Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In this lab, your team will use a calculator tape to represent the history of our planet. You will need a piece of tape

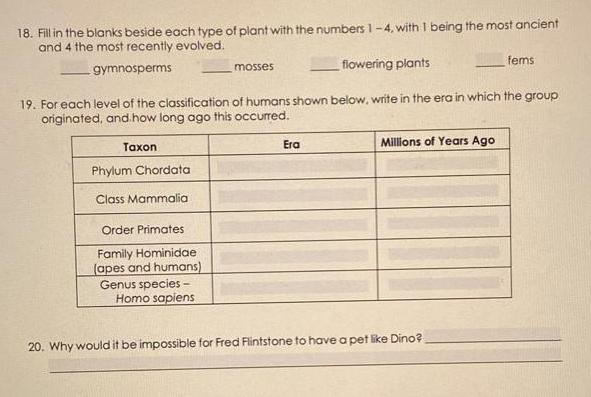

In this lab, your team will use a calculator tape to represent the history of our planet. You will need a piece of tape long enough to illustrate time from the formation of Earth to the present. Use a scale of 1 meter = 1 billion years. 1. How long should your tape be? 2. How many mm are in 1 meter? 3. How many years will a mm represent? 4. How many cm represent 0.6 by? a cm Refer to Table 1 in the lab to answer the following questions. This table shows significant events in the geologic history of Earth. To the right of the table, there is some general climate data as well as images showing the position of Earth's continents and oceans at various times. 5. Are the events listed in the top rows of the table the most ancient or the most recent? 6. Write in the 4 geologic eras (Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic) in the correct cells of the left column. 7. When scientists consider the possibility of life on other planets, they postulate that certain conditions are necessary for life as we know it to begin. One is protection from harmful radiation. What early Precambrian occurrence provided this protection? Where did Earth's 8. Did the early Earth have an oxygen-containing atmosphere? atmospheric oxygen come from? 9. Approximately how many years after Earth's formation did life appear? 10. What type of cells were the first living things? 11. How long after the appearance of prokaryotes did eukaryotes appear? 12. How long after the appearance of eukaryotes did multicellular organisms appear? 13. Refer to the maps beside Table 1 showing the positions of continents and oceans. Considering their habitat, why is there a good fossil record of Cambrian invertebrates (such as clams. marine snails, crabs) in North America? 14. Insects were the first animals to fly. How long after their evolution did wings evolve? 15. The word root "fer" means "full of". Why is the Carboniferous period given its name? 16. What plate tectonic event coincides with the Permian extinction?. 17. Fill in the blanks beside each type of tetrapod (vertebrate animal with 4 limbs) with the numbers 1-4, with 1 being the most ancient and 4 the most recently evolved. non-bird reptiles amphibians bird reptiles mammals 18. Fill in the blanks beside each type of plant with the numbers 1-4, with 1 being the most ancient and 4 the most recently evolved. gymnosperms flowering plants 19. For each level of the classification of humans shown below, write in the era in which the group originated, and how long ago this occurred. Taxon Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae (apes and humans) Genus species- Homo sapiens mosses Era Millions of Years Ago 20. Why would it be impossible for Fred Flintstone to have a pet like Dino? fems Era Time (mya) 1.8 2.2 4 23.8 30 45 50 60 65 140 150 200 225 250 275 345 354 360 365 370 395 400 425 428 430 460 510 530 543 550 700 720 1000 1500 2400 2800 3600 3800 3800 4300 4600 Table 1. Significant Events in Geologic Time. Event evolution of Homo sapiens first Homo genus First bipedal hominids (Ardipithecus. Australopithecus) "Golden Age of Mammals" (Miocene epoch) - due to expansive grasslands and radiation of grazing mammals first hominids (apes) first fully aquatic whales first monkeys first primates (lemurs, farsiers) mass extinction due to asteroid impact, including loss of dinosaurs first flowering plants first bird reptiles (Archaeopteryx) first mammals first dinosaur reptiles mass extinction (-90% of multicellular life goes extinct) first gymnosperm plants (cycads. Ginkgo.conifers) first reptiles Carboniferous period: coal-forming swamps with giant ferns, huge insects, amphibians first seed plants (now extinct) first amphibians (vertebrate conquest of land) first winged insects first vascular plants (ferns and their relatives) first insects first bony fish first land animals - millipede relatives first fish with jaws (including sharks) first known land fungi-mycorhizzae first land plants (nonvascular, relatives of mosses) first members of Phylum Chordata, including vertebrates "Cambrian explosion"-all animal phyla (except Bryozoa) present by close of Cambrian period first arthropods (trilobites) first known animals - sponges evolution of green algae first multicellular eukaryotes first eukaryotic cells (protists) clear evidence of significant O in atmosphere, oceans photosynthetic cyanobacteria O enters atmosphere first prokaryotic cells oceans form by condensation of atmospheric water crust solidifies: formation of oldest rocks on Earth ozone layer forms (UV barrier) formation of Earth present North and South America joined by land bridge, Uplift of the Sierra Nevada. Worldwide glaciation. 50 mya Continents continue to drift apart. Collision of India with Eurasia begins. Australia moves north from Antarctica Ice begins to form at South Pole 85 mya India separated from Madagascar, moves north: Rocky Mountains form. Climate mild, temperate. 260 mya Supercontinent Pangaea assembles. Building of Appalachian Mountains ends. Climate warm; little variation. 360 mya Laurahtia confish Supercontinent of Laurentia to the north and Gondwana to the south. Climate mild. 515 mya Supercontinent of Gondwana forms Oceans cover much of North America. Climate not well known.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.40 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 From the data available on the question is 1 meter 1 billion years and it is known that 1billion y...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


