Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
#include // // #include #include #define MAX_SPECIES_NAME_LENGTH 4096 // a struct to represent the date // a whale pod sighting was made struct date {
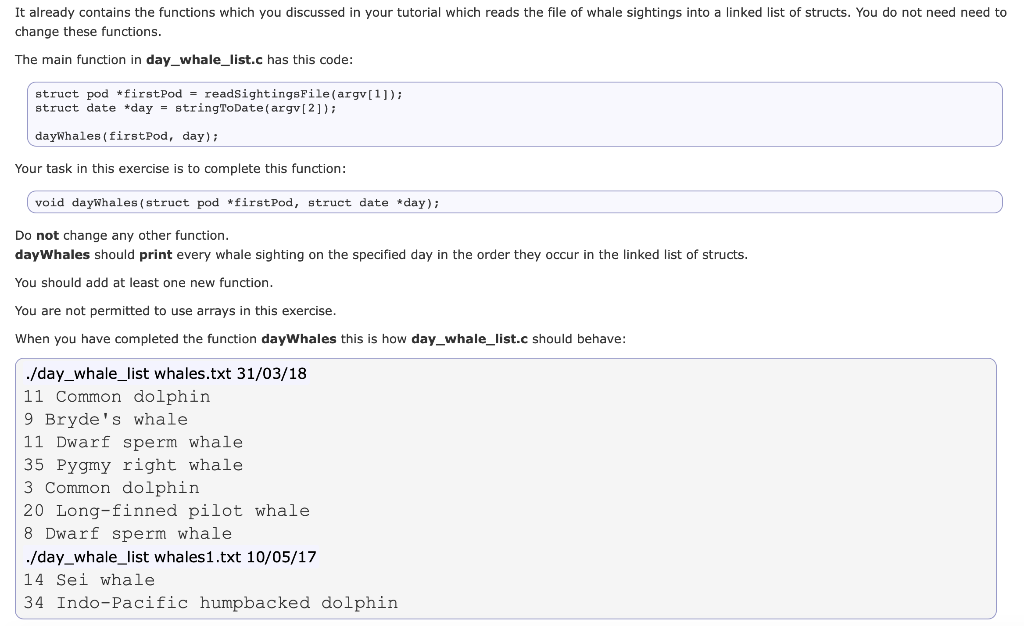
#includeIt already contains the functions which you discussed in your tutorial which reads the file of whale sightings into a linked list of structs. You do not need need to change these functions. The main function in day_whale_list.c has this code: struct pod *irstPodreadsightingsPile(argv[1]): struct date *day-stringToDate(argv[ 2]) dayWhales(firstpod, day) Your task in this exercise is to complete this function: void dayWhales (struct pod *firstPod, struct date *day); Do not change any other function. dayWhales should print every whale sighting on the specified day in the order they occur in the linked list of structs You should add at least one new function. You are not permitted to use arrays in this exercise When you have completed the function dayWhales this is how day_whale_list.c should behave: ./day_whale_list whales.txt 31/03/18 11 Common dolphin 9 Bryde's whale 11 Dwarf sperm whale 35 Pygmy right whale 3 Common dolphin 20 Long-finned pilot whale 8 Dwarf sperm whale /day_whale_list whales1.txt 10/05/17 14 Sei whale 34 Indo-Pacific humpbacked dolphin// // #include #include #define MAX_SPECIES_NAME_LENGTH 4096 // a struct to represent the date // a whale pod sighting was made struct date { int year; int month; int day; }; // a struct to represent a sighting // of a pod (group) of whales struct pod { struct pod *next; struct date *when; int howMany; char *species; }; struct pod *readSightingsFile(char filename[]); struct pod *readSighting(FILE *f); struct date *readDate(FILE *f); struct date *stringToDate(char *s); void dayWhales(struct pod *firstPod, struct date *day); // PUT YOUR FUNCTION DEFINITIONS HERE int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 3) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s ", argv[0]); return EXIT_FAILURE; } struct pod *firstPod = readSightingsFile(argv[1]); struct date *day = stringToDate(argv[2]); dayWhales(firstPod, day); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // Print the whale sightings, for the specified day. // One line containing number of whales and species // is printed for each sighting. void dayWhales(struct pod *firstPod, struct date *day) { // PUT YOUR CODE HERE } // PUT YOUR FUNCTIONS HERE // // DO NOT CHANGE THE FUNCTIONS BELOW HERE // // return linked list of sightings read from filename // exit called if there is an error struct pod *readSightingsFile(char filename[]) { FILE *f = fopen(filename, "r"); if (f == NULL) { fprintf(stderr,"error: file '%s' can not open ", filename); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } struct pod *firstSighting = NULL; struct pod *lastSighting = NULL; struct pod *sighting = readSighting(f); while (sighting != NULL) { if (firstSighting == NULL) { firstSighting = sighting; firstSighting->next = NULL; } else { lastSighting->next = sighting; } lastSighting = sighting; sighting = readSighting(f); } return firstSighting; } // read a whale sighting (date, number of whales, whale species) // return a pointer to a malloced struct containing these details // return NULL if a sighting can not be read struct pod *readSighting(FILE *f) { struct pod *p = malloc(sizeof (struct pod)); if (p == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "out of memory "); exit(1); } p->next = NULL; p->when = readDate(f); if (p->when == NULL) { free(p); return NULL; } int nScanned = fscanf(f, "%d", &(p->howMany)); if (nScanned != 1) { free(p); return NULL; } fgetc(f); char speciesBuffer[MAX_SPECIES_NAME_LENGTH]; if (fgets(speciesBuffer, MAX_SPECIES_NAME_LENGTH, f) == NULL) { free(p); return NULL; } // finish string at ' ' if there is one char *newlinePtr = strchr(speciesBuffer, ' '); if (newlinePtr != NULL) { *newlinePtr = '\0'; } // also finish string at ' ' if there is one - files from Windows will newlinePtr = strchr(speciesBuffer, ' '); if (newlinePtr != NULL) { *newlinePtr = '\0'; } // malloc a char array long enough to hold species name // and copy species to it p->species = malloc(strlen(speciesBuffer) + 1); if (p->species == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "out of memory "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } strcpy(p->species, speciesBuffer); return p; } // read a date in day/month/year format from stream f // return a pointer to a malloced date struct containing them // return NULL if a date can not be read struct date *readDate(FILE *f) { struct date *d = malloc(sizeof (struct date)); if (d == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "out of memory "); exit(1); } int n_scanned = fscanf(f, "%d/%d/%d", &(d->day), &(d->month), &(d->year)); if (n_scanned != 3) { free(d); return NULL; } return d; } // given a string containing a date in day/month/year format // return a pointer to a malloced date struct containing them // return NULL if a date can not be read struct date *stringToDate(char *s) { struct date *d = malloc(sizeof (struct date)); if (d == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "out of memory "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } int nScanned = sscanf(s, "%d/%d/%d", &(d->day), &(d->month), &(d->year)); if (nScanned != 3) { free(d); return NULL; } return d; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


