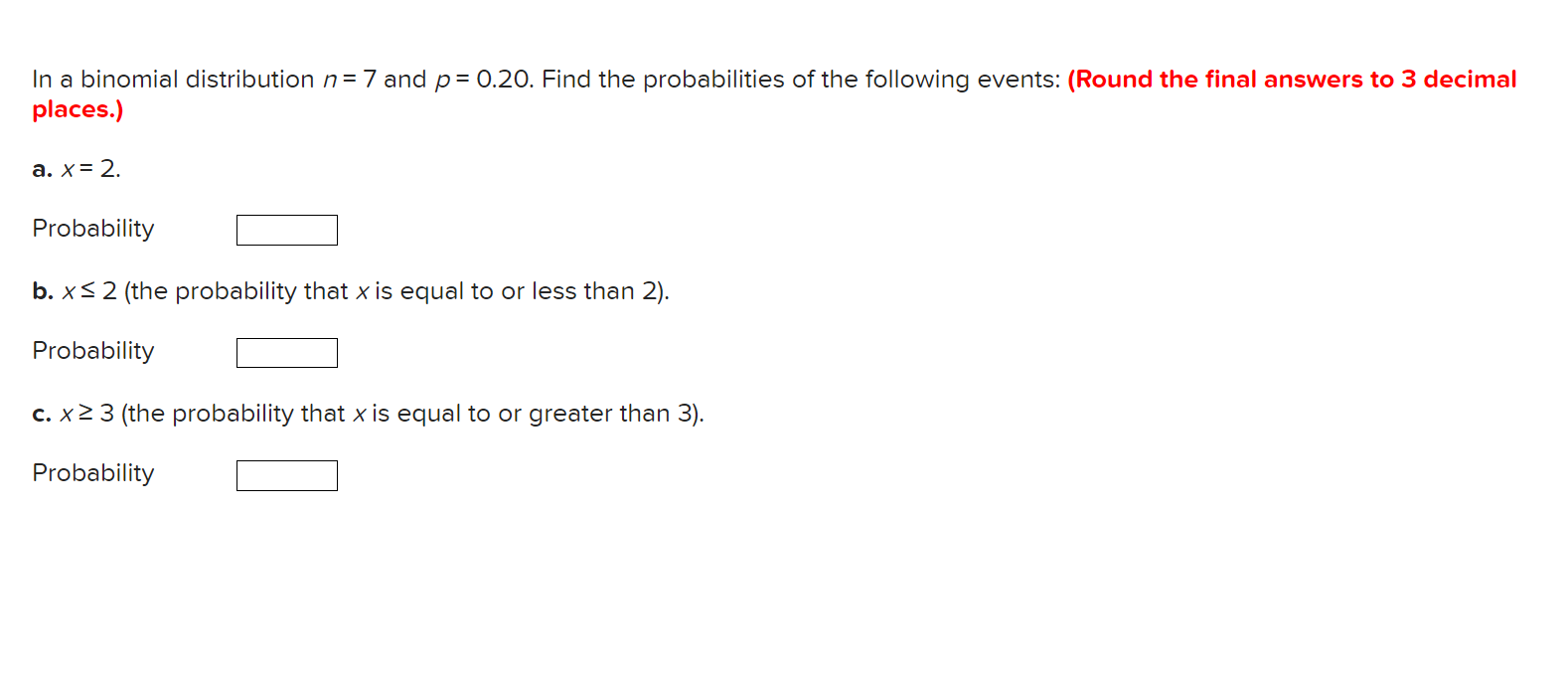
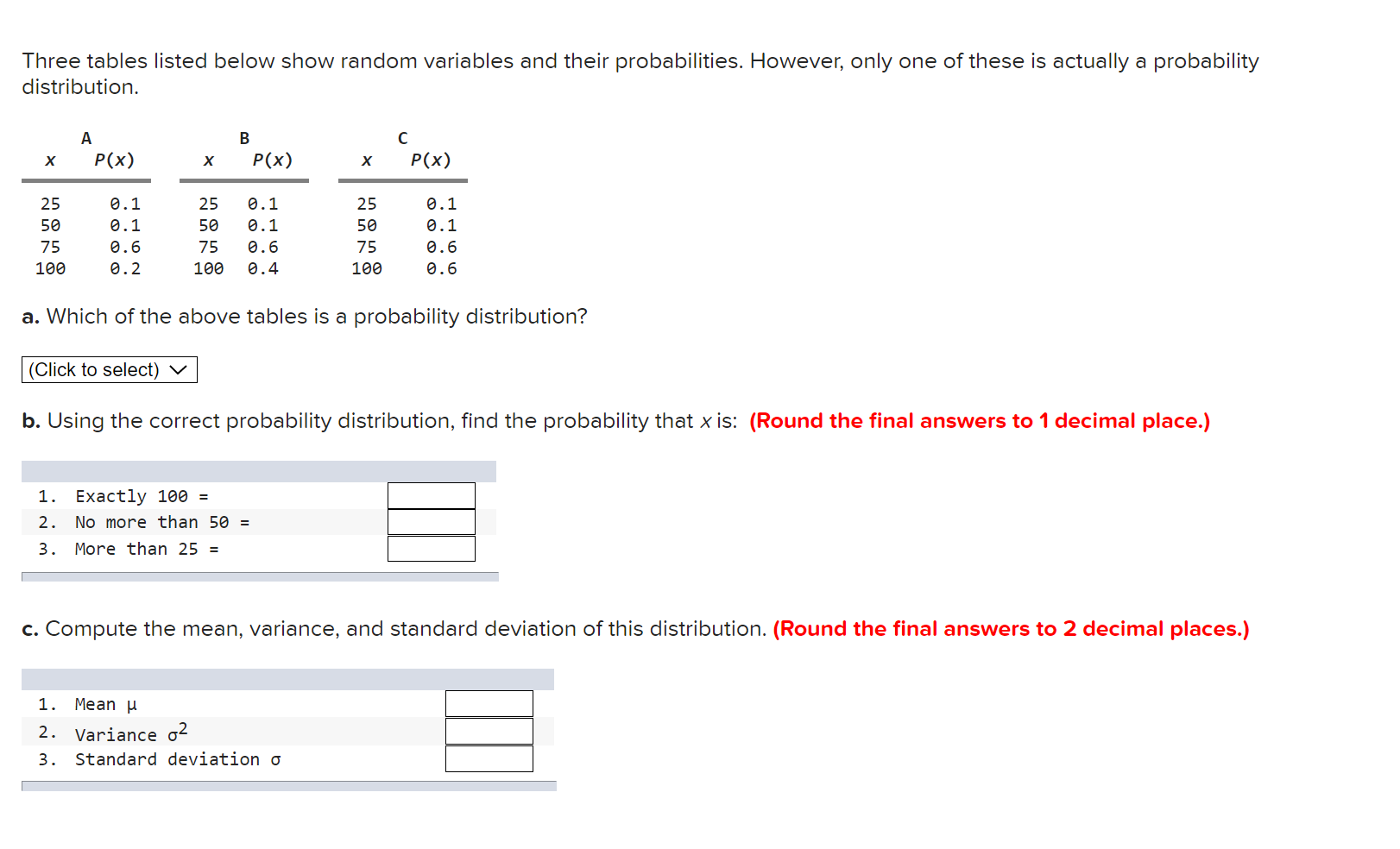
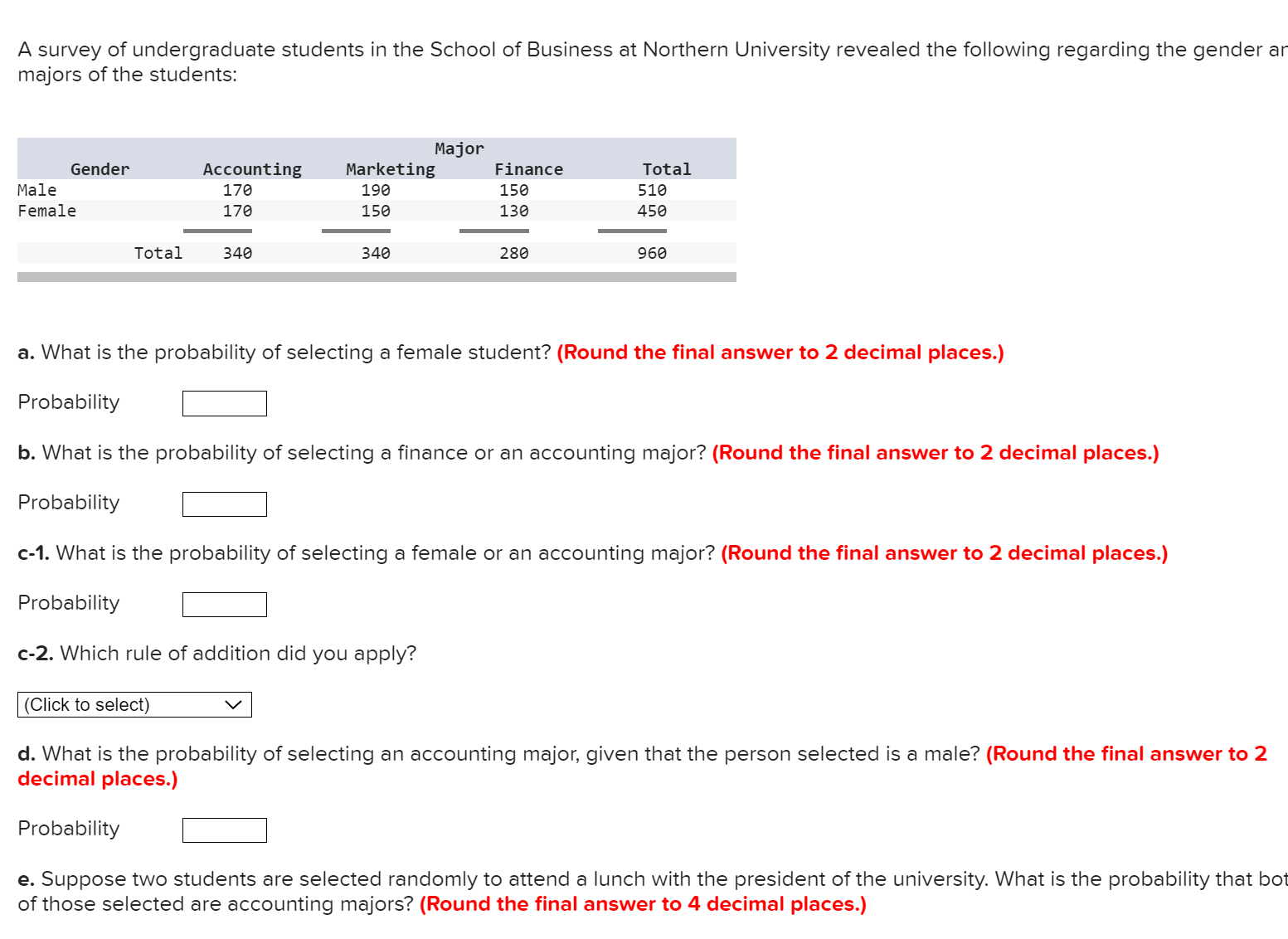
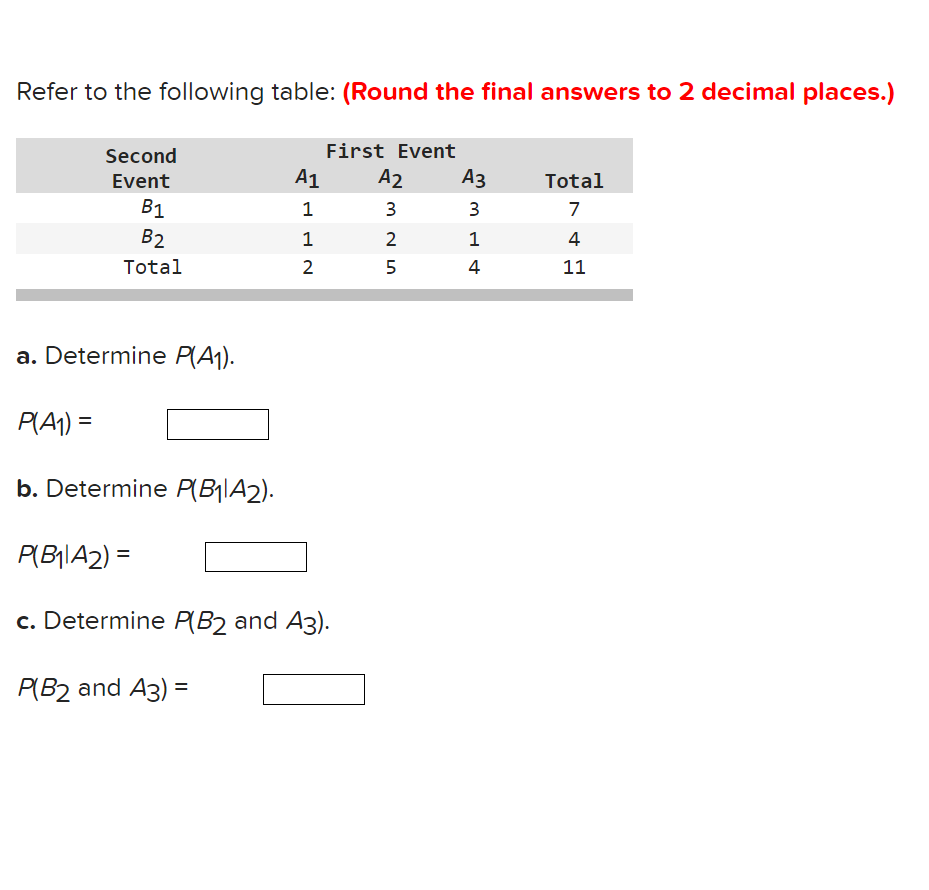
In a binomial distribution n = 7 and p= 0.20. Find the probabilities of the following events: (Round the final answers to 3 decimal places.) a.x=2. Probability b. XS 2 (the probability that XlS equal to or less than 2). Probability c. x Z 3 (the probability that X is equal to or greater than 3). Probability Three tables listed below show random variables and their probabilities. However, only one of these is actually a probability distribution. A B C x P(x) x P(x) x P(x) 25 9.1 25 9.1 25 9.1 59 0.1 59 9.1 58 6.1 75 9.6 75 9.6 75 9.6 199 9.2 199 9.4 199 9.6 a. Which of the above tables is a probability distribution? (Click to select) V b. Using the correct probability distribution.fi1d the probability that x is: (Round the final answers to 1 decimal place.) 1. Exactly me = 2. No more than 59 = 3. More than 25 = c. Compute the mean, variance, and standarc deviation of this distribution. (Round the final answers to 2 decimal places.) 1. Mean u Variance (:2 3. Standard deviation 0 A survey of undergraduate students in the School of Business at Northern University revealed the following regarding the gender ar majors of the students: Major- Gender Accounting Marketing Finance Total Male 176 199 156 516 Female 176 156 136 456 Total 346 349 286 966 a. What is the probability of selecting a female student? (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Probability b. What is the probability of selecting a finance or an accounting major? (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Probability c-1. What is the probability of selecting a female or an accounting major? (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Probability c-2. Which rule of addition did you apply? (Click to select) v d. What is the probability of selecting an accounting major, given that the person selected is a male? (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Probability e. Suppose two students are selected randomly to attend a lunch with the president of the university. What is the probability that bot of those selected are accounting majors? (Round the final answer to 4 decimal places.) Refer to the following table: (Round the final answers to 2 decimal places.) Second First Event Event '1 A2 A3 Total 51 1 3 3 7 52 1 2 1 4 Tota 1 2 5 4 11 a. Determine HA1), HA1) = b. Determine FIB-HA2). P(B1|A2) = c. Determine FIBZ and A3), H52 and A3) = Compute the mean and variance of the following discrete probability distribution: (Round the final answers to 2 decimal places.) X P(X) 4 0. 3 9 0. 3 13 0.4 Mean Variance