Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
II) (5 points) Why do you add NaOH in step 6? What does it accomplish? Explain briefly III) (5 points) Why do you add HCl

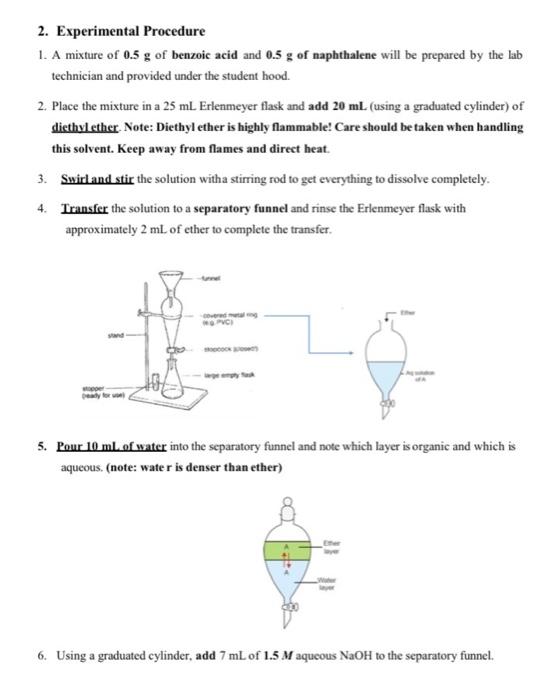
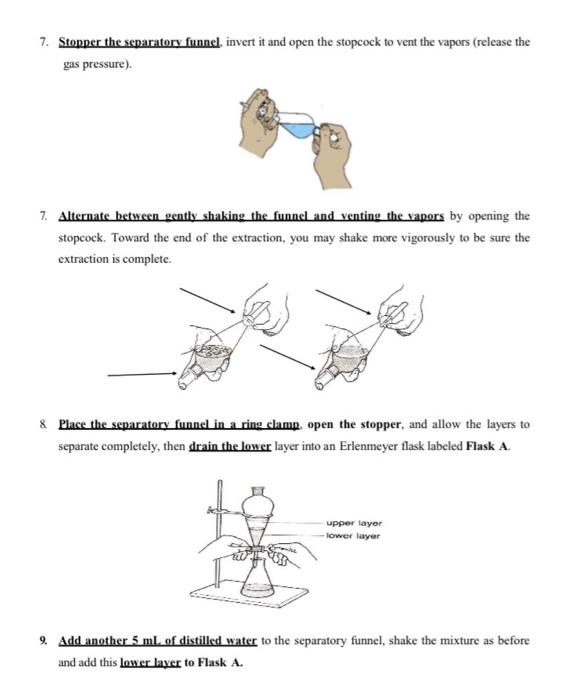
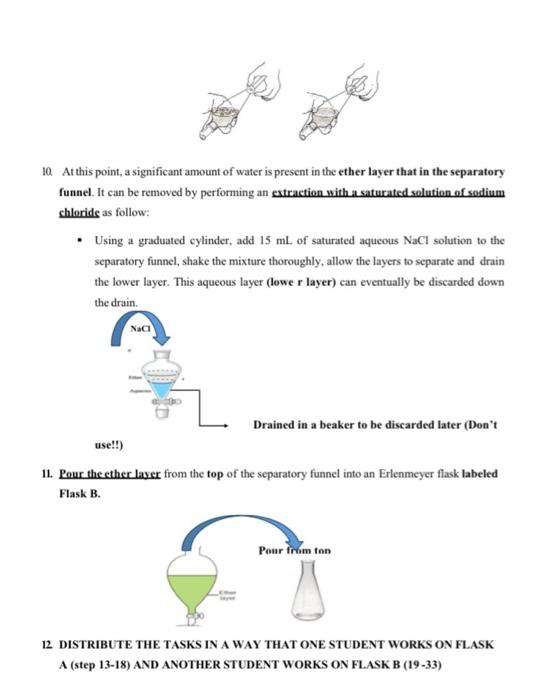
 II) (5 points) Why do you add NaOH in step 6? What does it accomplish? Explain briefly III) (5 points) Why do you add HCl in step 13? What does it accomplish? Explain briefly 2. Experimental Procedure 1. A mixture of 0.5 g of benzoic acid and 0.5 g of naphthalene will be prepared by the lab technician and provided under the student hood. 2. Place the mixture in a 25 mL Erlenmeyer flask and add 20 mL. (using a graduated cylinder) of dicthylcther. Note: Diethyl ether is highly flammable! Care should be taken when handling this solvent. Keep away from flames and direct heat. 3. Swirl and stir the solution with a stirring rod to get everything to dissolve completely. 4. Transfer the solution to a separatory funnel and rinse the Erlenmeyer flask with approximately 2 ml. of ether to complete the transfer. wa PVC 5. Pour 10 mL of water into the separatory funnel and note which layer is organic and which is aqueous. (note: water is denser than ether) 6. Using a graduated cylinder, add 7 mL of 1.5 M aqueous NaOH to the separatory funnel. 7. Stopper the separatory funnel. invert it and open the stopcock to vent the vapors (release the gas pressure). 7. Alternate between gently shaking the funnel and venting the vapors by opening the stopcock. Toward the end of the extraction, you may shake more vigorously to be sure the extraction is complete & Place the separatory funnel in a ring clamp, open the stopper, and allow the layers to separate completely, then drain the lower layer into an Erlenmeyer flask labeled Flask A. upper layer lower layer 9. Add another 5 mL of distilled water to the separatory funnel, shake the mixture as before and add this lower layer to Flask A. 10. At this point, a significant amount of water is present in the ether layer that in the separatory funnel. It can be removed by performing an extraction with a saturated solution of sodium chloride as follow: Using a graduated cylinder, add 15 ml of saturated aqueous NaCl solution to the separatory funnel, shake the mixture thoroughly, allow the layers to separate and drain the lower layer. This aqueous layer (lower layer) can eventually be discarded down the drain. Nach Drained in a beaker to be discarded later (Don't use!!) 11. Pour the ether layer from the top of the separatory funnet into an Erlenmeyer flask labeled Flask B. Pour from ton 12 DISTRIBUTE THE TASKS IN A WAY THAT ONE STUDENT WORKS ON FLASK A (step 13-18) AND ANOTHER STUDENT WORKS ON FLASK B (19-33) Before you start the extraction prepare cold water by adding 100 ml of distilled water in a small beaker and place the beaker in Ice bath 2.1. Elask.A (Extraction of Benzoic acid) 1 Acidify the contents of flask.A by adding approximately 6ml of 3 M hydrochloric acid (HCI) solution (more than half of the vial) to it. Be careful when handling concentrated acids. 14. Test the pH of the solution with indicator pH paper chart until a pH of 1-3) or lower is reached (color of the pH paper turns to red). 15. Cool the flask in an ice bath the collect the acidis product in Flask A by vacuum filtration on a Buchner funnel using two filter papers. 16 Wash with small amounts of cold water, then let them dry on the Buchner funnel 17. Collect the crystals on a pre-weighed watch glass 18 Calculate the weight of crystallized Benzoic Acid and determine the percent yield. 2.2. Flask B (Extraction of Naphthalene) 19. Add anhydrous sodium sulfate to the ether layer (Flask B) until some of it swirls freely. 2. Get a 50 mL beaker containing one boiling stone 21. Push a small plug of cotton into a funnel, place the beaker under the funnel, and decant (pour) the ether solution in Flask B and collect the filtrate in the beaker 2. Wash the drying agent in flask B with additional ether about 3 mL) to ensure complete transfer of the product to the beaker, 23. Place the beaker on the hotplate (the temperature of the hotplate should be around 70C) 11 Pag 24. Evaporate ether and leave behind the dry crude naphthalene. Note: naphthalene sublimes (changes directly from the solid phase to the vapor phase) at room temperature, therefore, you should aware to remove the beaker from the hotplate before all the sther evaporates)
II) (5 points) Why do you add NaOH in step 6? What does it accomplish? Explain briefly III) (5 points) Why do you add HCl in step 13? What does it accomplish? Explain briefly 2. Experimental Procedure 1. A mixture of 0.5 g of benzoic acid and 0.5 g of naphthalene will be prepared by the lab technician and provided under the student hood. 2. Place the mixture in a 25 mL Erlenmeyer flask and add 20 mL. (using a graduated cylinder) of dicthylcther. Note: Diethyl ether is highly flammable! Care should be taken when handling this solvent. Keep away from flames and direct heat. 3. Swirl and stir the solution with a stirring rod to get everything to dissolve completely. 4. Transfer the solution to a separatory funnel and rinse the Erlenmeyer flask with approximately 2 ml. of ether to complete the transfer. wa PVC 5. Pour 10 mL of water into the separatory funnel and note which layer is organic and which is aqueous. (note: water is denser than ether) 6. Using a graduated cylinder, add 7 mL of 1.5 M aqueous NaOH to the separatory funnel. 7. Stopper the separatory funnel. invert it and open the stopcock to vent the vapors (release the gas pressure). 7. Alternate between gently shaking the funnel and venting the vapors by opening the stopcock. Toward the end of the extraction, you may shake more vigorously to be sure the extraction is complete & Place the separatory funnel in a ring clamp, open the stopper, and allow the layers to separate completely, then drain the lower layer into an Erlenmeyer flask labeled Flask A. upper layer lower layer 9. Add another 5 mL of distilled water to the separatory funnel, shake the mixture as before and add this lower layer to Flask A. 10. At this point, a significant amount of water is present in the ether layer that in the separatory funnel. It can be removed by performing an extraction with a saturated solution of sodium chloride as follow: Using a graduated cylinder, add 15 ml of saturated aqueous NaCl solution to the separatory funnel, shake the mixture thoroughly, allow the layers to separate and drain the lower layer. This aqueous layer (lower layer) can eventually be discarded down the drain. Nach Drained in a beaker to be discarded later (Don't use!!) 11. Pour the ether layer from the top of the separatory funnet into an Erlenmeyer flask labeled Flask B. Pour from ton 12 DISTRIBUTE THE TASKS IN A WAY THAT ONE STUDENT WORKS ON FLASK A (step 13-18) AND ANOTHER STUDENT WORKS ON FLASK B (19-33) Before you start the extraction prepare cold water by adding 100 ml of distilled water in a small beaker and place the beaker in Ice bath 2.1. Elask.A (Extraction of Benzoic acid) 1 Acidify the contents of flask.A by adding approximately 6ml of 3 M hydrochloric acid (HCI) solution (more than half of the vial) to it. Be careful when handling concentrated acids. 14. Test the pH of the solution with indicator pH paper chart until a pH of 1-3) or lower is reached (color of the pH paper turns to red). 15. Cool the flask in an ice bath the collect the acidis product in Flask A by vacuum filtration on a Buchner funnel using two filter papers. 16 Wash with small amounts of cold water, then let them dry on the Buchner funnel 17. Collect the crystals on a pre-weighed watch glass 18 Calculate the weight of crystallized Benzoic Acid and determine the percent yield. 2.2. Flask B (Extraction of Naphthalene) 19. Add anhydrous sodium sulfate to the ether layer (Flask B) until some of it swirls freely. 2. Get a 50 mL beaker containing one boiling stone 21. Push a small plug of cotton into a funnel, place the beaker under the funnel, and decant (pour) the ether solution in Flask B and collect the filtrate in the beaker 2. Wash the drying agent in flask B with additional ether about 3 mL) to ensure complete transfer of the product to the beaker, 23. Place the beaker on the hotplate (the temperature of the hotplate should be around 70C) 11 Pag 24. Evaporate ether and leave behind the dry crude naphthalene. Note: naphthalene sublimes (changes directly from the solid phase to the vapor phase) at room temperature, therefore, you should aware to remove the beaker from the hotplate before all the sther evaporates)





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


