Question: #include using namespace std; class Digit { friend ostream& operator>(istream&, Digit&); // Overload the pre-increment operator as a friend function. friend Digit operator++(Digit&); // Overload
#include
using namespace std;
class Digit { friend ostream& operator>(istream&, Digit&);
// Overload the pre-increment operator as a friend function. friend Digit operator++(Digit&);
// Overload the post-increment operator as a friend function. friend Digit operator++(Digit&, int);
public: Digit(); Digit(int); void setDigit(int);
// Overload the pre-decrement operator as a member function. Digit operator--();
// Overload the post-decrement operator as a member function. Digit operator--(int);
private: int dig; };
Digit::Digit() { setDigit(0); }
Digit::Digit(int d) { setDigit(d); }
void Digit::setDigit(int d) { dig = d; }
// TODO: // Overload the pre-decrement operator as a member function. // Note that decrementing 0 should circle the digit back to 9. // Write your function here.
// TODO: // Overload the post-decrement operator as a member function. // Note that decrementing 0 should circle the digit back to 9. // Write your function here.
// TODO: // Overload the pre-increment operator as a friend function. // Note that incrementing 9 should circle the digit back to 0. // Write your function here.
// TODO: // Overload the post-increment operator as a friend function. // Note that incrementing 9 should circle the digit back to 0. // Write your function here.
ostream& operator
istream & operator>>(istream &isObject, Digit &d) { isObject >> d.dig; return isObject; }
int main() { cout
Digit digit;
cin >> digit;
cout
return 0; }
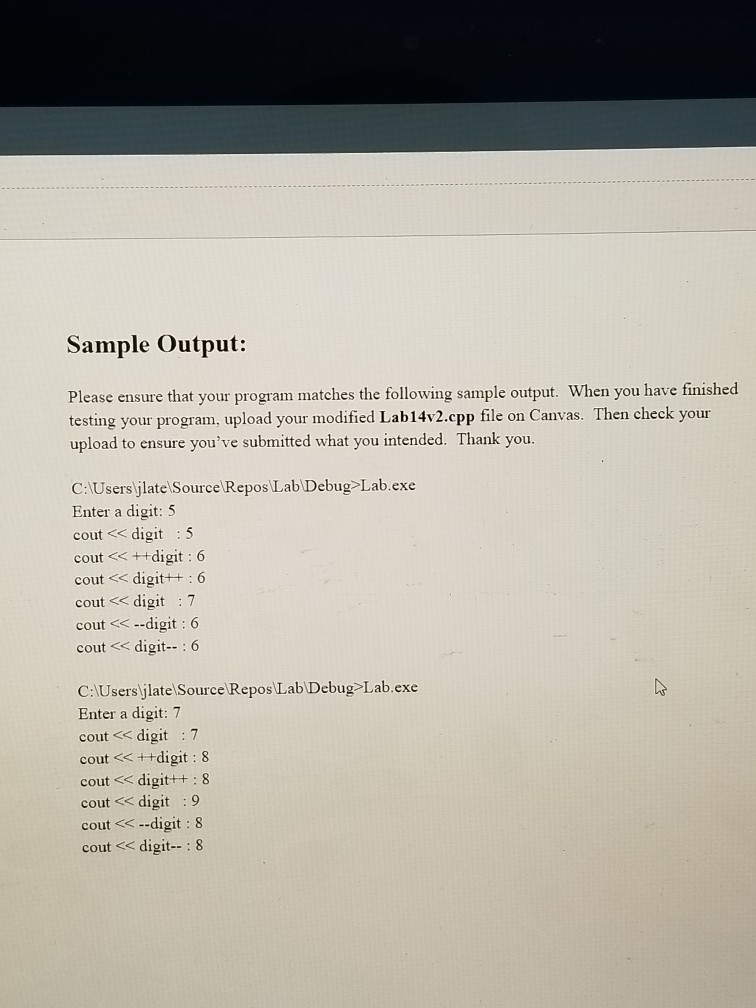
Objectives: Distinguishing between pre and post increment and decrement operators. Overloading these operators as member and non-member functions. Overloading the stream insertion and stream extraction operators as non-member (friend) . . functions Instructions: Download Lab14v2.cpp from Canvas. The Digit class's purpose is to store a single-digit number. Much of the code is provided for you. Read the given code, and then implement the following four functions: // Overload the pre-decrement operator as a member function Digit operator0: /I Overload the post-decrement operator as a memben function. Digit operator--(int); // Overload the pre-increment operator as a friend function friend Digit operator++ (Digit8); // overload the post-increment operator as a friend function. friend Digit operator++(Digit&, int) Note that when digit 8 is incremented, it becomes 9. But when digit 9 is incremented, it becomes 0. When digit 1 is decremented, it becomes 0. But when digit 0 is decremented, it becomes 9. The purpose of overloading these operators is so that we can perform increment and decrement operations on instances of a class Digit digit Instead of writing code that looks like this: digit.setDig(digit getDig0+ 1) We can instead simply write digit+t 1 Page Sample Output: Please ensure that your program matches the following sample output. When you have finished testing your program, upload your modified Lab14v2.cpp file on Canvas. Then check your upload to ensure you've submitted what you intended. Thank you. C:Users jlatel Source Repos Lab Debug Lab.exe Enter a digit: 5 cout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


