


 Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of . What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions.LOADING...
Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of . What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions.LOADING...
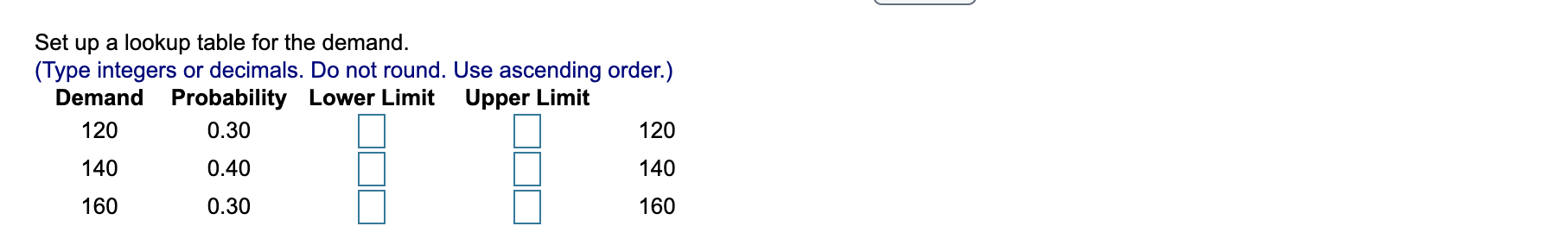
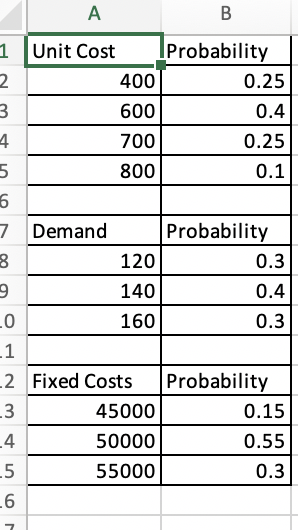
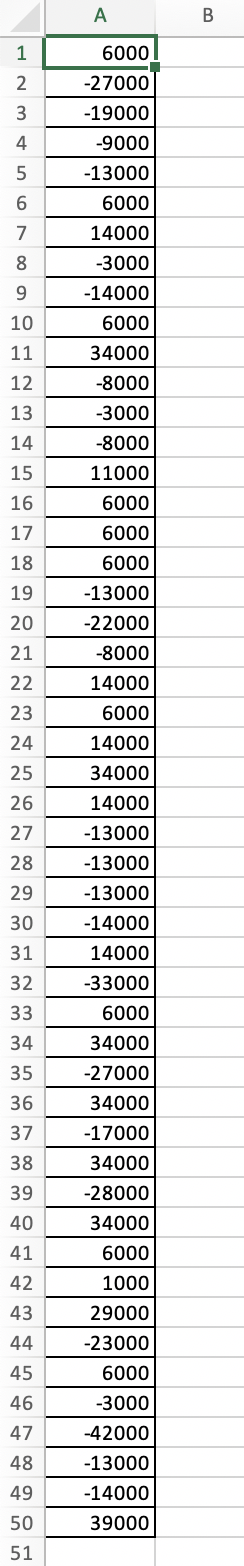
Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $1,000. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of 140. What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions Click here to view a sample of 50 simulation trial results. Set up a lookup table for the unit cost. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Unit Cost Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit $400 0.25 $400 $600 0.40 $600 $700 0.25 $700 $800 0.10 $800 Set up a lookup table for the demand. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Demand Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit 120 0.30 120 140 0.40 140 160 0.30 160 a Set up a lookup table for the fixed costs. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Fixed Costs Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit 45,000 0.15 $45,000 50,000 0.55 $50,000 55,000 0.30 $55,000 Suppose a Monte Carlo simulation using these lookup tables generated the 50 trial results in the problem statement. What is the average profit of this simulation? The average profit is $ (Round to the nearest dollar as needed.) A B 1 Unit Cost Probability 2 400 0.25 3 600 0.4 4 700 0.25 5 800 0.1 6 7 Demand Probability 8 120 0.3 9 140 0.4 LO 160 0.3 -1 2 Fixed Costs Probability _3 45000 0.15 4 50000 0.55 .5 55000 0.3 -6 0 7 A B 1 2 3 4 6000 -27000 -19000 -9000 -13000 6000 14000 5 6 7 8 -3000 9 -14000 10 6000 11 34000 12 13 -8000 -3000 -8000 14 15 16 11000 6000 6000 17 18 6000 19 20 -13000 -22000 -8000 21 22 14000 6000 23 24 14000 34000 25 26 14000 27 -13000 28 -13000 29 -13000 30 -14000 14000 31 32 -33000 6000 33 34 34000 -27000 35 36 34000 37 -17000 38 34000 -28000 39 40 34000 6000 41 42 1000 29000 43 44 -23000 6000 45 46 -3000 47 -42000 48 -13000 49 50 -14000 39000 51 Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $1,000. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of 140. What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions Click here to view a sample of 50 simulation trial results. Set up a lookup table for the unit cost. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Unit Cost Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit $400 0.25 $400 $600 0.40 $600 $700 0.25 $700 $800 0.10 $800 Set up a lookup table for the demand. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Demand Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit 120 0.30 120 140 0.40 140 160 0.30 160 a Set up a lookup table for the fixed costs. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Fixed Costs Probability Lower Limit Upper Limit 45,000 0.15 $45,000 50,000 0.55 $50,000 55,000 0.30 $55,000 Suppose a Monte Carlo simulation using these lookup tables generated the 50 trial results in the problem statement. What is the average profit of this simulation? The average profit is $ (Round to the nearest dollar as needed.) A B 1 Unit Cost Probability 2 400 0.25 3 600 0.4 4 700 0.25 5 800 0.1 6 7 Demand Probability 8 120 0.3 9 140 0.4 LO 160 0.3 -1 2 Fixed Costs Probability _3 45000 0.15 4 50000 0.55 .5 55000 0.3 -6 0 7 A B 1 2 3 4 6000 -27000 -19000 -9000 -13000 6000 14000 5 6 7 8 -3000 9 -14000 10 6000 11 34000 12 13 -8000 -3000 -8000 14 15 16 11000 6000 6000 17 18 6000 19 20 -13000 -22000 -8000 21 22 14000 6000 23 24 14000 34000 25 26 14000 27 -13000 28 -13000 29 -13000 30 -14000 14000 31 32 -33000 6000 33 34 34000 -27000 35 36 34000 37 -17000 38 34000 -28000 39 40 34000 6000 41 42 1000 29000 43 44 -23000 6000 45 46 -3000 47 -42000 48 -13000 49 50 -14000 39000 51





 Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of . What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions.LOADING...
Implement a financial simulation model for a new product proposal and determine a distribution of profits using the provided discrete distributions for the unit cost, demand, and fixed costs. Price is fixed at $. Simulate this model for 50 trials and a production quantity of . What is the average profit? Click here to view the discrete distributions.LOADING...





