Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In a piston-cylinder assembly, 1 kg mass of Refrigerant 134a undergoes a process with initial pressure of 1 MPa and quality of 45% to
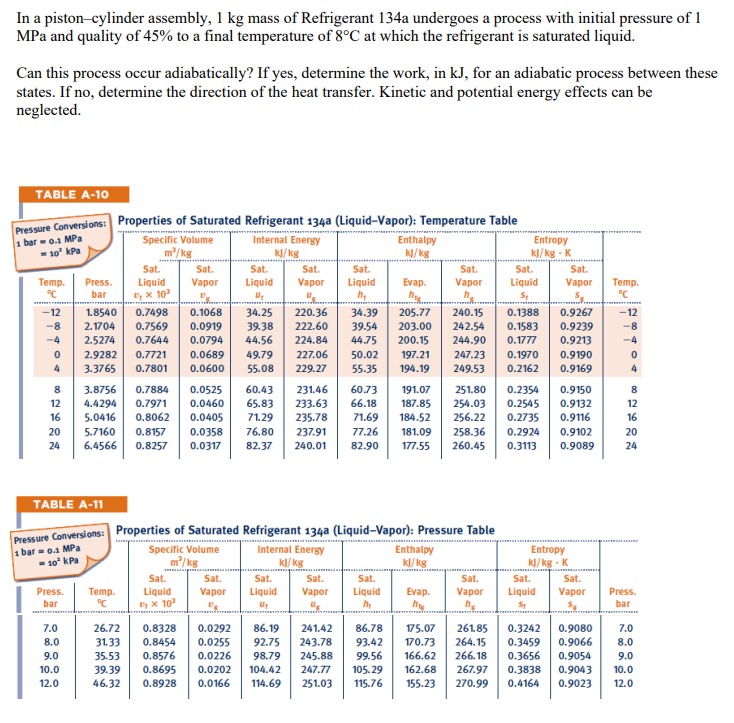
In a piston-cylinder assembly, 1 kg mass of Refrigerant 134a undergoes a process with initial pressure of 1 MPa and quality of 45% to a final temperature of 8C at which the refrigerant is saturated liquid. Can this process occur adiabatically? If yes, determine the work, in kJ, for an adiabatic process between these states. If no, determine the direction of the heat transfer. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. TABLE A-10 Pressure Conversions: Properties of Saturated Refrigerant 134a (Liquid-Vapor): Temperature Table 1 bar 0.1 MPa Specific Volume Internal Energy -10 kPa m/kg kJ/kg Enthalpy kJ/kg Entropy kJ/kg - K Sat. Sat. Temp. Press. Liquid Vapor Sat. Liquid Sat. Vapor Sat. Sat. Sat. Sat. Liquid Evap. Vapor Liquid Vapor Temp. bar x10 h h S C -12 1.8540 0.7498 0.1068 -8 2.1704 0.7569 -4 0 4 2.5274 0.7644 2.9282 0.7721 3.3765 0.7801 34.25 0.0919 39.38 0.0794 44.56 220.36 34.39 205.77 240.15 0.1388 0.9267 -12 222.60 224.84 39.54 203.00 242.54 0.1583 0.9239 -8 44.75 200.15 244.90 0.1777 0.9213 -4 0.0689 49.79 227.06 50.02 197.21 247.23 0.1970 0.9190 0 0.0600 55.08 229.27 55.35 194.19 249.53 0.2162 0.9169 4 82122 16 20 3.8756 0.7884 0.0525 4.4294 0.7971 0.0460 5.0416 0.8062 0.0405 5.7160 0.8157 0.0358 76.80 24 6.4566 0.8257 0.0317 82.37 60.43 231.46 60.73 191.07 251.80 0.2354 0.9150 65.83 233.63 66.18 187.85 254.03 0.2545 0.9132 71.29 235.78 71.69 184.52 256.22 0.2735 0.9116 237.91 240.01 77.26 82.90 181.09 258.36 177.55 260.45 0.2924 0.9102 0.3113 0.9089 82122 16 20 24 TABLE A-11 1 bar 0.1 MPa 10 kPa Pressure Conversions: Properties of Saturated Refrigerant 134a (Liquid-Vapor): Pressure Table Specific Volume m/kg Internal Energy kJ/kg Enthalpy kJ/kg Entropy kJ/kg K Sat. Press. bar Temp. C Liquid By x10 Sat. Vapor Sat. Liquid U Sat. Vapor Liquid Sat. Sat. Evap. h Vapor Sat. Liquid Sat. Vapor hg S Press. bar 7.0 26.72 0.8328 8.0 31.33 0.8454 9.0 35.53 0.8576 10.0 39.39 0.8695 12.0 46.32 0.8928 0.0292 86.19 0.0255 92.75 0.0226 98.79 0.0202 104.42 247.77 0.0166 114.69 251.03 241.42 86.78 243.78 93.42 245.88 99.56 105.29 115.76 175.07 261.85 0.3242 0.9080 170.73 264.15 0.3459 0.9066 166.62 266.18 0.3656 0.9054 162.68 267.97 155.23 270.99 7.0 8.0 9.0 0.3838 0.9043 10.0 0.4164 0.9023 12.0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


