Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In a lab-based course, a common activity is to measure the linear kinematics of motion in the 100- meter dash. This activity involves 10

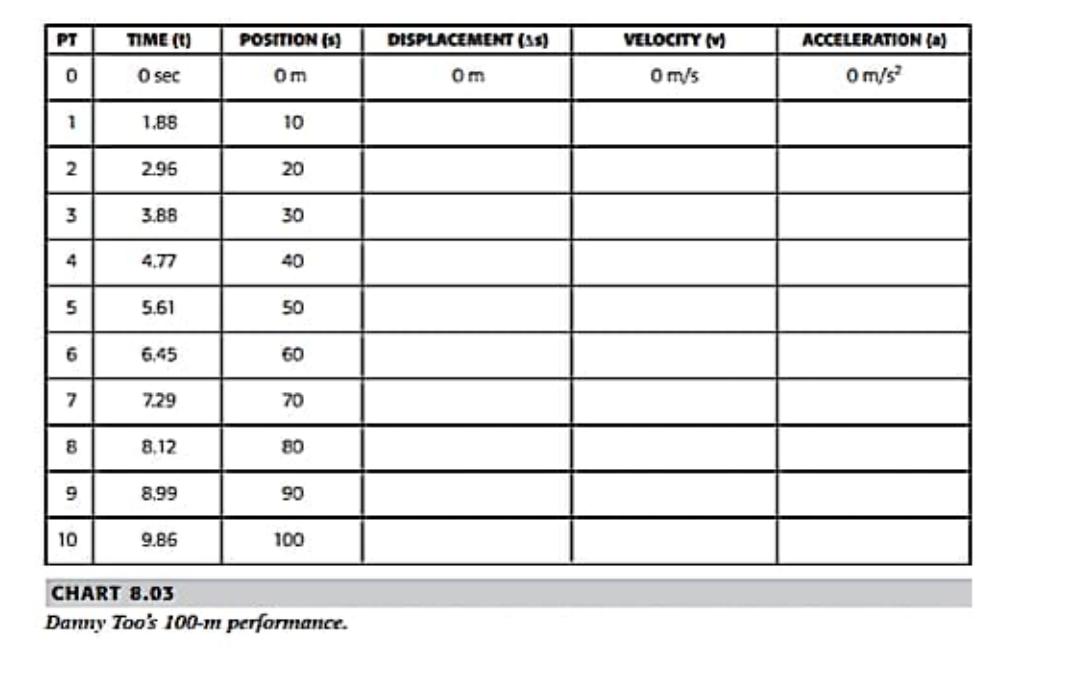
In a lab-based course, a common activity is to measure the linear kinematics of motion in the 100- meter dash. This activity involves 10 students acting as timers. Each student is placed at 10-meter intervals along the length of the course. At the starting line, Vo = 0, and to = 0. As the race begins, all students start a stopwatch (all are assumed to begin simultaneously). During the race, each student in succession stops the stopwatch at when the runner reaches that student's position (e.g., time at 10 m, 20 m, 30 m...). Using this protocol, the kinematics of motion can be calculated. Times and positions are recorded for Danny and myself in Chart 8.02 and 8.03 (consider these to be rough estimates). From this data, 1. Calculate displacement, velocity, and acceleration at each point in time for each runner. 2. Plot the velocity-time and the acceleration-time graphs. 3. Explain the outcome of the race. FT 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TIME ( O sec 1.86 2.87 3.8 4.66 5.55 6.38 721 8.11 8.98 9.83 POSITION (s) Om 10 20 30 40 2828 50 60 70 80 90 100 CHART 8.02 Chris Williams' 100-m performance. DISPLACEMENT (15) Om VELOCITY M 0 m/s ACCELERATION (a) 0 m/s PT 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TIME (1) 0 sec 1.88 2.95 3.88 4.77 5.61 6.45 7.29 8.12 8.99 9.86 POSITION (1) 0m 10 20 888888 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 CHART 8.03 Danny Too's 100-m performance. DISPLACEMENT (15) 0m VELOCITY () 0 m/s ACCELERATION (a) 0 m/s
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.33 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


