Question: import java.lang.reflect.Array; public class ArrayList extends List { private int size; private int capacity; private Object[] ls; // TODO: default: should create an arraylist that
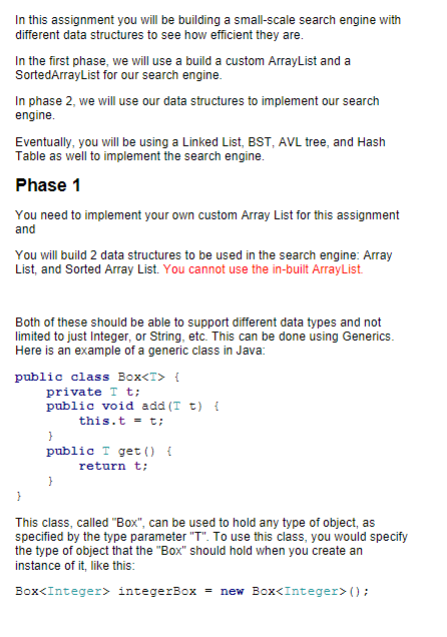
![private int capacity; private Object[] ls; // TODO: default: should create an](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66df5484a444a_19666df54841b3a2.jpg)


import java.lang.reflect.Array;
public class ArrayList
private int size;
private int capacity;
private Object[] ls;
// TODO: default: should create an arraylist that is capable of holding 10 element
public ArrayList(){
}
// TODO: second constructor - should create an arraylist that is capable of holding x element
public ArrayList(int capacity){
}
public int size(){
return this.size;
}
public E get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
if(index >= this.size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return (E) this.ls[index];
}
// TODO: insert --> takes some element and inserts it at the end of the arraylist, resizes to double capacity if no space
public void add(E value){
}
// TODO: delete - deletes an element at said index; moves elements such that there are no gaps in between them
public void delete(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
}
// TODO: searches one by one to find the element, if it doesn't exist then return -1
public int search(E value){
return -1;
}
// TODO: given some other arraylist, compare it to see if it has the same contents
public boolean equals(Object o){
return false;
}
// to help you
public String toString(){
String ret = "";
for(int i = 0; i
ret += i + ": "+ this.ls[i] + " ";
}
return ret;
}
}
abstract class List
abstract void add(E value);
abstract void delete(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException;
abstract E get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException;
abstract int search(E value);
public abstract boolean equals(Object o);
public abstract int size();
}
public class Node implements Comparable {
private String keyword;
private List
// TODO: given some keyword, and mode (1 = arraylist 2 = sorted arraylist) set up the Node
public Node(String keyword, int mode){
}
public String getKeyword(){
return this.keyword;
}
public List getReferences(){
return this.references;
}
public void insertReference(String website){
this.references.add(website);
}
// TODO: Compare some other Node to this Node, String compareTo is your bestfriend here; return -1 if the other object of comparison isn't a Node
public int compareTo(Object o){
return -1;
}
// TODO: similar to compareTo except in boolean format and is only concerned if the other Node has the same keyword or not
public boolean equals (Object o) {
if (o instanceof Node) {
Node other = (Node) o;
return this.keyword.equals(other.keyword);
}
else return false;
}
public String toString(){
return this.keyword + " " + this.references;
}
}
import org.jsoup.Jsoup;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Document;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SearchEngine {
private int mode;
private List
// TODO: build the SearchEngine's nodelist according to mode (1 = ArrayList; 2 = SortedArrayList); build the searchEngine
public SearchEngine(int mode) throws IOException {
}
public List
return this.nodeList;
}
// TODO: Go through the dataset and then create a new Node if the word hasn't been seen before. Add the current URL to its references
// if it hasn't been seen. If the node has been created already, add the current URL to its references. Add the Node to the the
// SearchEngine's nodeList
public void buildList() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("dataset.txt"));
String url;
while((url = reader.readLine()) != null){
Document doc = Jsoup.connect(url).get();
String text = doc.body().text().toLowerCase();
String[] words = text.split("\\s+"); // splits by whitespace
// logic here
}
reader.close();
System.out.println("Finished reading through all URLs");
}
// TODO: Return the node's reference list - if the term isn't found, return an empty list
public List
System.out.println("Searching for " + term + " using data structure mode " + mode + "...");
// Search logic goes here
// Example code for displaying results
System.out.println("Displaying results for " + term + ":");
System.out.println(" 1. URL 1: ");
System.out.println(" 2. URL 2: ");
System.out.println(" 3. URL 3: ");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter mode as in what data structure to use:");
System.out.println(" 1. Array List ");
System.out.println(" 2. Sorted Array List");
int mode = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("Building Search Engine...");
SearchEngine engine = new SearchEngine(mode);
String answer = "y";
while (answer.equals("y")) {
input.nextLine(); // consume the remaining newline character
System.out.print("Search (enter a term to query): ");
String term = input.nextLine();
engine.search(term);
System.out.print("Would you like to search another term (y)? ");
answer = input.nextLine();
}
input.close();
}
}
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
public class SortedArrayList
private int size;
private int capacity;
private Object[] ls;
// TODO: default: should create a sortedarraylist that is capable of holding 10 element
public SortedArrayList(){
}
// TODO: second constructor - should create a sortedarraylist that is capable of holding x element that size
public SortedArrayList(Class
}
public int size(){
return this.size;
}
public E get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
if(index >= this.size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return (E) this.ls[index];
}
// TODO: inserts element while maintaining the sorted order of the contents; resize to double capacity if no space
public void add(E value) {
}
// TODO: delete - deletes an element at said index; moves elements such that there are no gaps in between them
public void delete(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
}
// TODO: search - binary search O(log(n)) for the element; returns -1 if not found
public int search(E value){
return -1;
}
// TODO: given some other sortedarraylist, compare it to see if it has the same contents (also in same order)
public boolean equals(Object o){
return false;
}
// helper
public String toString(){
String ret = "";
for(int i = 0; i
ret += i + ": "+ this.ls[i] + " ";
}
return ret;
}
}
In this assignment you will be building a small-scale search engine with different data structures to see how efficient they are. In the first phase, we will use a build a custom ArrayList and a SortedArrayList for our search engine. In phase 2 , we will use our data structures to implement our search engine. Eventually, you will be using a Linked List, BST, AVL tree, and Hash Table as well to implement the search engine. Phase 1 You need to implement your own custom Array List for this assignment and You will build 2 data structures to be used in the search engine: Array List, and Sorted Array List. You cannot use the in-built ArrayList. Both of these should be able to support different data types and not limited to just Integer, or String, etc. This can be done using Generics. Here is an example of a generic class in Java: This class, called "Box", can be used to hold any type of object, as specified by the type parameter " T ". To use this class, you would specify the type of object that the "Box" should hold when you create an instance of it, like this: Box integerBox = new Box Integer> (); integerBox.add (new Integer (10)); Integer someinteger = integerBox.get (); We use generics such that we can use the same class/Object to declare instances of different types i.e ArrayList \& ArrayList . The details of the data structures are listed below: 1. Array List You need to implement the following: Your class should have 2 constructors: - The default constructor should initialize an array to store 10 elements (we call this capacity). What this means is that we can initially store 10 elements and that there are no elements currently in the list. - The second constructor should take in a number and initialize an array of this length. Furthermore, each constructor should also initialize the size of the list to be 0 (this is the total number of elements in the list). Add: Should take in the value to be inserted. It'll automatically add it to the end (for this assignment). You may need to resize the original array in order to complete this operation. Please double the capacity of the array if needed. For instance, lets assume that the capacity is 10 and there are already 10 elements in the list, and you are trying to insert another. The method should double the size of the array and copy all elements before inserting. Delete: Should take in an index that is to be deleted. If the index is negative, or equal or greater than the size (not the capacity), it should generate an IndexOutofBoundsException Otherwise, it should delete that item at provided index. You must ensure there are no holes in your list. Search: Should take in a value to search for and return the index of this item. If the item is not found, it should return 1. Get: Should take in an index. If the index is negative, or equal or greater than the size, it should generate an IndexOutOfBoundsException Othervise, it should return the item at the provided index. 2. Sorted Array List You need to implement the following: Your class should have 2 constructors: - The default constructor should initialize an array to store 10 elements (we call this capacity). What this means is that we can initially store 10 elements and that there are no elements currently in the list. - The second constructor should take in a number and initialize an array of this length. Furthermore, each constructor should also initialize the size of the list to be 0 (this is the total number of elements in the list). Add: Should take in the value to be inserted. It needs to insert this item, so that the list remains sorted. You may need to resize the original array in order to complete this operation. Please double the capacity of the array if needed. For instance, lets assume that the capacity is 10 and there are already 10 elements in the list, and you are trying to insert another. The method should double the size of the array and copy all elements before inserting. Delete: Should take in an index that is to be deleted. If the index is negative, or equal or greater than the size (not the capacity), it should generate an IndexOutO:BoundsException Othervise, it should delete that item at provided index. You must ensure there are no holes in your list. Search: Should take in a value to search for and return the index of this item. If the item is not found, it should retum -1. Since the list is sorted, you can use binary search to do this. Get: Should take in an index. If the index is negative, or equal or greater than the size, it should generate an IndexOutOfBounds Exception Othervise, it should return the item at the provided index. Test Cases Using Junit, please provide test cases that test the accuracy of your methods. You should test add, delete, get, and search. Remember, your tests should have 100% code coverage. Phase 2 You have a dataset (dataset.txt) containing a list of URLs. You have to read the contents of each webpage, and add the keyword with the associated URL so that if someone searches for the keyword, the results include that keyword. Dataset The text file contains a list of URLs which you need to read. Your main program should look like the following: import java.util. Scanner; publie elass SearehZngine \ private Srxing directory private int moder publie SearehZngine (String direetory, int mode) ( this. di rectory = directoryn this,mode = moder 3 publie void seareh (S5ring serm) \& Syotem, eut.println("Senrehing for " + term + " using data strueture mode " + mode + " ...") 1 // Search logie goos horo 1/ // Examplo codo for displaying rosules Syntem. eut.println("Displaying results for " + term +" " ") 7 Syotem, out. println (") 1. Docunent 1) a System. out. println (" 2. Docunent 2) a Syotem. out.printin (" 3. Docunent 3) a 1 public statie void main (5tring ll args) if Scanner input = new Scanner (Syztern. in) System. out.print ("Please enter the name of a directory: "): String directory = input.nextitie () : System. out.printin ("Enter mode as in what data structure to use:"): System, out, printin (" 1. Array list ") : Syotem, out,printin(" 2. Sorted Array list") : int mode = input.nextlit () : System, out. printin ("Building Search Bngine..."); SearchZngine engine = new SearchZngine (directory, mode) : String angwer ="y; while (answer.equals ("y)) [ input.nextline () : // consume the renaining newline character Syytem. out.print ("Search (enter a term to quety) : ") ; String term = input.nextline (1) ; engine. search (term) : System. out.print ("Would you like to search another term (y) ? ") ; \begin{tabular}{ll} & \multicolumn{1}{c}{ angver = input .nextine () ; } \\ & 3 \\ ingut.close () ; \end{tabular} To read a HTML webpage, you can use JSoup: String tert = doc.tochy) texefl; System.out printin(text) The following page shows you how to add a dependency: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/working-with-moduledependencies.html\#add-a-new-dependency The mode tells the search engine which data structure to use detailed below. 1. Array List You decide to use an Array List so that each element/Node would store 2 things: - Keyword - List of URLs the keyword appears in (another instance of ArrayList). You need to implement the add, and search operations for the Array List. Assume that the initial capacity of the ArrayList is 10 and every time you run out of space, you double the capacity. 2. Sorted Array List Same as 1 but in addition, you want to keep the array sorted. So when you add, you want to ensure that the keywords remain sorted. Assume that the initial capacity of the ArrayList is 10 and every time you run out of space, you double the capacity. Unlike 1, you can now use binary search to find a keyword. Explanation: Assume you are reading https:/llen.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google Drive. For each keyword, you need to store that keyword in the SearchEngine's arraylist as well as the fact that it appears in this web URL (the Node's Dataset Files loaded successfully. 47 URLs loaded from the folder in 3 seconds and 548 microseconds. Please enter a word to search: storage 2 result(s) found in 1 seconds and 431 microseconds. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Drive. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_hosting_service "Bonus: Can you improve the search engine by looking at how many times a keyword appears in a document and using that information to sort the results
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


