
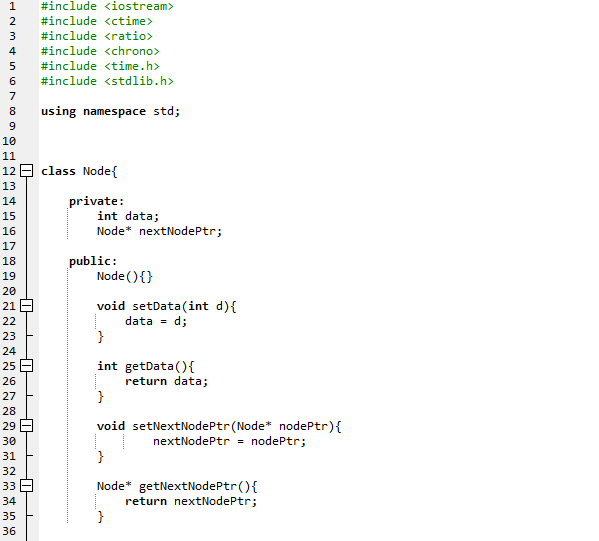
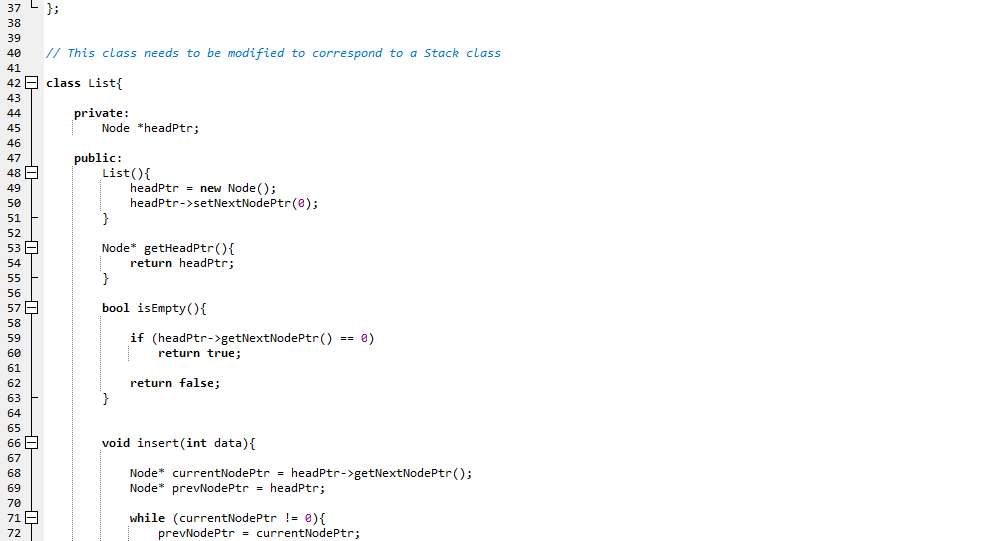




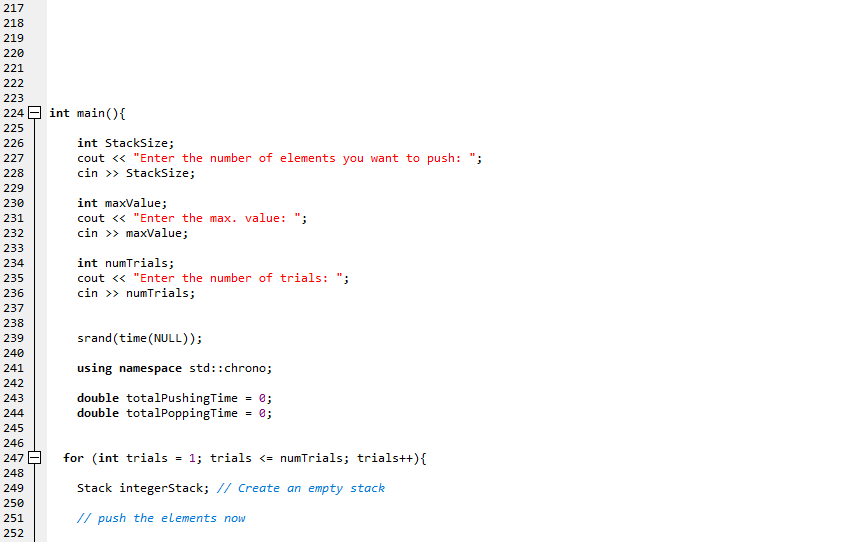
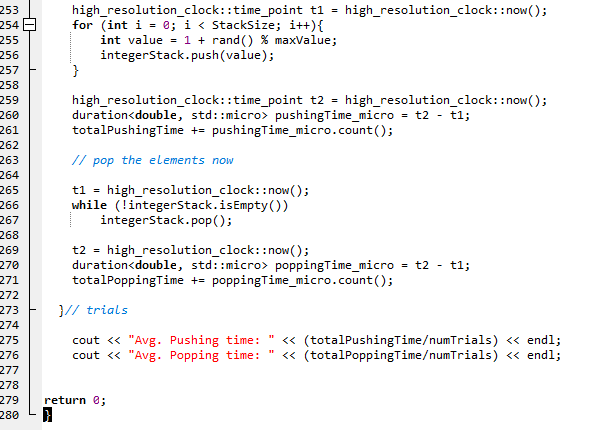
In this quiz, you will implement the Stack ADT as a singly linked list. As discussed in class, the push, pop and peek operations for a Stack can be accomplished using the insertAtIndex(0, data) deleteElement(0) and read(0) functions for a singly linked list respectively, where the '0' in the function calls corresponds to the insertlndex, deletelndex and readIndex. In such an implementation, the asymptotic time complexity is O(1) for all the three operations. You are given the code for a singly linked list with the Node and List classes and a main function that pushes a sequence of integers to a Stack and then pops them out. You are required to modify the code for the List class to now reflect the code for a Stack class (including the name change for the classes). Only those functions that are needed for a Stack class should be retained (and renamed as per the Stack ADT) and others should be removed. Also, the implementation for the push, pop and peek operations in the Stack class should not have any loops; but, conditional statements (like 'if) could be included. As you can see the code for the main function, the timers are setup for each trial and the times for the push and pop operations are measured (in microseconds) and then averaged out. You do not have to write any code in the main function. You run the complete code for three different values of the Stack Size: 10000, 100000, 1000000. The maximum value for any element is always 50000 and the number of trials is always 50 Report Submission (through Canvas): Submit everything together as one PDF file: (a - 60 pts) Your code for the Stack class (that is adapted from the code given to you for the List class) implementing the push, pop and peek operations in constant time, i.e., 0(1) time. (b - 10 pts) Tabulate the average run time (in microseconds) for the push and pop operations for the different values of the Stack Size. Also, add columns that include the ratio of the Stack Size to the average run times for each operation (push and pop) (c - 6 pts) Include screenshots of the outputs obtained for the average run time for each of the three Stack Size values (d - 12 pts) Explain why you observe a significant difference in the average run time for the push and pop operations? The push operation is expected to take a relatively longer time compared to the pop operation. Why is that? (e - 12 pts) Even though theoretically, the push and pop operations are expected to take constant time (i.e., O(1) time), you are more likely to observe the average run times of the push and pop operations to increase with Stack size. Why do you think we can still claim that these oper constant time? (Hint: Look at the values for the ratios of the Stack Size and the average run time for the push and pop operations that you computed and tabulated for (b)). ations theoretically take #include #include #include #include #include #include
1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 using namespace std; 12 class Node{ 13 private: 15 16 17 int data; Node* nextNodePtr; public: Node ) 19 20 21 void setData(int d) data d; 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 int getData()f return data; void setNextNodePtr(Node* nodePtr) nextNodePtr = nodePtr; Node* getNextNodePtr()i return nextNodePtr; 34 35 36 37 L 38 39 40 I/ This class needs to be modified to correspond to a Stack class 41 42 class Listf 43 private: 45 46 47 48 49 50 Node *headPtr; public: List) headPtr -new Node (); headPtr->setNextNodePtr(e); 52 53 54 Node* getHeadPtr) return headPtr 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 bool isEmpty) if (headPtr->getNextNodePtr)0) return true return false void insert (int data)i 67 68 69 70 71 72 Node* currentNodePtr - headPtr->getNextNodePtr) Node* prevNodePtr = headPtr; while (currentNodePtr- e)i prevNodePtr-currentNodePtr; currentNodePtr currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr); 75 76 Node* newNodePtr-new Node (); newNo newNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(0); prevNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(newNodePtr). dePtr->setData(data); 79 80 82 83 84 85 86 87 void insertAtIndex(int insertIndex, int data)\ Node* currentNodePtr - headPtr->getNextNodePtr) Node* prevNodePtr- headPtr; int index - 0; while (currentNodePtr 0) 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 if (index insert!ndex) break; prevNodePtr- currentNodePtr; currentNodePtr- currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr); indext+; Node* newNodePtr-new Node (); newNodePtr->setData(data); newNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(currentNodePtr); prevNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(newNodePtr). 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 int read(int readIndex){ 109 110 Node* currentNodePtr - headPtr->getNextNodePtr) Node* prevNodePtr- headPtr; int indexe; 112 113 while (currentNodePtr !=0){ 114 115 116 if (indexreadIndex) return currentNodePtr->getData); 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 prevNodePtr-currentNodePtr; currentNodePtr currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr); indext+ return -1; I/ an invalid value indicating I/ index is out of range void modifyElement(int modifyIndex, int data)\ Node* currentNodePtr- headPtr->getNextNodePtr); Node* prevNodePtr-headPtr; int index-0; while (currentNodePtr-0)5 if (index modifyIndex) currentNodePtr->setData (data); return; 144 prevNodePtr- currentNodePtr; 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 currentNodePtr currentNodePtr-)getNextNodePtr(); = index++; void deleteElementAtIndex(int deleteIndex) Node* currentNodePtr- headPtr->getNextNodePtr); Node* prevNodePtr-headPtr; Node* nextNodePtr- headPtr; int index-e; while (currentNodePtr- e) if (index -- deleteIndex){ nextNodePtr- currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr(); break; prevNodePtr- currentNodePtr; currentNodePtr -currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr); index++; 172 173 174 175 176 prevNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(nextNodePtr); 178 179 180 void deleteElement(int deleteData){ Node* currentNodePtr- headPtr->getNextNodePtr); Node* prevNodePtr-headPtr; Node* nextNodePtr- headPtr; 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216; while (currentNodePtr e) if (currentNodePtr->getData()deleteData){ nextNodePtr- currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr(); break; prevNodePtr currentNodePtr; currentNodePtr- currentNodePtr->getNextNodePtr); prevNodePtr->setNextNodePtr(nextNodePtr); void IterativePrint) Node* currentNodePtr- headPtr->getNextNodePtrO while (currentNodePtr- e) cout getData() getNextNodePtr); cout maxValue; int numTrials; cout numTrials; srand (time (NULL)); using namespace std::chrono; double totalPushingTime-0; double totalPoppingTime -0; Stack integerStack; I/ Create an empty stack // push the elements now high resolution clock::time point t1-high resolutionclock::now) for (int i-e; i pushingTime_micro-t2 tl; totalPushingTime +pushingTime micro.count(); pop the elements now t1- high_resolution_clock::now(); while (!integerStack.isEmpty)) integerStack.pop) t2 = high-resolution-clock ::now(); duration















