Question
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.*; public class TestIntegerBST { public static void main(String[] args) { testStudentBST(); } //end of main public static int sum(BST tree) {
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.*;
public class TestIntegerBST {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testStudentBST();
} //end of main
public static int sum(BST tree) { int sum = 0;
for (int n : tree) {
sum += n; }
return sum; }
public static void testStudentBST(){ BST tree = new BST();
int option, target;
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println(" ***************************"); System.out.println("* Testing Binary Search Tree *"); System.out.println("*************************** "); System.out.println("1. Insert an element"); System.out.println("2. Search for an element"); System.out.println("3. Delete an element"); System.out.println("4. Print in Breadth-First-Order"); System.out.println("5. Print in Pre-Order"); System.out.println("6. Print in In-Order"); System.out.println("7. Print in Post-Order"); System.out.println("9. Print the hight of the tree"); System.out.println("10. Print the number of nods"); System.out.println("11. Print the number of leaves"); System.out.println("12. Print the elements "); System.out.println("13. Exit");
System.out.print(" Select an Option [1...9] : "); option = reader.nextInt();
switch (option) { case 1:
tree.insert(scaneStudent()); break;
case 2:
System.out.print("Enter the Student id to search for: "); target = reader.nextInt();
Student result = tree.search(new Student(target));
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Student " + result + " was found in the tree"); } else {
System.out.println("Sorry, the Student was not found"); }
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Enter the Student id delete: "); tree.deleteByCopying(scaneStudent());
break;
case 4: tree.breadthFirst(); break;
case 5: tree.preorder(); break;
case 6: tree.inorder(); break;
case 7: tree.postorder(); break;
case 9:
System.out.println("The hight of the tree is " + tree.getHeight()); break;
case 10:
System.out.println("the number of nodes in the tree is " + tree.getCount()); break;
case 11:
System.out.println("The number of leaves is " + tree.leavesCount()); break;
case 12: tree.printTree(); break;
} //end of switch
} while (option != 13);
}
public static Student scaneStudent() {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
Student s = new Student();
System.out.println("Please enter the ID of the student:"); s.id = kb.nextInt();
System.out.println("Please enter the name:"); s.name = kb.next();
System.out.println("Please enter the GPA:"); s.gpa = kb.nextDouble();
return s; }
public static void testIntegerBST(){ BST tree = new BST(); int option, target;
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println(" ***************************"); System.out.println("* Testing Binary Search Tree *"); System.out.println("*************************** ");
System.out.println("1. Insert an element"); System.out.println("2. Search for an element"); System.out.println("3. Delete an element"); System.out.println("4. Print in Breadth-First-Order"); System.out.println("5. Print in Pre-Order"); System.out.println("6. Print in In-Order"); System.out.println("7. Print in Post-Order"); System.out.println("8. Print sum of the elements"); System.out.println("9. Print the hight of the tree"); System.out.println("10. Print the number of nods"); System.out.println("11. Print the number of leaves"); System.out.println("12. Print the elements "); System.out.println("13. Exit");
System.out.print(" Select an Option [1...9] : "); option = reader.nextInt();
switch (option) { case 1:
System.out.print("Enter the element to insert: "); tree.insert(reader.nextInt());
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("Enter the element to search for: "); target = reader.nextInt();
Integer result = tree.search(target);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Element, " + result + " was found in the tree"); } else {
System.out.println("Sorry, the element was not found"); }
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Enter the element delete: "); tree.deleteByCopying(reader.nextInt()); break;
case 4: tree.breadthFirst(); break;
case 5: tree.preorder(); break;
case 6: tree.inorder(); break;
case 7: tree.postorder(); break;
case 8:
System.out.print("Sum of the elements in the tree is: " + sum(tree)); break;
case 9:
System.out.println("The hight of the tree is " + tree.getHeight()); break;
case 10:
System.out.println("the number of nodes in the tree is " + tree.getCount()); break;
case 11:
System.out.println("The number of leaves is " + tree.leavesCount()); break;
case 12: tree.printTree(); break;
} //end of switch
} while (option != 13); }
}
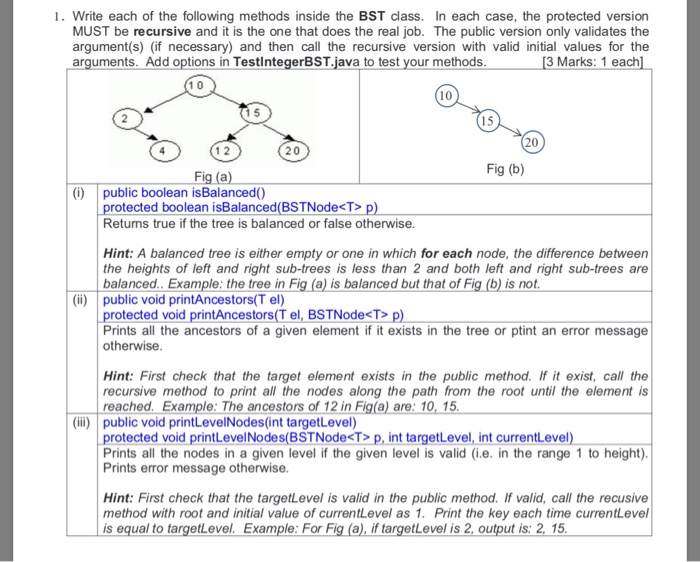
1. Write each of the following methods inside the BST class. In each case, the protected version MUST be recursive and it is the one that does the real job. The public version only validates the argument(s) (if necessary) and then call the recursive version with valid initial values for the arguments. Add options in TestlntegerBST.java to test your methods 3 Marks: 1 each 10 0 20 Fig (b) Fig (a) (i) public boolean isBalanced0) tected boolean isBalanced(BSTNode
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


