Question: Im attaching script here import copy from typing import List import re import csv import subprocess import os import json from pylint.lint import Run import

Im attaching script here
import copy
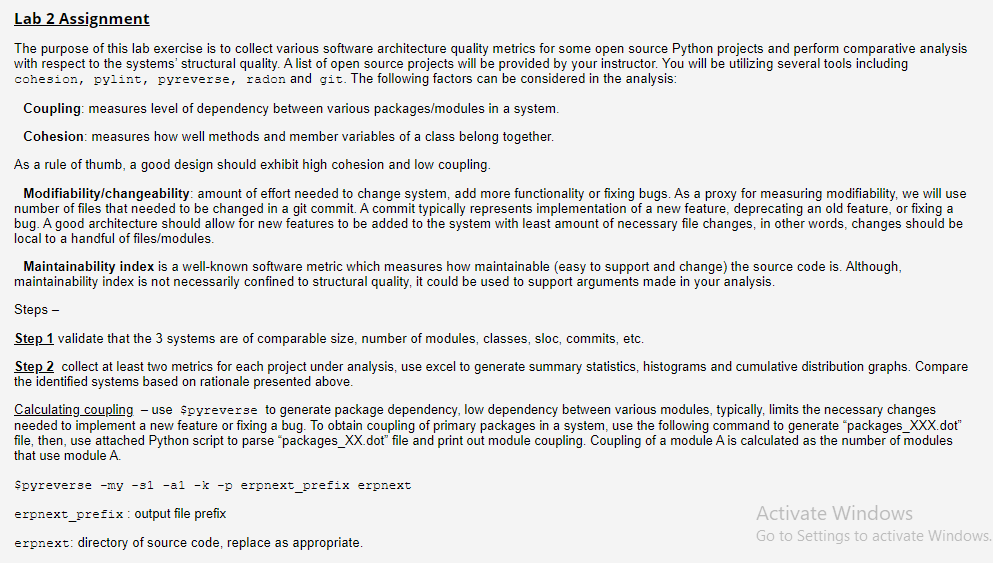
from typing import List import re import csv import subprocess import os import json from pylint.lint import Run import urllib import sys from models.module_metrics import CommitLog from generate_metrics import Repo from datastore.pg_store import PgDataStore class PyReverseClient: def __init__(self): self.pkg_fan_in = {} self.pkg_fan_out = {} def get_coupling(self, dot_path): # sample DOT line format: "2468" -> "2389" [arrowhead="open", arrowtail="none"]; # module 2468 has dependency (is coupled to) module 2389 coupling_line_pattern = r'^\"([0-9]+)\"\s->\s\"([0-9]+)\".*$' dot_file = open(dot_path) for line in dot_file: if '->' in line: coupling_line = re.search(coupling_line_pattern, line) if coupling_line: module_src, module_dst = coupling_line.group(1).strip(), coupling_line.group(2).strip() print('module {} is dependent on {}'.format(module_src, module_dst)) # keep track of number of fan in/out (dependecny) per module fan_out = self.pkg_fan_out.get(module_src, 0) self.pkg_fan_out.update({module_src: fan_out + 1}) fan_in = self.pkg_fan_in.get(module_dst, 0) self.pkg_fan_in.update({module_dst: fan_in + 1}) # using fan_in as coupding metric. for k, v in self.pkg_fan_in.items(): print(v) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample dot file for two projects, ERPNEXT and SEALOR ERP_NEXT_DOT='/home/omari/curated-python-projects/erpnext/packages_erpnext.dot' SALEOR_DOT = '/home/omari/curated-python-projects/saleor/packages_saleor.dot' # Create a client object. pyreverse_client = PyReverseClient() # print out coupling for all modules. pyreverse_client.get_coupling(dot_path=ERP_NEXT_DOT)Lab 2 Assignment The purpose of this lab exercise is to collect various software architecture quality metrics for some open source Python projects and perform comparative analysis with respect to the systems' structural quality. A list of open source projects will be provided by your instructor. You will be utilizing several tools including cohesion, pyiint, pyreverse, radon and git. The following factors can be considered in the analysis: Coupling: measures level of dependency between various packages/modules in a system. Cohesion: measures how well methods and member variables of a class belong together. As a rule of thumb, a good design should exhibit high cohesion and low coupling. Modifiability changeability amount of effort needed to change system, add more functionality or fixing bugs. As a proxy for measuring modifiability, we will use number of files that needed to be changed in a git commit. A commit typically represents implementation of a new feature, deprecating an old feature, or fixing a bug. A good architecture should allow for new features to be added to the system with least amount of necessary file changes in other words, changes should be local to a handful of files/modules. Maintainability index is a well-known software metric which measures how maintainable (easy to support and change) the source code is. Although, maintainability index is not necessarily confined to structural quality, it could be used to support arguments made in your analysis. Steps - Step 1 validate that the 3 systems are of comparable size, number of modules, classes, sloc, commits, etc. Step 2 collect at least two metrics for each project under analysis, use excel to generate summary statistics, histograms and cumulative distribution graphs. Compare the identified systems based on rationale presented above. Calculating coupling - use spyreverse to generate package dependency, low dependency between various modules, typically, limits the necessary changes needed to implement a new feature or fixing a bug. To obtain coupling of primary packages in a system, use the following command to generate "packages_XXX.dot" file, then, use attached Python script to parse packages_XX.dot" file and print out module coupling. Coupling of a module A is calculated as the number of modules that use module A. Spyreverse -my-31 -al -* -p erpnext_prefix erpnext erpnext_prefix: output file prefix erpnext: directory of source code, replace as appropriate. Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Windows This command should generate a file called packages_eronext_prefix.dot that consists of all modules and their dependencies. A simple Python script is provided by your instructor and can be used to parse the packages.dot file (packages_erpnext_prefix.dot ) and print out coupling for all modules. CLICK FOR SCRIPT Calculating Cohesion - find class cohesion for all classes in the a project by executing the following command: $cohesion -d erpnext/ grep Total sed '3/\3\{1, \}Total: .\$$/11/' Commit Size - find number of files changed in git commits by using the following command. The command needs to be executed from within the git directory of the project $git log --stat grep '[0-9]{1, V file [s] * changed' sed 's/([0-9]{1,5}V file./1/" Maintainability Index - find MI for all modules in a project by using the following command. fradon mi -3 saleor/ grep -v ERROR sed '3/.* - .*([09]{1,}.*/\1/' saleor/: directory of source code, replace as appropriate Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Window Step 3 based on summary statistics of collected metrics, write 1 to 2 page report discussing and summarizing the structural quality of the projects under study. Lab 2 Assignment The purpose of this lab exercise is to collect various software architecture quality metrics for some open source Python projects and perform comparative analysis with respect to the systems' structural quality. A list of open source projects will be provided by your instructor. You will be utilizing several tools including cohesion, pyiint, pyreverse, radon and git. The following factors can be considered in the analysis: Coupling: measures level of dependency between various packages/modules in a system. Cohesion: measures how well methods and member variables of a class belong together. As a rule of thumb, a good design should exhibit high cohesion and low coupling. Modifiability changeability amount of effort needed to change system, add more functionality or fixing bugs. As a proxy for measuring modifiability, we will use number of files that needed to be changed in a git commit. A commit typically represents implementation of a new feature, deprecating an old feature, or fixing a bug. A good architecture should allow for new features to be added to the system with least amount of necessary file changes in other words, changes should be local to a handful of files/modules. Maintainability index is a well-known software metric which measures how maintainable (easy to support and change) the source code is. Although, maintainability index is not necessarily confined to structural quality, it could be used to support arguments made in your analysis. Steps - Step 1 validate that the 3 systems are of comparable size, number of modules, classes, sloc, commits, etc. Step 2 collect at least two metrics for each project under analysis, use excel to generate summary statistics, histograms and cumulative distribution graphs. Compare the identified systems based on rationale presented above. Calculating coupling - use spyreverse to generate package dependency, low dependency between various modules, typically, limits the necessary changes needed to implement a new feature or fixing a bug. To obtain coupling of primary packages in a system, use the following command to generate "packages_XXX.dot" file, then, use attached Python script to parse packages_XX.dot" file and print out module coupling. Coupling of a module A is calculated as the number of modules that use module A. Spyreverse -my-31 -al -* -p erpnext_prefix erpnext erpnext_prefix: output file prefix erpnext: directory of source code, replace as appropriate. Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Windows This command should generate a file called packages_eronext_prefix.dot that consists of all modules and their dependencies. A simple Python script is provided by your instructor and can be used to parse the packages.dot file (packages_erpnext_prefix.dot ) and print out coupling for all modules. CLICK FOR SCRIPT Calculating Cohesion - find class cohesion for all classes in the a project by executing the following command: $cohesion -d erpnext/ grep Total sed '3/\3\{1, \}Total: .\$$/11/' Commit Size - find number of files changed in git commits by using the following command. The command needs to be executed from within the git directory of the project $git log --stat grep '[0-9]{1, V file [s] * changed' sed 's/([0-9]{1,5}V file./1/" Maintainability Index - find MI for all modules in a project by using the following command. fradon mi -3 saleor/ grep -v ERROR sed '3/.* - .*([09]{1,}.*/\1/' saleor/: directory of source code, replace as appropriate Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Window Step 3 based on summary statistics of collected metrics, write 1 to 2 page report discussing and summarizing the structural quality of the projects under study
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


