
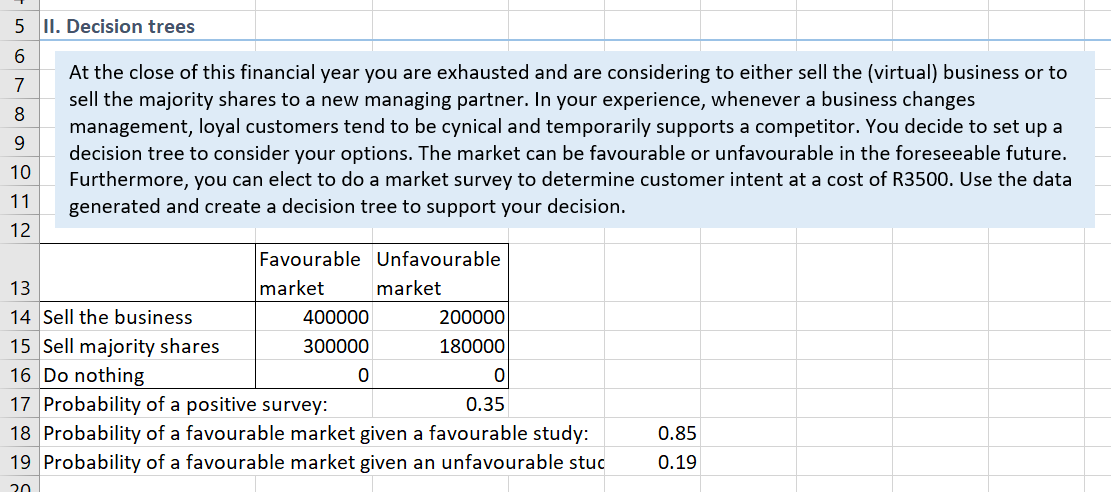
III. Markov analysis You decide to do a simple market survey irrespective of your first decision. One question is posed to the first 20 customers who search a keyword related to your business on the internet. Participants were asked about the likelihood of supporting: 1 = your business; 2 = competitor A; or 3 = competitor B from one month to the next The survey results are shown in the Excel file. a) Use the survey results to compile a matrix of transition probabilities and complete this table: Your business Competitor A Competitor B P= (9) . . Tip: You need to count the number of occurrences (frequency) for each of the following categories: support for your business in the and second months; support for your business in the first month and competitor A in the second; support for your business in the first month and competitor B in the second; support for competitor A in the first month and your business in the second; support for competitor A in the first and second months; support for competitor A in the first month and competitor B in the second; support for competitor B in the first month and your business in the second; support for competitor B in the first month and competitor A in the second; and support for competitor B in the first and second months. b) What is the steady state for the three businesses? n = n Pat: TI 2 TT 3 . . (3) c) How long will it take for the market to reach stability? (1) W XL 22C Oo BE 5 II. Decision trees 6 At the close of this financial year you are exhausted and are considering to either sell the (virtual) business or to 7 sell the majority shares to a new managing partner. In your experience, whenever a business changes 8 management, loyal customers tend to be cynical and temporarily supports a competitor. You decide to set up a 9 decision tree to consider your options. The market can be favourable or unfavourable in the foreseeable future. 10 Furthermore, you can elect to do a market survey to determine customer intent at a cost of R3500. Use the data 11 generated and create a decision tree to support your decision. 12 Favourable Unfavourable 13 market market 14 Sell the business 400000 200000 15 Sell majority shares 300000 180000 16 Do nothing 0 0 17 Probability of a positive survey: 0.35 18 Probability of a favourable market given a favourable study: 0.85 19 Probability of a favourable market given an unfavourable stuc 0.19 20 III. Markov analysis You decide to do a simple market survey irrespective of your first decision. One question is posed to the first 20 customers who search a keyword related to your business on the internet. Participants were asked about the likelihood of supporting: 1 = your business; 2 = competitor A; or 3 = competitor B from one month to the next The survey results are shown in the Excel file. a) Use the survey results to compile a matrix of transition probabilities and complete this table: Your business Competitor A Competitor B P= (9) . . Tip: You need to count the number of occurrences (frequency) for each of the following categories: support for your business in the and second months; support for your business in the first month and competitor A in the second; support for your business in the first month and competitor B in the second; support for competitor A in the first month and your business in the second; support for competitor A in the first and second months; support for competitor A in the first month and competitor B in the second; support for competitor B in the first month and your business in the second; support for competitor B in the first month and competitor A in the second; and support for competitor B in the first and second months. b) What is the steady state for the three businesses? n = n Pat: TI 2 TT 3 . . (3) c) How long will it take for the market to reach stability? (1) W XL 22C Oo BE 5 II. Decision trees 6 At the close of this financial year you are exhausted and are considering to either sell the (virtual) business or to 7 sell the majority shares to a new managing partner. In your experience, whenever a business changes 8 management, loyal customers tend to be cynical and temporarily supports a competitor. You decide to set up a 9 decision tree to consider your options. The market can be favourable or unfavourable in the foreseeable future. 10 Furthermore, you can elect to do a market survey to determine customer intent at a cost of R3500. Use the data 11 generated and create a decision tree to support your decision. 12 Favourable Unfavourable 13 market market 14 Sell the business 400000 200000 15 Sell majority shares 300000 180000 16 Do nothing 0 0 17 Probability of a positive survey: 0.35 18 Probability of a favourable market given a favourable study: 0.85 19 Probability of a favourable market given an unfavourable stuc 0.19 20








