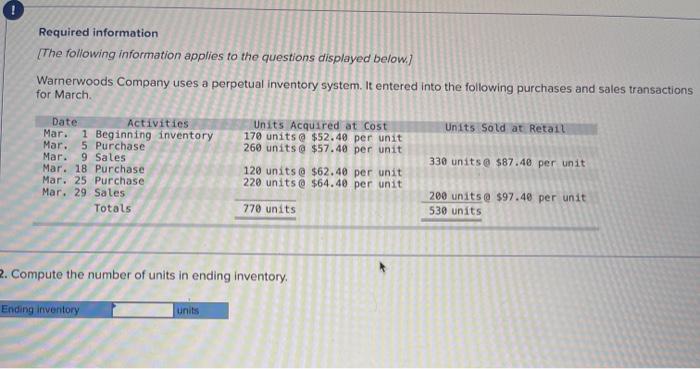
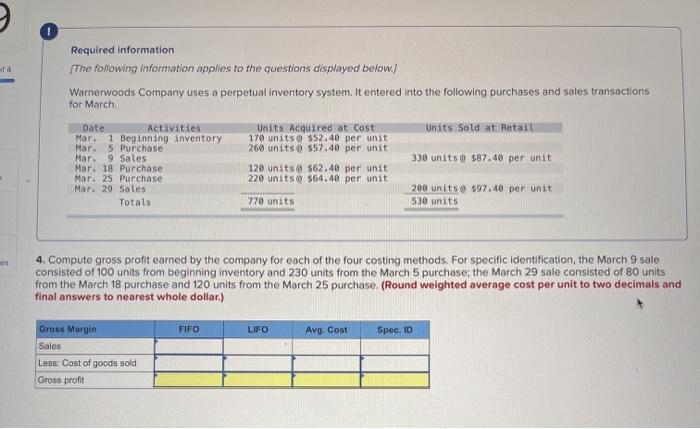
LL Tante Sales June an tres, Teymur 200 women t.com economico 2. Domine the cost og the cost og & the cost red to detect UFO Determine the cost assigned intory and the te verground cost per We Are Coste Cooper Costa de $12.00 $ 234000 Determine the cost and to ending Inventory and to cost of goods sold using Fr. (Round cost per un to decimal places Perpetual Fro: Good Purchased Cost per Cost of Good Sold of units Cost per Cost of Goods sold Inventor Balance Coupe of units Sold 195 January $12.00 $ 2.540 00 January to January 20 January 25 January 30 Total Refruired a Required 2 Red Determine the cost signed to ending inventory and to cost of poods sold in LIFO round cost per unit to 2 decima aces Perpetual LO Google Purchased Cost of Goods Bold or Date Coster of units Cooper Cost of Goods Cost per Inventory sold of units Sold nyt 155 $ 12.00 - 5234000 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 A company reports the following beginning inventory and two purchases for the month of January, On January 26, the company sells 390 units Ending inventory at January 31 totals 150 units. Beginning inventory on January 1 Purchase on January 9 Purchase on January 25 Units 350 80 110 Unit Cost $ 3.40 3.60 3.70 Required: Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the FIFO method. Cost of Goods Sold Perpetual FIFO: Goods purchased Date # of Cost per units unit Inventory Balance of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Cost per # of units unit Inventory Balance January 1 January S 0.00 January 25 January 26 Totais Prev 1 of 10 !!! Next > Walberg Associates, antique dealers. purchased goods for $38,100. Terms of the purchase were FOB shipping point, and the cost of transporting the goods to Walberg Associates's warehouse was $1,500. Walberg Associates insured the shipment at a cost of $210. Prior to putting the goods up for sale, they cleaned and refurbished them at a cost of $550, Determine the cost of inventory Cost of inventory Total cost of inventory $ 0 Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 170 units @ $52.40 per unit 260 units @ $57.40 per unit 330 units @ $87.40 per unit Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 120 units $62.40 per unit 220 units @ $64.40 per unit 200 units @ $97.40 per unit 530 units 770 units Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost per Cost of Goods # of units Unit Available for Sale Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 Total Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units Sold at Retail Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals Units Acquired at cost 170 units @ $52.40 per unit 260 units@ $57.40 per unit 120 units @ $62.48 per unit 220 units@ $64.40 per unit 330 units@ $87.40 per unit 770 units 200 units @ $97.48 per unit 530 units 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory Ending inventory units Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Date Activities Units Acquired at cost Units sold at Retail Mar. 1 Beginning inventory 170 units @ $52.48 per unit Mar, 5 Purchase 260 units@ $57.40 per unit Mar. 9 Sales 330 units o $87.40 per unit Mar. 18 Purchase 120 units@ $62.40 per unit Mar. 25 Purchase 220 units@ $64.40 per unit Mar. 29 Sales 200 units $97.40 per unit Totals 770 units 530 units 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 100 units from beginning inventory and 230 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 80 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar) FIFO LIFO Avg. Cost Spec.ID Gross Margin Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


