Question
In a perfectly competitive market, if a firm finds it is producing an amount of output such that its marginal cost is less than its
In a perfectly competitive market, if a firm finds it is producing an amount of output such that its marginal cost is less than its price, it will
1 point
A) immediately shut down for the short run.
B) be maximizing profits.
C) increase its output to increase its profit.
D) decrease its output to increase its profit.
2. In perfect competition, ________.*
1 point
A) there are restrictions on entry into the market
B) firms in the market have advantages over firms that plan to enter the market
C) only firms know their competitors' prices
D) there are many firms that sell identical products
If a perfectly competitive market is in long-run equilibrium and there is a permanent decrease in demand, then
1 point
A) some firms will incur economic losses.
B) firms are no longer maximizing profits.
C) some firms must immediately exit.
D) each firm must produce less output in the new long run equilibrium and earn less economic profit.
Which of the following is FALSE regarding a perfectly competitive firm?*
1 point
A) The firm can charge a lower price than its competitors and thereby sell more output and increase its profits.
B) The firm always earns a normal profit.
C) The firm's marginal revenue is horizontal.
D) The firm's minimum efficient scale is small relative to the market demand.
The short-run supply curve for a perfectly competitive firm is its
1 point
A) marginal cost curve above the horizontal axis.
B) marginal cost curve above its shutdown point.
C) average cost curve above the horizontal axis.
D) average cost curve above its shutdown point.
5. If the firm is producing 4 packets of biscuits, to maximize its profit it will
1 point
A) increase its output.
B) decrease its output.
C) continue producing packets of biscuits.
D) shut down.
6. A firm's shutdown point is the quantity and price at which the firm's total revenue just equals its
1 point
A) total cost.
B) total variable cost.
C) total fixed cost.
D) marginal cost.
. Explain why, in the long run, the price of a product produced by a perfectly competitive industry will be driven down to the minimum long-run average cost.
Why is a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve identical to its marginal revenue curve?
What sort of competition (if any) exists among perfectly competitive firms?
Provide a local example of the perfectly competitive market and describe the commodities it provides, the locations in which this market exists. (3 marks)
A. Use the graph for a perfectly competitive firm producing T-shirts to answer the following questions. Find:The profit maximizing price and quantity. (2 marks)

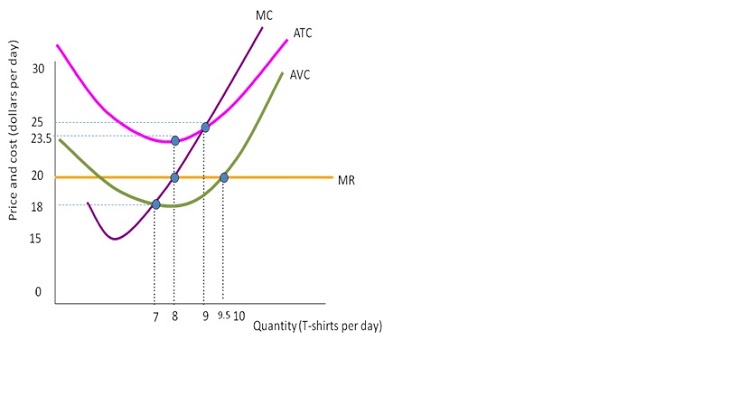
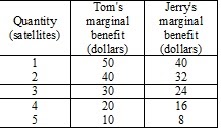
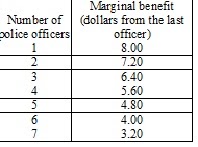
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


