


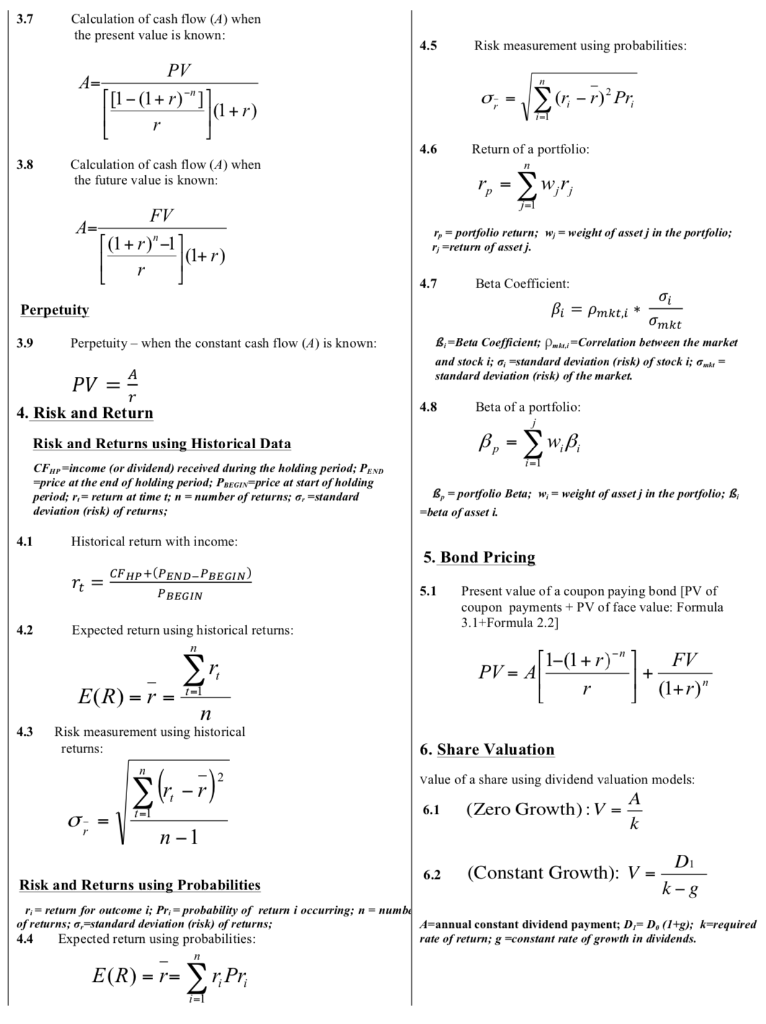
In 2014 Angelo purchased a 20-year, 5.60% p.a. semi- annual coupon paying bond with a Face Value (FV) of $100 000, as he was attracted by the fixed income stream in order to fund his retirement expenses. a) What is the price of this bond in 2019 (15 years remaining) at a current market interest rate of 4.80% p.a.? (2 marks) Show formula, variables, calculation and a concluding. statement in your response. b) Would the return for an investor on a corporate bond be higher or lower than the return on a treasury note? Explain why. (2 marks) In 2014 Frances purchased a 10-year, 3.80% p.a. semi- annual paying coupon bond with a Face Value (FV) of $1 000 000, as she was attracted by the fixed income stream in order to fund her retirement expenses. a) What is the price of this bond in 2019 (5 years remaining) at a current market interest rate of 1.60% p.a.? (2 marks) Show formula, variables, calculation and a concluding statement in your response. b) Describe the relationship between bond prices and interest rates. (2 marks) c) Frances decided to sell the bond from part a) and will invest the proceeds by buying blue chip shares. Explain whether this is wise by Frances by discussing the advantages and disadvantages of shares. (2 marks) 1. Simple interest 2.6 Number of time periods at compound interest I= simple interest; P = principal;r=interest rate p.a.; 1 = time in terms of a year; FV = future value; PV = present value; FV Ln( PV Ln(1+r) 1.1 Calculation of simple interest: n= I= Pxrxt Future value of principal at simple interest: 1.2 FV-PV (1+rxt)) Present value at simple interest: 3. Annuities 4= cash flow received paid; FV-future walue; PV=present value; r=interest rate per compounding period n-number of periods; 1.3 Ordinary Annuities FV PV=FV(1+(rxt) 'or PV=- (1+(rxt)) Yield at simple interest: 3.1 1.4 Present value of n payments of A at interest rate : FV r=-X - PV Number of time periods at simple interest: 1-(1+r) PV = A - [] 1.5 3.2 Future value of n payments of A at interest rater FV t = -X PV --- (1+r)"-1 FV = A / 1 3.3 2. Compound interest FV=future value; PV=present value; r=interest rate per compounding period; n=number of periods; m=number of compounding periods in one year; is =effective rute p.a.; now = nominal rate p.a. Calculation of cash flow (A) when the present value is known: PV A= 2.1 Future value of principal at compound interest: [1-(1+r)" FV=PV (1+r)" 3.4 1 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the future value is known: 2.2 Present value at compound interest: A= FV PV = FV (1+r)" or PV = (1+r)" Effective annual interest rate when nominal interest rate is known: FV [(1 + r)" -1 4712) 2.3 Annuity Due 3.5 Present value of an annuity due: 1 m Nominal annual interest rate when effective interest rate is known: 2.4 [[1-(1+r)"] PV = A - 0-1772" 1+r) 1 3.6 m = m Future value of an annuity due: m[{1+1,3% -1)] 2.5 Yield at compound interest: (1+r)"-1 FV=1[+/-1300 =A 1 FV r = PV -- -1 3.7 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the present value is known: 4.5 Risk measurement using probabilities: PV A- [1-(1+r)"] 0 = * (r; - 1)? Pr; (1+r) 1 4.6 Return of a portfolio: 3.8 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the future value is known: - 2wr A * Talep'4]=> FV (1+r)"-1 r, = portfolio return; w = weight of assetj in the portfolio; -return of asset. (1+r) Perpetuity 4.7 Beta Coefficient: 0 Bi = Pmkt, i * Omkt B-Beta Coefficient; PwCorrelation between the marker and stock i; ; Estandard deviation (risk) of stock i;= standard deviation (risk) of the market. 3.9 Perpetuity - when the constant cash flow (A) is known: PV = 4 r 4.8 4. Risk and Return Beta of a portfolio: , -, Risk and Returns using Historical Data CFwp-income (or dividend) received during the holding period; PEND =price at the end of holding period; Peegin=price at start of holding period; r;=return at time t; n = number of returns; 6, Estandard deviation (risk) of returns, B, - portfolio Beta; w;= weight of assetj in the portfolio: B beta of asseri 4.1 Historical return with income: 5. Bond Pricing rt CFHp+(PEND-PBEGIN) PBEGIN 5.1 Present value of a coupon paying bond [PV of coupon payments + PV of face value: Formula 3.1+Formula 2.2] 4.2 Expected return using historical returns: (1-(1+r)" = A FV PV-11-1***) + (1+r)" E(R) = r = n Risk measurement using historical returns: 4.3 6. Share Valuation (; -,) ri- Value of a share using dividend valuation models: A 6.1 (Zero Growth): V = k II 0 = n-1 D 6.2 (Constant Growth): V = k-g Risk and Returns using Probabilities r;=return for outcome i; Pr, probability of return i occurring; n-numbe of returns; 6,=standard deviation (risk) of returns; 4.4 Expected return using probabilities: A=annual constant dividend payment; D=D. (1+g); k=required rate of return; g =constant rate of growth in dividends. E(R) = r=










