Question: In this assignment, another new concept- Inheritance- will be introduced, which extends the notion of reusability with Classes and Objects Objeetives to be met 1

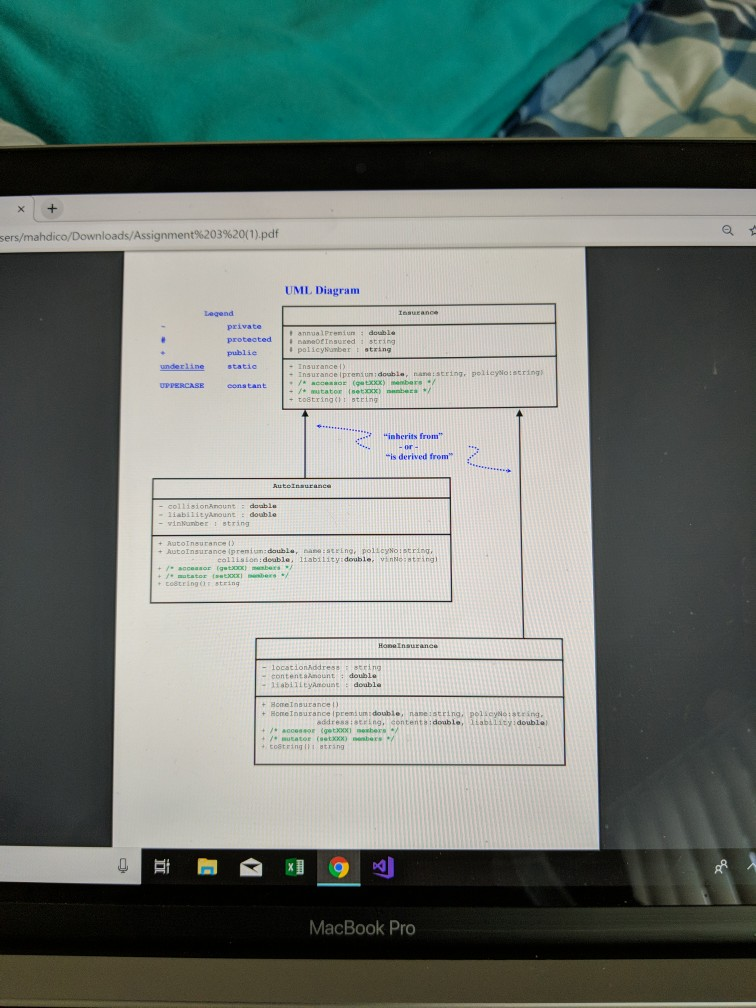
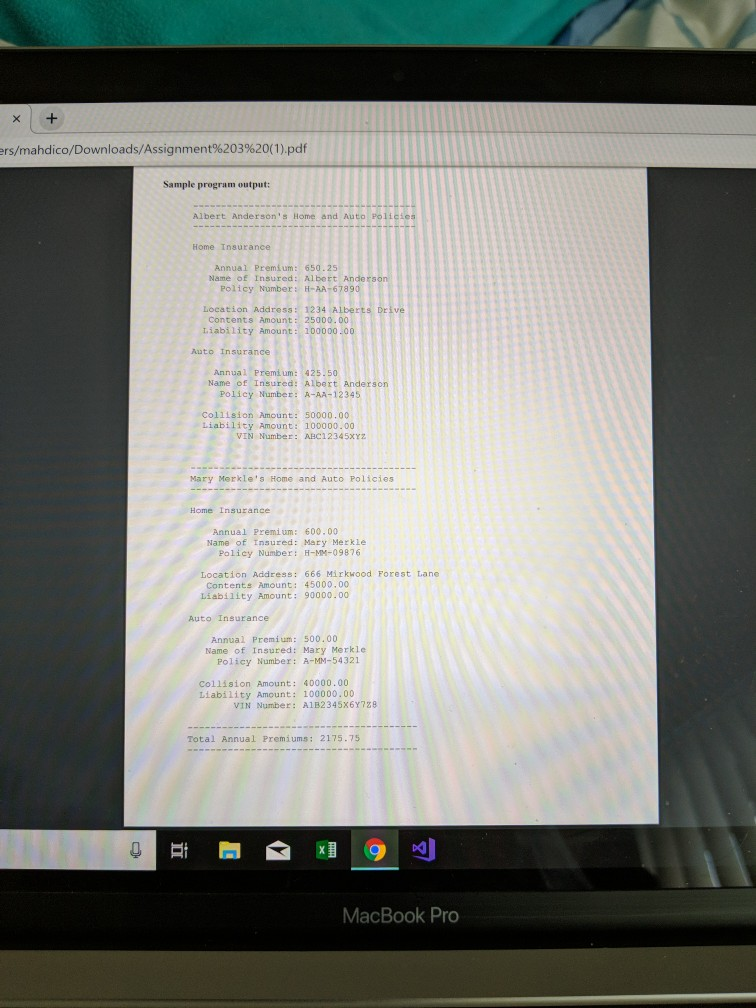
In this assignment, another new concept- Inheritance- will be introduced, which extends the notion of reusability with Classes and Objects Objeetives to be met 1 Demonstrate your understanding of how to define a Simple Inheritance with 3 classes Define objects that demonstrate the use of derived class constructors 3Demonstrate how to override a member function. Use a model for two classes derived from the same "common" class as shown here Base--> Derived-> AutoInsurance Home Insurance will complete this assignment by writing a new class for the base class and each derived class based on the UMI diagrams that accompany this assignment. The base class (Insurance) represents the attributes (data) and behavior (functions) common to both derived classes, whereas each derived class (AutoInsurance and HomeInsurance) represents a different kind (type) of base class. Both derived classes are subclasses that derive inherit") data and functions from the base class. The data and functions defined in the Insurance class will encapsulate only those characteristics that are common (general) to both derived classes, for example: annual premium, name of insured, and policy number and methods for constructing and accessing those fields Both derived classes will inherit (acquire) those features already defined in the base elass. The data defined in both the AutoInsurance and Homelnsurance classes will provide additional characteristics that are unique (specific) to only those policies. For example: the Autolnsurance class will define VIN number, whereas the Homelnsurance class will define address of the residency. Each of these classes also will define and/or modi other functions for constructing and accessing their data members. Minimum requirements The classes, their relationship, and their members must adhere to the UML diagram with one exception-you will later change the access level for data members in the base class from protected to private Your program must define at least 4 objects (2 for each derived class) demonstrating all4 derived class construetors you will write You should initialize 2 objects with literal values when using the constructors with arguments but get user input and then call the setxxx member functions for the 2 objeets defined by the default (0-arg) constructors In both derived classes, override the tostring ) member function defined in the base class, and use this function to get the strings to display the data for each of the 4 objects. Use the initialization list with derived class constructors to pass data inherited from the base class to the appropriate constructor in that class Change the data in the base class "private" and use (call) public base class member functions in the derived class where necessary Include a total at the end of your output that is the sum of all 4 annual premiums. ahdico/Downloads/Assignment%203%20(1).pdf Considerations: Work with a modest number of fields and member functions to make testing your classes easier. For example, write your first derived class with just one field and two constructors and test it; then add the getxxx and setxxx functions and test those; Then try building that part of the tostring() functions and test that; Finally, add other members until you get that entire class working. Then write the other derived class following the same pattern and test it. As you should know by now, waiting until the end before compiling and testing only makes debugging more complicated and more time consuming. (Impatience usually results in additional aggravation and setback)! . Remember that private data members in a base class cannot be accessed directly by functions in derived classes, but protected base class data members can be accessed from derived classes. constructors and access (observer) member functions should be declared public. Obviously . Constructors are not inherited. Each class must define its own constructorfs). The same rules apply to each class: if no constructor is defined, a default will be provided; if one or more constructors with arguments are defined, there is no default unless you write one. Each derived class definition header must use the correct syntax along with the base class name to inherit the data and functions defined in the base class. Each member inherited also inherits the same access right that was used to define that member in the base class . Although constructors are not inherited, a derived class constructor may call a base class constructor from its initialization list to handle that part of the initialization. Otherwise, the compiler inserts a call to the base class default constructor (if one exists). Member "functions" defined protected or public in the base class may be used (called) by functions defined in each derived class and (if public) by objects of each derived class. When organizing the classes in your inheritance with a multi-file project, each class should be split into 2 separate files (6 all together): 3 containing the class declarations only and 3 containing the implementations (definitions) for those declarations. Your main program will be in a separate (7th) file, which will "include" the 3 header files that declare each class Additional Requirements: Include your name at the top of the main program files as a comment. Before you compress (zip) your completed assignment, be sure to close Visual Studio, and if you want you can delete the Debug and ipch folders and big database file. MacBook Pro sers/mahdico/Downloads/Assignment%203%20( 1 ) pdf UML Diagram Legend private annua lPreniun double protec PocBaneOE Insured string # policyNumber : string publie underline tatic + Insurance Iprens un double, nane:string, polleywo:scring) tostring: str "inherits from" "is derived from collisionanguntdoabl liabiiieyanount double rinNumber 1 string AutoInsurance ipreniun: double, ane:atring, policyno:string collislon: deuble, liability:double vinNeatringl tionhddress contentaknount double iabilltyancunt double + HoneIosurance Ipremi um: double, nane:string, pelscyo:string. addresa:string, contents :double, 1iabt1ity idouble) costringil string Hi MacBook Pro
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


