Question
In this assignment, you will implement a dynamic array. Dynamic arrays provide all the advantages of static arrays--random access, sequential access, compactnessplus the capability to
In this assignment, you will implement a dynamic array. Dynamic arrays provide all the advantages of static arrays--random access, sequential access, compactnessplus the capability to change size.
Static arrays are high-performing data structures with little overhead. Because array elements are stored in contiguous memory, indexing and iteration are fast; insertion and removal of array elements, however, requires shifting the remaining elements.
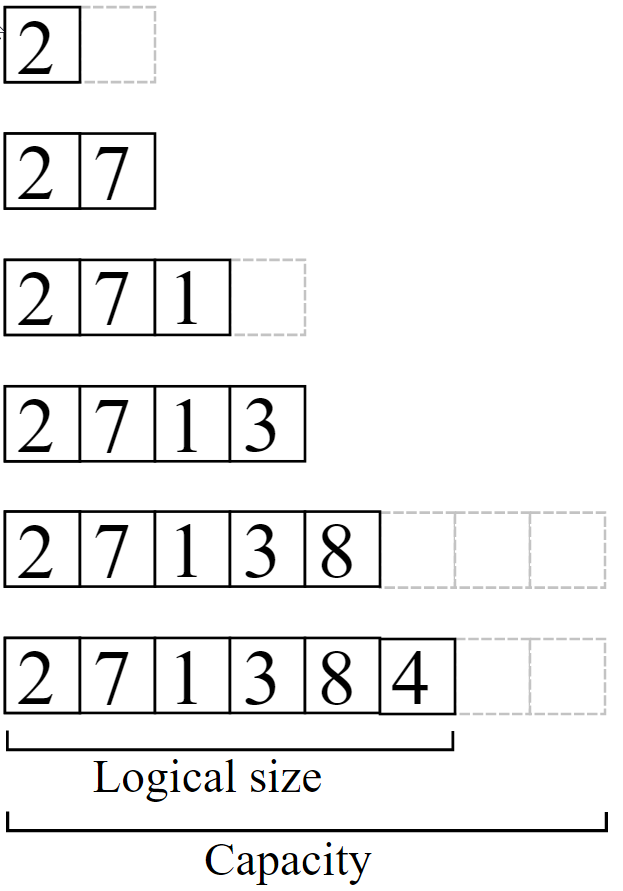
Dynamic arrays wrap a static array divided into two parts: a used part storing the actual elements; an unused part reserved for new elements. The number of elements used by the dynamic array is referred to as its size; the length of the underlying static array is referred to as its capacity.
As elements are added to the end or middle of the dynamic array, its size grows. When the arrays size equals its capacity, the dynamic array must be resized. Resizing a dynamic array requires that a new array be allocated and that the original elements be copied into the new array. Dynamic arrays are usually resized by a large amount, referred to as the growth factor, to minimize the cost of resizing: allocating a new array and copying the existing elements.
The C++ vector class in the Standard Template Library is an example of a dynamic array. Internally, vectors use a dynamically allocated array to store elements. Elements are accessed by their position in the underlying array.
Implement the following dynamic array:
//This is driver code.
#include
using namespace std; using namespace cs20a;
void display(DynamicIntArray &d, string title = "");
int main() { DynamicIntArray d1;
cout
for (int i = 0; i
d1.insert(2, 999999); display(d1, "insert(2, 999999);");
d1.remove(2); display(d1, "d1.remove(2);");
d1[3] = 888888; display(d1, "d1[3] = 888888;");
DynamicIntArray d2 = d1; display(d1, "DynamicIntArray d2 = d1;");
if (d1 == d2) cout
d2[3] = 777777; display(d2, "d2[3] = 777777;");
if (d1 == d2) cout
DynamicIntArray d3;
d3 = d1; display(d3, "d3 = d1;");
if (d1 == d3) cout
d3.add(666666); display(d3, "d3.add(666666);");
d3.remove(3); display(d3, "d3.remove(3);");
d3.clear(); display(d3, "d3.clear();");
if (d3.isEmpty()) cout
system("pause"); return 0; }
void display(DynamicIntArray &d, string title) { if (title != "") cout
// THIS IS DynamicIntArray.h
#pragma once #include
namespace cs20a { class DynamicIntArray { public: DynamicIntArray(); explicit DynamicIntArray(int size); DynamicIntArray(const DynamicIntArray & d);
~DynamicIntArray(); DynamicIntArray & operator= (const DynamicIntArray& rhs);
bool isEmpty() const; int getUsed() const; int getCapacity() const;
void add(int element); void insert(int i, int element); int remove(int i);
void clear();
int& operator[](int i);
friend std::ostream& operator
private: int used, capacity; int* elements;
void expandCapacity(); }; }
// Please implement the below cpp file. and show me the output if u possible.
#include "DynamicIntArray.h"
namespace cs20a { here }
2 7 2 7 1 2 7 1 3 2 7 1 3 8 2 7 1 3 4 Logical size Capacity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


