Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In the classic model for electrical conduction, electron mobility in a metal wire is defined as = where v is the drift velocity of
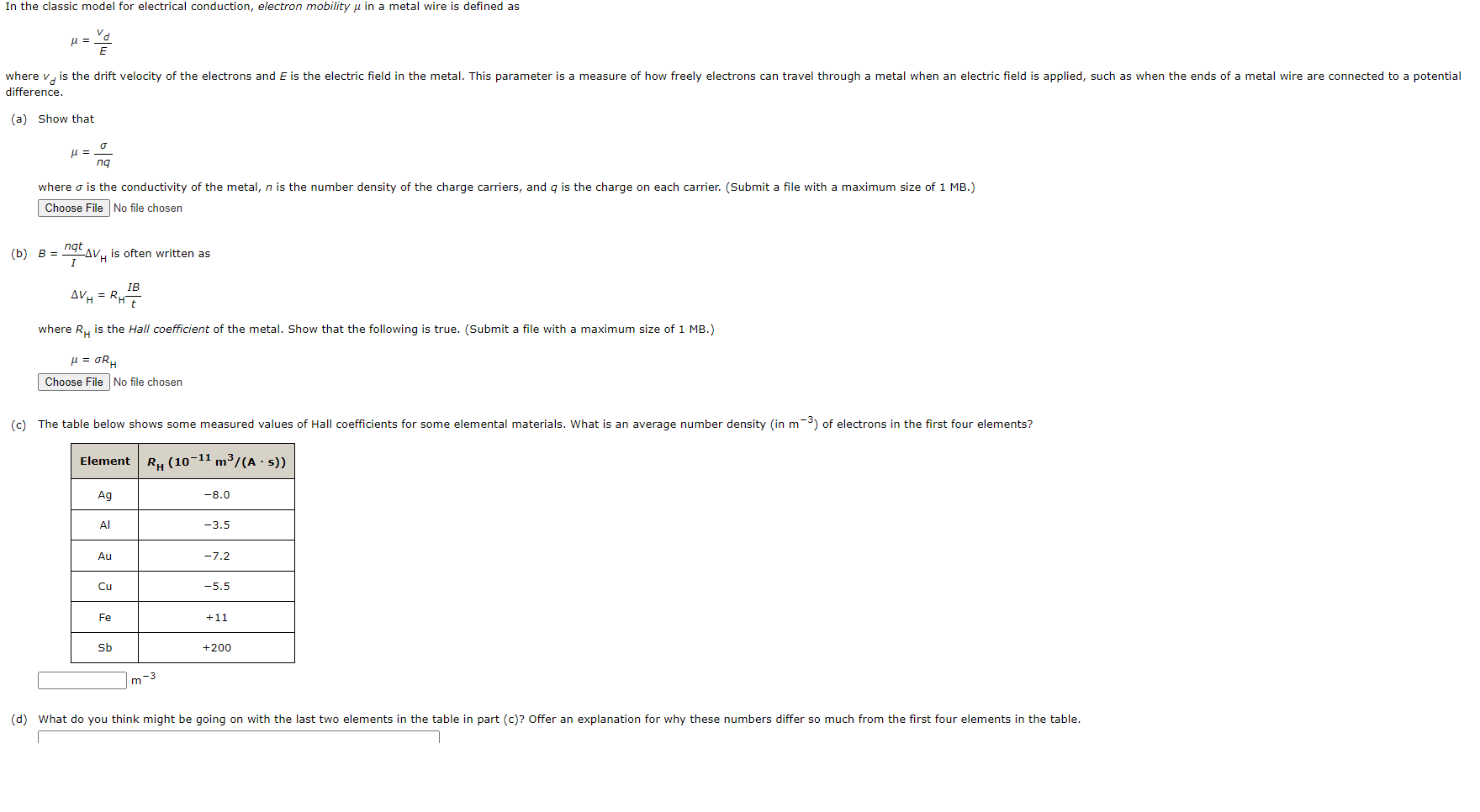
In the classic model for electrical conduction, electron mobility in a metal wire is defined as = where v is the drift velocity of the electrons and E is the electric field in the metal. This parameter is a measure of how freely electrons can travel through a metal when an electric field is applied, such as when the ends of a metal wire are connected to a potential difference. (a) Show that ng where is the conductivity of the metal, n is the number density of the charge carriers, and q is the charge on each carrier. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen (b) B = ngt I is often written as LAVH AV = RHE IB where R is the Hall coefficient of the metal. Show that the following is true. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) = RH Choose File No file chosen (c) The table below shows some measured values of Hall coefficients for some elemental materials. What is an average number density (in m) of electrons in the first four elements? Element R (10-11 m/(As)) Aq -8.0 -3.5 Au -7.2 Cu -5.5 Fe +11 Sb +200 m-3 (d) What do you think might be going on with the last two elements in the table in part (c)? Offer an explanation for why these numbers differ so much from the first four elements in the table.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


