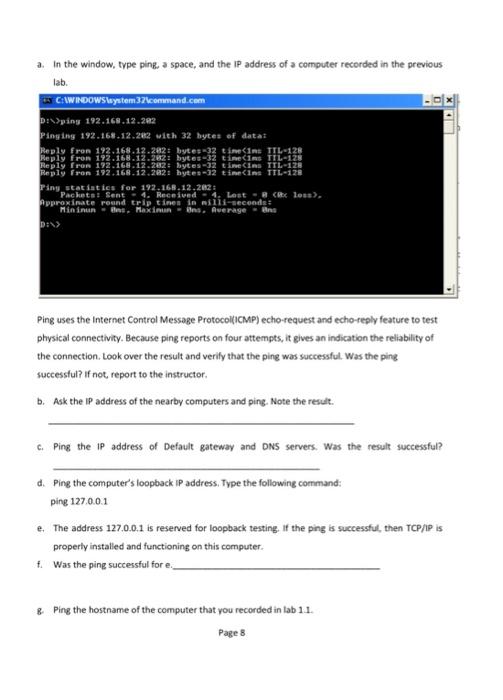
In this exercise, you will determine the correct class for a given IP address. 2. Which address class (es) will allow you to have more than 1000 hosts per network? 3. Which address (es) will allow only 254 hosts per network? 4. Identify invalid IP address: Circle the portion of the IP address that would be invalid if it were assigned to a host, and then explain why it is invalid. a) 131.107.256.80 b) 222.222.255.222 c) 231.200.1.1 d) 126.10.0 e) 0.127.4.100 f) 190.72.0 g) 127.1.1 h) 198.121.254.255 i) 255.255.255.255 Network Configuration Step 1. Connect to the internet. Establish and verify connectivity to the Internet. This step ensures the computer has an IP address. Step 2. Gather TCP/IP configuration information. a. Use the Start menu to open the command prompt (Start>Programs>Accessories>Command Prompt or Start>Programs>Command Prompt). b. Type ipconfig and press Enter key. The speiling of the ipconfig is critical, but the case is not. c. The screen shows the IP address, subnet mask and the default gateway. The IP address and the default gateway should be in the same network or subnet; otherwise this host wouldn't be able to communicate outside the network. Page 5 Step 3. Record the following TCP/ /P information for this computer. a. IP address: b. Subnet maski c. Default gateway: Step 4. Compare this computer's TCP/IP configuration to that of others on the LAN. If this computer is on a LAN, compare the information of several machines (Hosts). a. Are there any similarities? b. What is similar about the IP addresses? c. What is similar about the default gateway? d. Record a couple of the IP addresses (of your nearby hosts) 1. 2. 3. Step 5. Check additional TCP/IP configuration information. a. To see more information, type ipconfig/all and press Enter key. The figure shows the detailed IP configuration of this computer on the screen. b. You should see the following information: the host name (computer name), the Physical address of this machine, IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and DNS Servers. c. In the LAN, compare your result with a few nearby computers. What similarities do you see in the physical (MAC) address? d. Write down the computer's host name: e. Write down the host names of a couple of other computer: a. b. C. 4. Step 6. Close the screen when finished. B: Using PING TRACERT from a Woricstation Sept 1. Establish and verify connectivity to the Internet. This step ensures that the computer has an IP address. Step 2. Open the Command prompt(MS-DOS). Ping the IP address of another computer. a. In the window, type ping. a space, and the IP address of a computer recorded in the previous lab. Ping uses the internet Control Message Protocol(ICMP) echo-request and echo-reply feature to test physical connectivity. Because ping reports on four attempts, it gives an indication the reliability of the connection. Look over the result and verify that the ping was successful. Was the ping successful? If not, report to the instructor. b. Ask the IP address of the nearby computers and ping. Note the result. c. Ping the IP address of Default gateway and DNS servers. Was the result successful? d. Ping the computer's loopback IP address. Type the following command: ping 127.0.0.1 e. The address 127.0.0.1 is reserved for loopback testing, If the ping is successful, then TCP/1P is properly installed and functioning on this computer. f. Was the ping successful for e. g. Ping the hostname of the computer that you recorded in lab 1.1. Page 8 h. Ping the Microsoft websitelwww.microsoff. com) Step 3. Trace the route to the Umm-alqura university website: type tracert and press Enter key. The result shows the complete route to the site and the number of hops in path. Trace a local host name or IP address in your local area network (LAN). Record the output and interpret. Step 4. Close the window. Also see "pathping ip or host" command. Which only shows path from source to destination