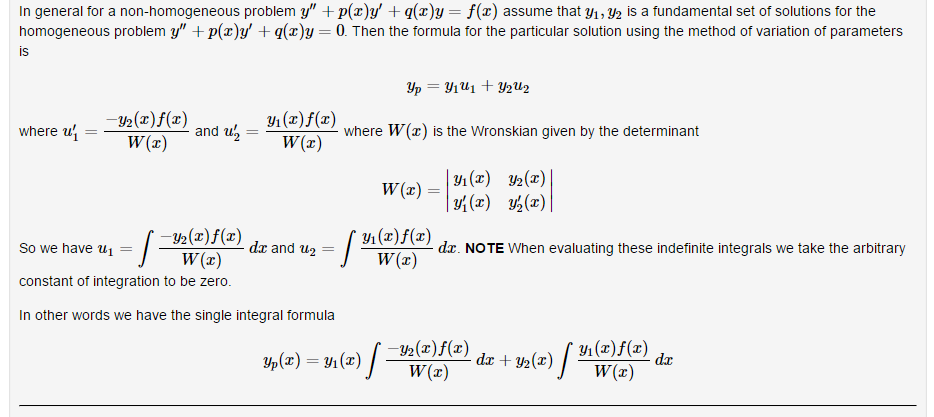
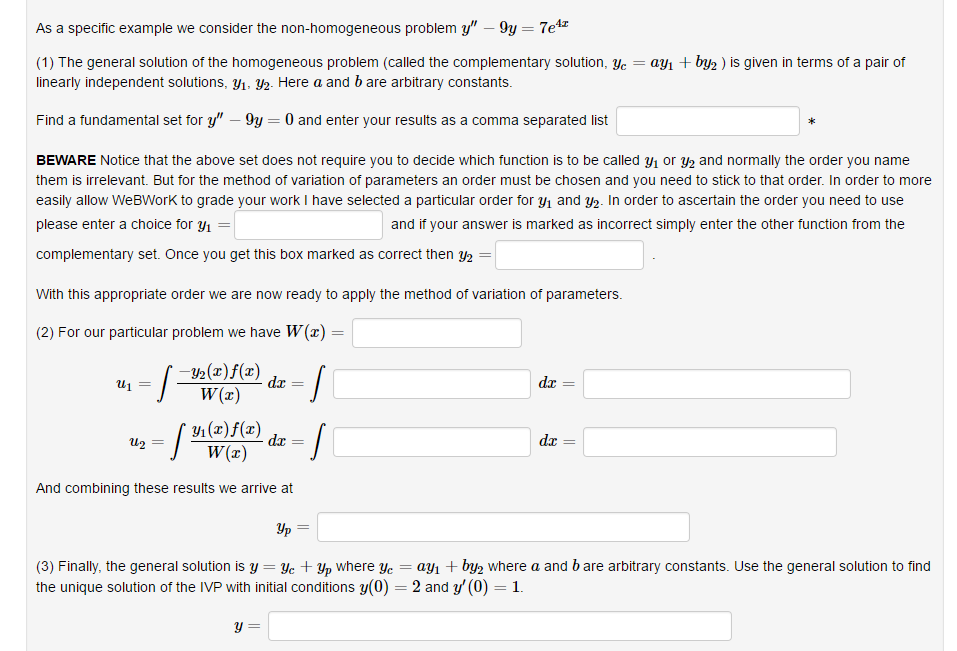
In general for a nonhomogeneous problem 9\" + p(z}y' + q[z)y 2 Hz] assume that 1:1, y; is a fundamental set of solutions for the homogeneous problem 3.0\" l p(z)y' + (1(3):; 2 I]. Then the formula for the particular solution using the method of variation of parameters 9p = 91111 + 102'\": -D'2(3)f{$) , _ mtft where u\" = and u 1 1! \"13} where \"7(3) is the Wronskian given by the determinant WM 91(3) 232(3) W\") = ' yum) yum) Sowe have ul 2 walzlflz) mm \"2 2 f more) dz. NOTE When evaluatin these indenite inte rals we take the arbitra What We) 9 g \" constant of integration to be zero. In other words we have the single integral formula As a specific example we consider the nonhomogeneous problem y" 9y 2 To\" (1} The general solution of the homogeneous problem (called the complementary solution, y: 2 am + 173.5: J is given in terms ofa pair of linearly independent solutions, yl, gig. Here a and b are arbitrary constants. Find a fundamental set for y\" 91; = [l and enter your results as a comma separated list 1: BEWARE Notice that the above set does not require you to decide which function is to be called yl or y? and normally the order you name them is irrelevant. But for the method of variation of parameters an order must be chosen and you need to stick to that order. In order to more easily allow WeBWorK to grade your work I have selected a particular order for yl and Liz. In order to ascertain the order you need to use please enter a choice for y1 = and ifyour answer is marked as incorrect simply enter the other function from the complementary set. Once you get this box marked as correct then gig 2 With this appropriate order we are now ready to apply the method of variation of parameters. (2} For our particular problem we have \"7(2) 2 u, = m:_):)(2) dz: 1 dz = y (3)313le z f 1W(z]d3 =f dz 2 And combining these results we arrive at HP: {3] Finally, the general solution is y 2 ya + yp where ya = (11,11 + by; where a and bare arbitrary constants. Use the general solution to nd the unique solution of the NP with initial conditions yl] = 2 and 36(0) = 1. y